Abstract
Purpose
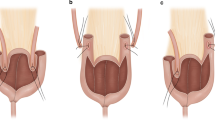
Orthotopic neobladder reconstruction has become a standard form of urinary diversion in many centers for patients undergoing radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. There is still controversy about the best technique for construction of the neobladder, and especially whether it is necessary to include an antireflux mechanism.
Methods
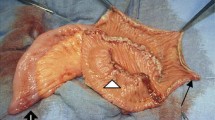
We designed a prospective randomized clinical trial comparing two forms of ileal neobladder: the Studer pouch and the T-pouch. The latter includes an extraserosal tunneled afferent limb which prevents reflux from the pouch to the kidneys. The primary endpoint of the study is renal function and anatomy at 3 years following surgery, with secondary endpoints including early and late postoperative complications, renal infections and need for secondary procedures.
Results
To date we have randomized 462 patients over approximately 6 years, with a planned full enrollment of 550 patients. Ten percent of patients have been withdrawn because they did not undergo the planned orthotopic diversion due to a positive urethral margin on frozen section. We expect approximately 70% of patients to be alive and available for follow-up at 3 years, which will give us ample power to detect clinically meaningful differences in the outcome of these two diversions.
Conclusion
This trial has been feasible and randomization has been acceptable to most patients. Long-term follow-up of the patients on this trial should be able to definitively answer the question of the importance of an antireflux mechanism in the orthotopic neobladders construction.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hautmann RE (2003) Urinary diversion: ileal conduit to neobladders. J Urol 169:834–842. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000029010.97686.eb
Kristjansson A, Mansson W (1999) Refluxing or nonrefluxing ureteric anastomosis. BJU Int 84:905–910. doi:10.1046/j.1464-410x.1999.00395.x
Kristjansson A, Mansson W (2004) Renal function in the setting of urinary diversion. World J Urol 22:172–177. doi:10.1007/s00345-004-0431-y
Studer UE, Burkhard FC, Schumacher M, Kessler TM, Thoeny H, Fleischmann A, Thalmann GN (2006) Twenty years experience with an ileal orthotopic low pressure bladder stubstitute—lessons to be learned. J Urol 176:161–166. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(06)00573-8
Berglund B, Kock NG, Philipson NL (1987) Volume capacity and pressure characteristics of the continent ileal reservoir used for urinary diversion. J Urol 137:29–34
Abol-Enein H, Ghoneim MA (1994) A novel uretero-ileal reimplantation technique: the serous lined extramural tunnel. A preliminary report. J Urol 151:1193–1197
Stein JP, Lieskovsky G, Ginsberg DA, Bochner BH, Skinner DG (1998) The T pouch: an orthotopic ileal neobladder incorporating a serosal lined ileal antireflux technique. J Urol 159:1836–1842. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(01)63170-7
Stein JP, Skinner DG (2000) Application of the T-mechanism to an orthotopic (T-pouch) neobladder: a new era of urinary diversion. World J Urol 18:315–323. doi:10.1007/s003450000144
Stein JP, Skinner DG (2006) Surgical atlas: the orthotopic T-pouch ileal neobladder. BJU Int 98:469–482. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2006.06383.x
Stein JP, Lieskovsky G, Cote R, Groshen S, Feng A-C, Boyd S, Skinner E, Bochner B, Thangathurai D, Mikhail M, Raghanvan D, Skinner DG (2001) Radical cystectomy in the treatment of invasive bladder cancer: long-term results in 1054 patients. J Clin Oncol 19:666–675
Theony HC, Sonnenschein MJ, Madersbacher S, Vock P, Studer UE (2002) Is ileal orthotopic bladder substitution with an afferent tubular segment detrimental to the upper urinary tract in the long term? J Urol 168:2030–2034. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(05)64289-9
Waidlich R, rink F, Kriegmair M, Tatsch K, Schmeller N (1998) A study of reflux in patients with an ileal orthotopic bladder. Br J Urol 81:241–246
Suriano F, Gallucci M, Flammia GP, Musco S, Alcini A, Imbalzano G, Dicuonzo G (2008) Bacteriuria in patients with an orthotopic ileal neobladder: urinary tract infection or asymptomatic bacteriuria?. BJU Int 101:1576–1579. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2007.07366.x
Perimenis P, Burkhard F, Kessler TM, Gramann T, Studer UE (2004) Ileal orthotopic bladder substitute combined with an afferent tubular segment: long-term upper urinary tract changes and voiding pattern. Eur Urol 46:604–609. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2004.07.009
Minervini A, Boni G, Salinitri G, Mariani G, Minervini R (2005) Evaluation of renal function and upper urinary tract morphology in the ileal orthotopic neobladder with no antireflux mechanism. J Urol 173:144–147
Madersberger S, Schmidt J, Eberle JM, Thoeny HC, Burkhard F, Hochreiter W, Studer UE (2003) Long-term outcome of ileal conduit urinary diversion. J Urol 169:985–990. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000051462.45388.14
Clark PE, Montie JE, Klein EA (1999) Long-term follow up of renal function and upper tract status after ileal conduit urinary diversion. J Urol 161:247A. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(01)61765-8
Philip NH, Williams JL, Byers CE (1980) Ileal conduit urinary diversion: long-term follow-up in adults. Br J Urol 52:515–519
Richie JP, Skinner DG, Waisman J (1974) The effect of reflux on the development of pyelonephritis in urinary diversion: an experimental study. J Surg Res 16:256–261. doi:10.1016/0022-4804(74)90040-7
St Clair SR, Hixon CJ, Richey ML (1996) Enterocystoplasty and reflux nephropathy in the canine model. J Urol 148:728–732
Kristjansson A, Wallin L, Mansson W (1995) Renal function up to 16 years after conduit (refluxing or anti-reflux anastomosis) or continent urinary diversion. 1. Glomerular filtration rate and patency of uretero-intestinal anastomosis. Br J Urol 76:539–545
Kristjansson A, Wallin L, Mansson W (1995) Renal function up to 16 years after conduit (refluxing or anti-reflux anastomosis) or continent urinary diversion. 2. Renal scarring and location of bacteriuria. Br J Urol 76:546–550
Elder DD, Moisey CU, Rees RW (1979) A long-term follow-up of the colonic conduit operation in children. Br J Urol 51:462–465
Hill JT, Ransley PG (1983) The colonic conduit: a better method of urinary diversion? Br J Urol 55:629–631
Althausen AF, Hagen-Cook K, Hendren WH (1978) Non-refluxing colon conduit: experience with 70 cases. J Urol 120:35–39
Song C, Kang T, Hong J-H, Kim C-S, Ahn H (2006) Changes in the upper urinary tract after radical cystectomy and urinary diversion: a comparison of antirefluxing and refluxing orthotopic bladder substitutes and ileal conduit. J Urol 175:185–189. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(05)00068-6
Hautmann S, Chun KHF, Currlin E, Braun P, Huland H, Juenemann KP (2006) Refluxing chimney versus nonrefluxing LeDuc ureteroileal anastomosis for orthotopic ileal neobladder: a comparative analysis for patients with bladder cancer. J Urol 175:1389–1394. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(05)00709-3
Elmajian DA, Stein JP, Esrig D, Freeman JA, Skinner EC, Boyd SD, Lieskovsky G, Skinner DG (1006) The Kock ileal neobladder: updated experience in 295 male patients. J Urol 156(3):920–925. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(01)65663-5
Stein JP, Freeman JA, Esrig D, Elmajian DA, Tarter TH, Skinner EC, Boyd SD, Huffman JL, Lieskovsky G, Skinner DG (1996) Complications of the afferent antireflux valve mechanism in the Kock ileal reservoir. J Urol 155:1579–1584. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(01)66131-7
Stein JP, Dunn MD, Quek ML, Miranda G, Skinner DG (2004) The orthotopic T pouch ileal neobladder: experience with 209 patients. J Urol 172:584–587. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000131651.77048.73
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skinner, E.C., Skinner, D.G. Does reflux in orthotopic diversion matter? A randomized prospective comparison of the Studer and T-pouch ileal neobladders. World J Urol 27, 51–55 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-008-0341-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-008-0341-5