Abstract
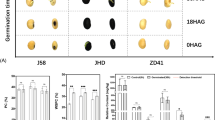
Environmental factors such as light, temperature, and humidity affecting the top and bottom node of the soybean plant, are important determinants of the seed constituents, and these are neglected over the years. Therefore, this study was designed to determine the anthocyanin, proanthocyanidin (PA), sucrose, oil, protein, and metabolite content of four black soybean to identify the changes during seed development stages at different node positions of the soybean plant. The soybean stem was divided into two equal parts depending on the number of nodes. Seeds with uniform size at the top and bottom node were harvested at R6: full-size seed, R7: physiological maturity, and R8: when 95% of the pods were matured. Among the four varieties used, the E314 accounted for the highest anthocyanin content (2.43 mg g−1) at the top node of R8 stage. In addition, at the top node, increased PA contents were observed, and the maximum content (3.14 mg g−1) was obtained at the R7 stage in E314 cultivar. Sucrose content declined as the seed matured from R6 to R8 with the highest content (9.77 mg g−1) at the top node of R6 stage. The metabolic pathway analysis revealed that node position had profoundly influenced the metabolic profile including lysine biosynthesis, arachidonic acid metabolism, and fatty acid biosynthesis at the various development stages of the seed. Our results provide optimum growth stage and node position of soybean seed to be harvested to obtain maximum seed components since seed harvested at the top position contained higher protein, anthocyanin, and PA than seed from the bottom node.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Lateif K, Bogusz D, Hocher V (2012) The role of flavonoids in the establishment of plant roots endosymbioses with arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi, rhizobia and Frankia bacteria. Plant Signal Behav 7:636–641. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.20039
Akula R, Ravishankar GA (2011) Influence of abiotic stress signals on secondary metabolites in plants. Plant Signal Behav 6:1720–1731. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.6.11.17613
Asproudi A, Piano F, Anselmi G et al (2015) Proanthocyanidin composition and evolution during grape ripening as affected by variety Nebbiolo and Barbera cv. OENO One 49:59
Baskar V, Venkatesh R, Ramalingam S (2018) Flavonoids (Antioxidants Systems) in Higher Plants and Their Response to Stresses. In: Gupta DK, Palma JM, Corpas FJ (eds) Antioxidants and Antioxidant Enzymes in Higher Plants. Springer, Cham, pp 253–268
Bellaloui N (2012) Soybean seed phenol, lignin, and isoflavones and sugars composition altered by foliar boron application in soybean under water stress. FNS 03:579–590. https://doi.org/10.4236/fns.2012.34080
Bellaloui N, Gillen AM (2010) Soybean seed protein, oil, fatty acids, N, and S partitioning as affected by node position and cultivar differences. AS 1:110–118. https://doi.org/10.4236/as.2010.13014
Bellaloui N, Bruns HA, Abbas HK et al (2015) Agricultural practices altered soybean seed protein, oil, fatty acids, sugars, and minerals in the Midsouth USA. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00031
Bennett JO, Krishnan AH, Wiebold WJ, Krishnan HB (2003) Positional effect on protein and oil content and composition of soybeans. J Agric Food Chem 51:6882–6886. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf034371l
Bueno PCP, Lopes NP (2020) Metabolomics to characterize adaptive and signaling responses in legume crops under abiotic stresses. ACS Omega 5:1752–1763. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b03668
Cádiz-Gurrea M, Borrás-Linares I, Lozano-Sánchez J et al (2017) Cocoa and grape seed byproducts as a source of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory proanthocyanidins. IJMS 18:376. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020376
Caldwell CR, Britz SJ, Mirecki RM (2005) Effect of Temperature, elevated carbon dioxide, and drought during seed development on the isoflavone content of dwarf soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merrill] grown in controlled environments. J Agric Food Chem 53:1125–1129. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0355351
Cheynier V, Comte G, Davies KM et al (2013) Plant phenolics: recent advances on their biosynthesis, genetics, and ecophysiology. Plant Physiol Biochem 72:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2013.05.009
Coutinho ID, Henning LMM, Döpp SA et al (2018) Flooded soybean metabolomic analysis reveals important primary and secondary metabolites involved in the hypoxia stress response and tolerance. Environ Exp Bot 153:176–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.05.018
Das A, Rushton P, Rohila J (2017) Metabolomic profiling of soybeans (Glycine max L.) reveals the importance of sugar and nitrogen metabolism under drought and heat stress. Plants 6:21. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants6020021
de Gonçalves JF, C, Barreto DC de S, Santos Junior UM dos, et al (2005) Growth, photosynthesis and stress indicators in young rosewood plants (Aniba rosaeodora Ducke) under different light intensities. Braz J Plant Physiol 17:325–334. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1677-04202005000300007
Deng J, Yang C, Zhang J et al (2017) Organ-specific differential nmr-based metabonomic analysis of soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] fruit reveals the metabolic shifts and potential protection mechanisms involved in field mold infection. Front Plant Sci 8:508. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00508
Dennis T, Li X, Xiao X et al (2020) Spatiotemporal shading regulates anthocyanin, proanthocyanidin, and sucrose accumulation in black soybean seeds. Agron J 112:708–718. https://doi.org/10.1002/agj2.20138
Dixon RA, Xie D, Sharma SB (2005) Proanthocyanidins – a final frontier in flavonoid research? New Phytol 165:9–28. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2004.01217.x
Falcone Ferreyra ML, Rius SP, Casati P (2012) Flavonoids: biosynthesis, biological functions, and biotechnological applications. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2012.00222
Ha TJ, Lee JH, Shin S-O et al (2009) Changes in anthocyanin and isoflavone concentrations in black seed-coated soybean at different planting locations. J Crop Sci Biotechnol 12:79–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-009-0093-9
Ha J, Kim M, Kim MY et al (2018) Transcriptomic variation in proanthocyanidin biosynthesis pathway genes in soybean (Glycine spp.): variation in proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in soybean. J Sci Food Agric 98:2138–2146. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.8698
Huber SC, Li K, Nelson R et al (2016) Canopy position has a profound effect on soybean seed composition. PeerJ 4:e2452. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.2452
Hussain MI, Al- Dakheel AJ, Reigosa MJ (2018) Genotypic differences in agro-physiological, biochemical and isotopic responses to salinity stress in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) plants: prospects for salinity tolerance and yield stability. Plant Physiol Biochem 129:411–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.06.023
Hwang E-Y, Song Q, Jia G et al (2014) A genome-wide association study of seed protein and oil content in soybean. BMC Genom 15:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-1
Jung SC, Martinez-Medina A, Lopez-Raez JA, Pozo MJ (2012) Mycorrhiza-induced resistance and priming of plant defenses. J Chem Ecol 38:651–664. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-012-0134-6
Katiyar SK, Pal HC, Prasad R (2017) Dietary proanthocyanidins prevent ultraviolet radiation-induced non-melanoma skin cancer through enhanced repair of damaged DNA-dependent activation of immune sensitivity. Semin Cancer Biol 46:138–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.04.003
Koch K (2004) Sucrose metabolism: regulatory mechanisms and pivotal roles in sugar sensing and plant development. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:235–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2004.03.014
Kovinich N, Saleem A, Arnason JT, Miki B (2012) Identification of two anthocyanidin reductase genes and three red-brown soybean accessions with reduced Anthocyanidin Reductase 1 mRNA, activity, and seed coat Proanthocyanidin Amounts. J Agric Food Chem 60:574–584. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf2033939
Kruger MJ, Davies N, Myburgh KH, Lecour S (2014) Proanthocyanidins, anthocyanins and cardiovascular diseases. Food Res Int 59:41–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2014.01.046
Li P, Dong Q, Ge S et al (2016) Metabolic engineering of proanthocyanidin production by repressing the isoflavone pathways and redirecting anthocyanidin precursor flux in legume. Plant Biotechnol J 14:1604–1618. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12524
Li D, Wang P, Luo Y et al (2017) Health benefits of anthocyanins and molecular mechanisms: update from recent decade. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 57:1729–1741. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2015.1030064
Maddonni GA, Otegui ME, Cirilo AG (2001) Plant population density, row spacing and hybrid effects on maize canopy architecture and light attenuation. Field Crop Res 71:183–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4290(01)00158-7
Meng L-S, Li Y-Q, Liu M-Q, Jiang J-H (2016) The Arabidopsis ANGUSTIFOLIA3-YODA gene cascade induces anthocyanin accumulation by regulating sucrose levels. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01728
Meng L-S, Xu M-K, Wan W et al (2018) Sucrose Signaling regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis through a MAPK cascade in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 210:607–619. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.118.301470
Muzquiz M, Varela A, Burbano C et al (2012) Bioactive compounds in legumes: pronutritive and antinutritive actions. Implications for nutrition and health. Phytochem Rev 11:227–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-012-9233-9
Nile SH, Park SW (2014) Edible berries: bioactive components and their effect on human health. Nutrition 30:134–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2013.04.007
Pervaiz T, Songtao J, Faghihi F et al (2017) Naturally Occurring anthocyanin, structure, functions and biosynthetic pathway in fruit plants. J Plant Biochem Physiol. https://doi.org/10.4172/2329-9029.1000187
Prati S, Baravelli V, Fabbri D et al (2007) Composition and content of seed flavonoids in forage and grain legume crops. J Sep Sci 30:491–501. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.200600383
Shi H, Wang B, Yang P et al (2016) Differences in sugar accumulation and mobilization between sequential and non-sequential senescence wheat cultivars under natural and drought conditions. PLoS One 11:e0166155. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0166155
Singh B, Singh JP, Kaur A, Singh N (2017a) Phenolic composition and antioxidant potential of grain legume seeds: a review. Food Res Int 101:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2017.09.026
Singh B, Singh JP, Singh N, Kaur A (2017b) Saponins in pulses and their health promoting activities: a review. Food Chem 233:540–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.04.161
Todd JJ, Vodkin LO (1993) Pigmented soybean (Glycine max) seed coats accumulate proanthocyanidins during development. Plant Physiol 102:663–670. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.102.2.663
Tsuda T (2012) Dietary anthocyanin-rich plants: biochemical basis and recent progress in health benefits studies. Mol Nutr Food Res 56:159–170. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201100526
Xu BJ, Chang SKC (2007) A comparative study on phenolic profiles and antioxidant activities of legumes as affected by extraction solvents. J Food Sci 72:S159–S166. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3841.2006.00260.x
Zhang G, Li P, Zhang W, Zhao J (2017) Analysis of multiple soybean phytonutrients by near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy. Anal Bioanal Chem 409:3515–3525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0288-8
Zhang H, Yasmin F, Song B-H (2019) Neglected treasures in the wild — legume wild relatives in food security and human health. Curr Opin Plant Biol 49:17–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2019.04.004
Zoratti L, Karppinen K, Luengo Escobar A et al (2014) Light-controlled flavonoid biosynthesis in fruits. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00534
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFD0300209), China Agriculture Research System (CARS-04-PS19) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (31301277).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL and WY; Conceptualization. DT and MAA: Data curation. DT, MAA, AU, XH, and HHJ; Formal analysis. JL; funding acquisition. JL; Investigation. JL and WY; Methodology. JL and WY; Project administration. JL and WY; Resources. MUF, C-WX, XX, and KSC: Software. JL; Supervision. JL; Validation. DT, MAA, and AU; Visualization. DT, MAA, Jiang Liu and WY; Roles/Writing—original draft; Writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Sudhir K. Sopory.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takpah, D., Asghar, M.A., Raza, A. et al. Metabolomics Analysis Reveals Soybean Node Position Influence on Metabolic Profile of Soybean Seed at Various Developmental Stages. J Plant Growth Regul 42, 6788–6800 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-023-11048-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-023-11048-2