Abstract
Objectives
To assess the accuracy of intra-rectal coil magnetic resonance imaging (ER-MRI) for staging early prostate cancer (EPC).
Materials and methods
ER-MRI was performed with the Magnetom Symphony 1.5 Tesla system. ER-MRI and pathology findings were statistically correlated.
Results
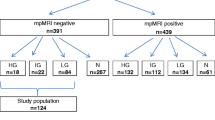
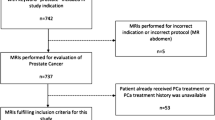
One hundred and fifty-four consecutive patients underwent radical prostatectomy (RRP) for EPC (cT1c-2 Nx M0). An average age was 66, mean PSA 11.04 µg/L (median 7.33 µg/L) and mean pathologic Gleason score 6. Pathology detected 97 out of 154 patients (63 %) as EPC and 57 cases (37 %) as extra-prostate extension (EPED) (pT3) with extra-capsular extension (ECE) (pT3a) in 41 (27 %) and seminal vesicle invasion (SVI) (pT3b) in 16 (10 %). ER-MRI staged 100 patients (65 %) as cT2 and 54 (35 %) as EPED with ECE in 37 cases (24 %) and SVI in 17 (11 %). ER-MRI sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, overall accuracy resulted respectively 0.78, 0.96, 0.86, 0.92, 0.91 for ECE as well as 0.88, 0.98, 0.82, 0.99 and 0.97 for SVI.
Conclusion
ER-MRI was effective in detecting preoperative EPC under-staging. In the next future, multi-parametric 3-Tesla ER-MRI will be the procedure for diagnosing, staging and following-up prostate cancer patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wheeler TM, Dillioglugil O, Kattan MW et al (1998) Clinical and pathological significance of the level and extent of capsular invasion in clinical stage T1–2 prostate cancer. Hum Pathol 29:856–862
Hull GW, Rabbani F, Abbas F et al (2002) Cancer control with radical prostatectomy alone in 1,000 consecutive patients. J Urol 167:528–534
Villers A, Lemaitre L, Haffner J et al (2009) Current status of MRI for the diagnosis, staging and prognosis of prostate cancer: implications for focal therapy and active surveillance. Curr Opin Urol 19:274–282
Joseph T, McKenna DA, Westphalen AC et al (2009) Pretreatment endorectal magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging features of prostate cancer as predictors of response to external beam radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 73:665–671
Riaz N, Afaq A, Akin O et al (2012) Pretreatment endorectal coil magnetic resonance imaging findings predict biochemical tumor control in prostate cancer patients treated with combination brachytherapy and external-beam radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Phys Epub ahead of print
Sciarra A, Barrentsz J, Bjartell A et al (2010) Advances in magnetic resonance imaging: how they are changing the management of prostate cancer. Eur Urol 59:962–967
Flemming ID, Cooper JS, Hemson DE et al (1997) America joint committee on cancer staging manual, 5th edn. JP Lippincott, Philadelphia, pp 219–222
Schnall MD, Imai Y, Tomaszewski J et al (2002) Prostate cancer: local staging with endorectal surface coil MR imaging. Radiology 178:797–802
Krebs TL, Silverman JM (1992) Clinical utility of endorectal surface coil imaging of the prostate gland. RSNA Abstr Number 1006:275
Chelsky MJ, Schnall MD, Seidmon EJ et al (1993) Use of endorectal surface coil magnetic resonance imaging for local staging of prostate cancer. J Urol 150:391–395
D’Amico A, Whittington R, Malkowicz SB et al (1994) A multivariable analysis of clinical factors predicting for pathologic features associated with local failure after radical prostatectomy of prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 30:293–302
D’Amico A, Schnall M, Whittington R et al (1998) Endorectal coil magnetic resonance imaging identifies locally advanced prostate cancer in select patients with clinically localized disease. Urology 51:449–454
Nakashima J, Tanimoto A, Imai Y et al (2004) Endorectal MRI for prediction of tumor site, tumor size, and local extension of prostate cancer. Urology 64:101–105
Brassel S, Krueger WR, Choi J et al (2004) Correlation of endorectal coil magnetic resonance imaging of the prostate with pathologic stage. World J Urol 22:289–292
Wang L, Mullerad M, Chen H et al (2004) Prostate cancer: incremental value of endorectal MR imaging findings for prediction of extracapsular extension. Radiology 232:133–139
Zhang JQ, Loughlin KR, Zou KH et al (2007) Role of endorectal coil magnetic resonance imaging in treatment of patients with prostatic cancer and in determining radical prostatectomy surgical margin status: report of a single surgeon’s practise. Urology 69:1134–1137
Futterer JJ, Engelbrecht Jager GJ et al (2007) Prostate cancer: comparison of local staging accuracy of pelvic phased-array coil alone versus integrated endorectal-pelvic phased array coils. Local staging accuracy of prostate cancer using endorectal coil MR imaging. Eur Radiol 17:1055–1065
D’Amico A, Whittington R, Schnall M et al (1995) The impact of the inclusion of endorectal coil magnetic resonance imaging in a multivariate analysis to predict clinically unsuspected extraprostatic cancer. Cancer 75:2368–2372
Perotti M, Kaufman R, Jenings TA et al (1996) Endo-rectal coil magnetic resonance imaging in clinically localized prostate cancer: is it accurate? J Urol 156:106–109
Rorvik J, Halvorsen OJ, Albrektsen G et al (1999) MRI with endorectal coil for staging clinically localised prostate cancer prior to radical prostatectomy. Eur Rad 9:29–34
Lee SH, Park KK, Choi KH et al (2010) Is endorectal coil necessary for the staging of clinically localized prostate cancer? Comparison of non-endorectal versus endorectal MR imaging. World J Urol 28:667–672
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Porcaro, A.B., Borsato, A., Romano, M. et al. Accuracy of preoperative endo-rectal coil magnetic resonance imaging in detecting clinical under-staging of localized prostate cancer. World J Urol 31, 1245–1251 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-012-0900-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-012-0900-7