Abstract
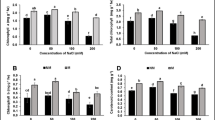
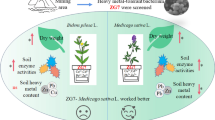
Microalgae are an effective soil biostimulant. However, pathways for the enhancement of plant growth are still unclear. In this study, the effects of Chlorella vulgaris (C. vulgaris) on wheat growth promotion and its direct and indirect mechanisms were investigated under hydroponic experiment condition in pots in a constant temperature indoor laboratory. Living C. vulgaris showed significant promoting effect on wheat growth in terms of root length (52.41%), shoot length (44.44%) and dry weight (13.86%). Besides the function of supplying inorganic nutrient, the organic molecules in the culture supernatant and cell extract of C. vulgaris promoted wheat growth directly through interaction with the plant roots. The culture supernatant fraction increased root length, shoot length and dry weight of wheat by 27.59%. 11.84%, 16.53%, respectively. The cell extract fraction had a larger effect with the increase in root length, shoot length and dry weight by 33.10%, 20.86% and 27.10%, respectively. Changes in the bacterial community in the rhizosphere under co-culturing of bacteria and microalgae was also investigated to determine indirect mechanisms on plant growth promotion. The results showed living C. vulgaris and rhizosphere bacteria had a synergistic interaction. Compared with initial rhizosphere bacterial community at genus level, the number of beneficial rhizosphere bacteria such as Sphingobacterium, Comamonas, Acetobacter and Mucilaginibacter significantly increased when co-cultured with the supernatant of C. vulgaris. In conclusion, considering the presence of bacteria in the soil environment, it is important to maintain the activity of microalgal cells to release extracellular polymer substances sustainably to promote plant growth.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez AL, Weyers SL, Goemann HM, Peyton BM, Gardner RD (2021) Microalgae, soil and plants: a critical review of microalgae as renewable resources for agriculture. Algal Res 54:102200
An XC, Wang ZF, Teng XM, Zhou RR, Wang XX, Xu M, Lian B (2022) Rhizosphere bacterial diversity and environmental function prediction of wild salt-tolerant plants in coastal silt soil. Ecol Ind 134:108503
Anwar MS, Paliwal A, Firdous N, Verma A, Kumar A, Pande V (2019) Co-culture development and bioformulation efficacy of psychrotrophic PGPRs to promote growth and development of Pea (Pisum sativum) plant. J Gen Appl Microbiol 65(2):88–95
Asada K (1999) The water-water cycle in chloroplasts: scavenging of active oxygens and dissipation of excess photons. Annual Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 50(1):601–639
Battacharyya D, Babgohari MZ, Rathor P, Prithiviraj B (2015) Seaweed extracts as biostimulants in horticulture. Sci Hortic 196:39–48
Bello AS, Saadaoui I, Ben-Hamadou R (2021) “Beyond the source of bioenergy”: microalgae in modern agriculture as a biostimulant, biofertilizer, and anti-abiotic stress. Agronomy 11(8):1610
Brasil, B.D.S.A.F., Siqueira, F.G.d., Salum, T.F.C., Zanette, C.M., Spier, M.R (2017) Microalgae and cyanobacteria as enzyme biofactories. Algal Res 25: 76-89
Bumandalai O, Tserennadmid R (2019) Effect of Chlorella vulgaris as a biofertilizer on germination of tomato and cucumber seeds. Int J Aquatic Biol-IJAB 7(2):95–99
Burns DL, Barbieri JT, Iglewski BH, Rappuoli R (2014) Emerging infectious diseases. Bacterial Toxins B(3): 917–929.
César C, Marisa F, Natacha N, Artur F, Nereida C (2019) Marine vs freshwater microalgae exopolymers as biosolutions to microplastics pollution. Environ Pollut 249:372–380
Chentir I, Hamdi M, Doumandji A, Hadjsadok A, Ouada HB, Nasri M, Jridi M (2017) Enhancement of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) production in Spirulina (Arthrospira sp.) by two-step cultivation process and partial characterization of their polysaccharidic moiety. Int J Biol Macromol 105(2): 1412
Chew W, Ling K, Chuan T, Juan C, Yap J, Ying J, Suan HN (2017) Microalgae biorefinery: High value products perspectives. Bioresource Technol 229: 53-62
Dao GH, Wu GX, Wang XX, Zhang TY, Zhan XM, Hu HY (2018) Enhanced microalgae growth through stimulated secretion of indole acetic acid by symbiotic bacteria. Algal Res 33:345–351
Dineshkumar R, Subramanian J, Gopalsamy J, Jayasingam P, Arumugam A, Kannadasan S, Sampathkumar P (2017) The Impact of Using Microalgae as Biofertilizer in Maize (Zea mays L.). Waste Biomass Valorization 10(5): 1101–1110.
Dutta P, Muthukrishnan G, Gopalasubramaiam SK, Dharmaraj R, Karuppaiah A, Loganathan K, Periyasamy K, Pillai MA, Upamanya GK, Boruah S, Deb L, Kumari A, Mahanta M, Heisnam P, Mishra AK (2022) Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) and its mechanisms against plant diseases for sustainable agriculture and better productivity. Biocell 46(8):1843–1859
Felix-Cuencas L, Garcia-Trejo JF, Lopez-Tejeida S, de Leon-Ramirez JJ, Gutierrez-Antonio C, Feregrino-Perez AA (2021) Nitrogen and phosphorus flux in wastewater from three productive stages in a hyperintensive tilapia culture. Water Reuse 11(3):520–530
Friml J, Palme K (2002) Polar auxin transport—old questions and new concepts? Plant Mol Biol 49(3–4):273–284
Gitau MM, Farkas A, Balla B, Ordog V, Futo Z, Maroti G (2021) Strain-specific biostimulant Effects of Chlorella and Chlamydomonas Green Microalgae on Medicago truncatula. Plants-Basel 10(6):1060
Graziani G, Ritieni A, Cirillo A, Cice D, Di Vaio C (2020) Effects of biostimulants on annurca fruit quality and potential nutraceutical compounds at harvest and during storage. Plants-Basel 9(6):3096
Hajnal-Jafari T, Seman V, Stamenov D, Duric S (2020) Effect of Chlorella vulgaris on growth and photosynthetic pigment content in swiss chard (Beta vulgaris L. subsp. cicla). Pol J Microbiol 69:1–4
Hedden P, Thomas S, Stephen G (2012) Gibberellin biosynthesis and its regulation. Biochem J 444(1):11–25
Hu CY, Ren SC, Lin YL, Zhang JC, Zhu YY, Xiong C, Wang QB (2021) Kinetics of diatrizoate degradation by ozone and the formation of disinfection by-products in the sequential chlorination. Water Reuse 11(4):560–571
Kang Y, Kim M, Shim C, Bae S, Jang S (2021) Potential of algae-bacteria synergistic effects on vegetable production. Front Plant Sci 12:656662
Kholssi R, Marks EAN, Montero O, Mate AP, Debdoubi A, Rad C (2018) The growth of filamentous microalgae is increased on biochar solid supports. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 13:182–185
Kim JF, Jeong H, Lee JS, Choi SH, Ha M, Hur CG, Kim JS, Lee S, Park HS, Park YH, Oh TK (2008) Complete genome sequence of Leuconostoc citreum KM20. J Bacteriol 190(8):3093–3094
Liu XY, Hong Y, Gu WP (2021) Influence of light quality on Chlorella growth, photosynthetic pigments and high-valued products accumulation in coastal saline-alkali leachate. Water Reuse 11(2):301–311
Lv J, Zhao F, Feng J, Liu Q, Nan F, Liu X, Xie S (2020) The impact of particulate and soluble organic matter on physicochemical properties of extracellular polymeric substances in a microalga Neocystis mucosa SX. Algal Res 51:102064
Lv J, LS, Feng J, Liu Q, Guo J, Wang L, Jiao S, Xie S (2019) Effects of microalgal biomass as biofertilizer on the growth of cucumber and microbial communities in the cucumber rhizosphere. Turk J Bot 44(2): 167-+.
Markovska YK, Gorinova NI, Nedkovska MP, Miteva KM (2009) Cadmium-induced oxidative damage and antioxidant responses in Brassica juncea plants. Biol Plant 53(1):151–154
Martini F, Beghini G, Zanin L, Varanini Z, Zamboni A, Ballottari M (2021) The potential use of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and Chlorella sorokiniana as biostimulants on maize plants. Algal Res 60:102515
Meng WJ, Cheng ZJ, Sang YL, Zhang MM, Rong XF, Wang ZW, Tang YY, Zhang XS (2017) Type-B arabidopsis response regulators specify the shoot stem cell niche by dual regulation of Wuschel. Plant Cell 29(6):1357
Mógor ÁF, Ördög V, Lima GPP, Molnár Z, Mógor G (2017) Biostimulant properties of cyanobacterial hydrolysate related to polyamines. J Appl Phycol 30(1):453–460
Mu RM, Jia YT, Ma GX, Liu LR, Hao KX, Qi F, Shao YY (2021) Advances in the use of microalgal-bacterial consortia for wastewater treatment: Community structures, interactions, economic resource reclamation, and study techniques. Water Environ Res 93(8):1217–1230
Munees A, Kibret M (2014) Mechanisms and applications of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria: current perspective. J King Saud Univ Sci 26(1):1–20
Mutale-Joan C, Redouane B, Najib E, Yassine K, Lyamlouli K, Laila S, Zeroual Y, Hicham EA (2020) Screening of microalgae liquid extracts for their bio stimulant properties on plant growth, nutrient uptake and metabolite profile of Solanum lycopersicum L. Sci Rep 10(1):2820
Nafees M, Ullah S, Ahmed I (2022) Modulation of drought adversities in Vicia faba by the application of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and biochar. Microsc Res Tech 85(5):1856–1869
Ordog V, Stirk WA, van Staden J, Novak O, Strnad M (2004) Endogenous cytokinins in three genera of microalgae from the chlorophyta. J Phycol 40(1):88–95
Ortiz-Moreno ML, Solarte-Murillo LV, Sandoval-Parra KX (2020) Biofertilization with chlorophyta and cyanophyta: an alternative for organic food production. Acta Biológica Colombiana 25(2):303–313
Saddozai UK, Baloch MS, Alizai AA, Khakwani AA (2022) Wheat genotypes potential with longest coleoptile length sown at different sowing depths. Pak J Bot 54(4):1349–1358
Schreiber C, Schiedung H, Harrison L, Briese C, Ackermann B, Kant J, Schrey SD, Hofmann D, Singh D, Ebenhoh O, Amelung W, Schurr U, Mettler-Altmann T, Huber G, Jablonowski ND, Nedbal L (2018) Evaluating potential of green alga Chlorella vulgaris to accumulate phosphorus and to fertilize nutrient-poor soil substrates for crop plants. J Appl Phycol 30(5):2827–2836
Sharma GK, Khan SA, Shrivastava M, Bhattacharyya R, Sharma A, Gupta DK, Kishore P, Gupta N (2021) Circular economy fertilization: Phycoremediated algal biomass as biofertilizers for sustainable crop production. J Environ Manage 287:112295
Skorupskaite V, Makareviciene V, Sendzikiene E, Gumbyte M (2019) Microalgae Chlorella sp. cell disruption efficiency utilising ultrasonication and ultrahomogenisation methods. J Appl Phycol 31(4): 2349–2354.
Smith D (1993) Long-term preservation of test strains (Fungus). Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 31(3):227–230
Steinrücken P, Erga SR, Mjos SA, Kleivdal H, Prestegard SK (2017) Bioprospecting North Atlantic microalgae with fast growth and high polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) content for microalgae-based technologies. Algal Res 26:392–401
Stirk WA, Ördög V, Jäger J (2002) Cytokinin- and auxin-like activity in Cyanophyta and microalgae. J Appl Phycol 14(3):215–221
Suleiman AKA, Lourenço KS, Clark C, Luz RL, da Silva GHR, Vet LEM, Cantarella H, Fernandes TV, Kuramae EE (2020) From toilet to agriculture: fertilization with microalgal biomass from wastewater impacts the soil and rhizosphere active microbiomes, greenhouse gas emissions and plant growth. Resour Conserv Recycl 161:104924
Sun TP (2010) Gibberellin-GID1-DELLA: a pivotal regulatory module for plant growth and development. Plant Physiol 154(2):567–570
Sun Y, Wang H, Guo G, Pu Y, Yan B (2014) The isolation and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from the marine microalgae Isochrysis galbana. Carbohyd Polym 113:22–31
Sunarpi H, Nikmatullah A, Ambana Y, Ilhami BTK, Abidin AS, Ardiana N, Kirana IAP, Kurniawan NSH, Rinaldi R, Jihadi A, Prasedya ES (2021) Phytohormone content in brown macroalgae Sargassum from Lombok coast, Indonesia. IOP Conf Ser 712(1):012042
Tarakhovskaya ER, Maslov YI, Shishova MF (2007) Phytohormones in algae. Russ J Plant Physiol 54(2):163–170
Urquiaga S, Cruz KHS, Boddey RM (1992) Contribution of Nitrogen-Fixation to Sugar-Cane-N-15 And Nitrogen-Balance Estimates. Soil Sci Soc Am J 56(1):105–114
Viegas C, Gouveia L, Goncalves M (2021) Aquaculture wastewater treatment through microalgal. Biomass potential applications on animal feed, agriculture, and energy. J Environ Manag 286: 112187.
Wake H, Akasaka A, Umetsu H, Ozeki Y, Shimomura K, Matsunaga T (1992) Enhanced germination of artificial seeds by marine cyanobacterial extract. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 36(5):684–688
Wang Q, Ge C, Xu SA, Wu Y, Yang X (2020) The endophytic bacterium Sphingomonas SaMR12 alleviates Cd stress in oilseed rape through regulation of the GSH-AsA cycle and antioxidative enzymes. BMC Plant Biol 20(1): 63.
Wu Y, Zaiden N, Cao B (2018) The core- and pan-genomic analyses of the genus comamonas: from environmental adaptation to potential virulence. Front Microbiol 9:3096
Wu H, Haig T, Pratley J, Lemerle D, An M (2001) Allelochemicals in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.): cultivar difference in the exudation of phenolic acids. J Agricult Food Chem 49(8): 3742–3745.
Xie Y, Wang Z, Cheng X, Qiu R, Hamoud YA, Hong C, Zong X, Wang Y, Agathokleous E, Guo X (2022) Dissecting the combined effects of cultivar, fertilization, and irrigation on rhizosphere bacterial communities and nitrogen productivity in rice. Sci Total Environ 835:155534
Yan Hu, Lingli Lu, Shengke T, Senman Li, Xiaoxia L (2018) Cadmium-induced nitric oxide burst enhances Cd tolerance at early stage in roots of a hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii partially by altering glutathione metabolism. Sci Total Environ 650(2):2761–2770
Zhang Z, Tang L, Zhang Y (2018) Algae-bacteria interactions and their ecological functions in the ocean. Microbiol China 45(9):2043–2053
Zikmanis P, Brants K, Kolesovs S, Semjonovs P (2020) Extracellular polysaccharides produced by bacteria of the Leuconostocgenus. World J Microbiol Biotechnol (formerly MIRCEN J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol) 36(11):161
Zou Y, Zeng Q, Li H, Liu H, Lu Q (2020) Emerging technologies of algae-based wastewater remediation for bio-fertilizer production: a promising pathway to sustainable agriculture. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 96(3):551–563
Funding
This study was supported by China National Funds For Distinguished Young Scientists (Grant numbers- 51925803), and Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant numbers- 52000122; 51878388).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S-NW: formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing—original draft. S-HG: writing—review & editing. L-LZ: conceptualization, methodology, funding acquisition, writing—review & editing. JZ: funding acquisition, writing—review & editing
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Wendy Stirk.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, SN., Ge, SH., Zhuang, LL. et al. Multiple Pathways for the Enhancement of Wheat Growth by Chlorella vulgaris. J Plant Growth Regul 43, 550–562 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-023-11113-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-023-11113-w