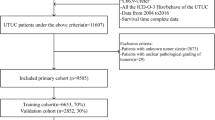
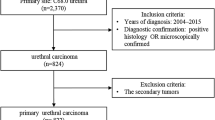
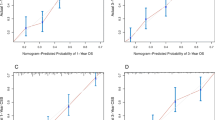
Abstract
Objectives
To identify the predictive tools which have emerged recently in the field of urothelial carcinomas.
Materials and methods
We performed a thorough MEDLINE literature review using a combination of the following keywords: urothelial carcinoma, transitional cell carcinoma, bladder, renal pelvis, ureter, predictive tools, predictive models and nomograms. We found 117 articles, but only the relevant reports were selected.
Results
The majority of available tools are prediction models, particularly nomograms. These models combine good performance accuracy with ease of use. They appear to be more accurate than risk grouping or tree modeling and are more suitable for clinicians than artificial intelligence. The most recent nomograms have been designed to be used in daily clinical practice and are even available as computer or smartphone applications. They focus on pathological outcomes or more frequently on survival statistics or recurrence risk after surgery. They provide an accurate prediction of disease evolution and may help clinicians to choose the most appropriate treatment option. However, these prediction tools still need to be validated and regularly utilized.
Conclusion
Predictive tools represent very helpful clinical decision-making aids but need to be validated in larger populations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A (2012) Cancer statistics 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 62:10–29
Catto JW, Yates DR, Rehman I, Azzouzi AR, Patterson J, Sibony M et al (2007) Behavior of urothelial carcinoma with respect to anatomical location. J Urol 177:1715–1720
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E (2010) Cancer statistics 2010. CA Cancer J Clin 60:277–300
Nguyen CT, Stephenson AJ, Kattan MW (2010) Are nomograms needed in the management of bladder cancer? Urol Oncol 28:102–107
Lughezzani G, Briganti A, Karakiewicz PI, Kattan MW, Montorsi F, Shariat SF et al (2010) Predictive and prognostic models in radical prostatectomy candidates: a critical analysis of the literature. Eur Urol 58:687–700
Vickers AJ (2011) Prediction models: revolutionary in principle, but do they do more good than harm? J Clin Oncol 29:2951–2952
Vickers AJ, Cronin AM (2010) Everything you always wanted to know about evaluating prediction models (but were too afraid to ask). Urology 76:1298–1301
Shariat SF, Capitanio U, Jeldres C, Karakiewicz PI (2009) Can nomograms be superior to other prediction tools? BJU Int 103:492–495; discussion 495–497
D’Amico AV, Whittington R, Malkowicz SB, Schultz D, Blank K, Broderick GA et al (1998) Biochemical outcome after radical prostatectomy, external beam radiation therapy, or interstitial radiation therapy for clinically localized prostate cancer. JAMA 280:969–974
Kattan MW (2003) Comparison of Cox regression with other methods for determining prediction models and nomograms. J Urol 170:S6–S10
Catto JW, Linkens DA, Abbod MF, Chen M, Burton JL, Feeley KM et al (2003) Artificial intelligence in predicting bladder cancer outcome: a comparison of neuro-fuzzy modeling and artificial neural networks. Clin Cancer Res 9:4172–4177
Shariat SF, Karakiewicz PI, Godoy G, Lerner SP (2009) Use of nomograms for predictions of outcome in patients with advanced bladder cancer. Ther Adv Urol 1:13–26
Kattan MW, Vickers AJ, Yu C, Bianco FJ, Cronin AM, Eastham JA et al (2009) Preoperative and postoperative nomograms incorporating surgeon experience for clinically localized prostate cancer. Cancer 115:1005–1010
Catto JW, Abbod MF, Linkens DA, Larre S, Rosario DJ, Hamdy FC (2009) Neurofuzzy modeling to determine recurrence risk following radical cystectomy for nonmetastatic urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Clin Cancer Res 15:3150–3155
Fernandez-Gomez J, Madero R, Solsona E, Unda M, Martinez-Pineiro L, Ojea A et al (2011) The EORTC tables overestimate the risk of recurrence and progression in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer treated with bacillus Calmette-Guerin: external validation of the EORTC risk tables. Eur Urol 60:423–430
Karakiewicz PI, Shariat SF, Palapattu GS, Perrotte P, Lotan Y, Rogers CG et al (2006) Precystectomy nomogram for prediction of advanced bladder cancer stage. Eur Urol 50:1254–1262
Taylor JM, Feifer A, Savage CJ, Maschino AC, Bernstein M, Herr HW et al (2012) Evaluating the utility of a preoperative nomogram for predicting 90-day mortality following radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. BJU Int 109:855–859
Vickers AJ, Cronin AM, Kattan MW, Gonen M, Scardino PT, Milowsky MI et al (2009) Clinical benefits of a multivariate prediction model for bladder cancer: a decision analytic approach. Cancer 115:5460–5469
El-Mekresh M, Akl A, Mosbah A, Abdel-Latif M, Abol-Enein H, Ghoneim MA (2009) Prediction of survival after radical cystectomy for invasive bladder carcinoma: risk group stratification, nomograms or artificial neural networks? J Urol 182:466–472
Bassi P, Sacco E, De Marco V, Aragona M, Volpe A (2007) Prognostic accuracy of an artificial neural network in patients undergoing radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: a comparison with logistic regression analysis. BJU Int 99:1007–1012
Bochner BH, Kattan MW, Vora KC (2006) Postoperative nomogram predicting risk of recurrence after radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. J Clin Oncol 24:3967–3972
Shariat SF, Karakiewicz PI, Palapattu GS, Amiel GE, Lotan Y, Rogers CG et al (2006) Nomograms provide improved accuracy for predicting survival after radical cystectomy. Clin Cancer Res 12:6663–6676
Shariat SF, Chromecki TF, Cha EK, Karakiewicz PI, Sun M, Fradet Y et al (2012) Risk stratification of organ confined bladder cancer after radical cystectomy using cell cycle related biomarkers. J Urol 187:457–462
Bassi PF, Bongiovanni L, Racioppi M, Volpe A, D’Agostino D, Gardi M (2011) Postoperative nomogram for invasive bladder cancer: does it really work? A multicenter cohort study. Urol Oncol 29:698–702
Nuhn P, May M, Sun M, Fritsche HM, Brookman-May S, Buchner A et al (2012) External validation of postoperative nomograms for prediction of all-cause mortality, cancer-specific mortality, and recurrence in patients with urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Eur Urol 61:58–64
Zaak D, Burger M, Otto W, Bastian PJ, Denzinger S, Stief CG et al (2010) Predicting individual outcomes after radical cystectomy: an external validation of current nomograms. BJU Int 106:342–348
Shariat SF, Karakiewicz PI, Ashfaq R, Lerner SP, Palapattu GS, Cote RJ et al (2008) Multiple biomarkers improve prediction of bladder cancer recurrence and mortality in patients undergoing cystectomy. Cancer 112:315–325
Gakis G, Todenhofer T, Renninger M, Schilling D, Sievert KD, Schwentner C et al (2011) Development of a new outcome prediction model in carcinoma invading the bladder based on preoperative serum C-reactive protein and standard pathological risk factors: the TNR-C score. BJU Int 108:1800–1805
Riester M, Taylor JM, Feifer A, Koppie T, Rosenberg JE, Downey RJ et al (2012) Combination of a novel gene expression signature with a clinical nomogram improves the prediction of survival in high-risk bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res 18:1323–1333
Margulis V, Lotan Y, Montorsi F, Shariat SF (2008) Predicting survival after radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. BJU Int 102:15–22
Favaretto RL, Shariat SF, Savage C, Godoy G, Chade DC, Kaag M et al (2012) Combining imaging and ureteroscopy variables in a preoperative multivariable model for prediction of muscle-invasive and non-organ confined disease in patients with upper tract urothelial carcinoma. BJU Int 109:77–82
Jeldres C, Sun M, Lughezzani G, Isbarn H, Shariat SF, Widmer H et al (2010) Highly predictive survival nomogram after upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma. Cancer 116:3774–3784
Yates DR, Hupertan V, Colin P, Ouzzane A, Descazeaud A, Long JA et al (2012) Cancer-specific survival after radical nephroureterectomy for upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma: proposal and multi-institutional validation of a post-operative nomogram. Br J Cancer 106:1083–1088
Cha EK, Shariat SF, Kormaksson M, Novara G, Chromecki TF, Scherr DS et al (2012) Predicting clinical outcomes after radical nephroureterectomy for upper tract urothelial carcinoma. Eur Urol 61:818–825
Messer JC, Terrell JD, Herman MP, Ng CK, Scherr DS, Scoll B, et al (2011) Multi-institutional validation of the ability of preoperative hydronephrosis to predict advanced pathologic tumor stage in upper-tract urothelial carcinoma. Urol Oncol. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2011.07.011
Margulis V, Youssef RF, Karakiewicz PI, Lotan Y, Wood CG, Zigeuner R et al (2010) Preoperative multivariable prognostic model for prediction of nonorgan confined urothelial carcinoma of the upper urinary tract. J Urol 184:453–458
Roupret M, Zigeuner R, Palou J, Boehle A, Kaasinen E, Sylvester R et al (2011) European guidelines for the diagnosis and management of upper urinary tract urothelial cell carcinomas: 2011 update. Eur Urol 59:584–594
Roupret M, Hupertan V, Seisen T, Colin P, Xylinas E, Yates DR, et al (2012) Prediction of cancer-specific survival after radical nephroureterectomy for upper tract urothelial carcinoma: development of an optimized post-operative nomogram using decision curve analysis. J Urol. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2012.10.057
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Drouin, S.J., Yates, D.R., Hupertan, V. et al. A systematic review of the tools available for predicting survival and managing patients with urothelial carcinomas of the bladder and of the upper tract in a curative setting. World J Urol 31, 109–116 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-012-1008-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-012-1008-9