Abstract
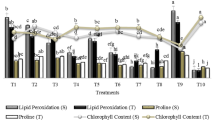
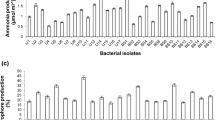
Despite of extensive research in isolating and identifying plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria, the rhizosphere of weeds is still ignored. The current study demonstrates a great opportunity to isolate and identify novel beneficial microbes from weed rhizosphere having the potential to improve plant growth. Nine bacterial strains were isolated from the rhizosphere of Cyperus rotundus L. found in three different crops, i.e., cotton, maize, and rice, and screened for plant growth-promoting (PGP) traits. Out of nine isolates, two isolates (WBN01 and WBN02) possessed all PGP traits and showed the potential for ammonia production, protease activity, and catalase activity. Both strains were N2 fixers, secreted indole acetic acid (IAA), and showed phosphate (P)-solubilizing potential, among which WBN01 had higher IAA production (8.69 µg/mL) and P-solubilization (53.83 µg/mL) capacity. These strains were identified as Enterobacter spp. based on their morpho-physiological characters, 16S rRNA gene analysis, and phylogenetic analysis. Greenhouse experiment showed that the inoculation of isolates to wheat plants significantly improved their growth and photosynthetic machinery. On the other hand, these isolates down-regulated photosynthetic electron transport, absorption, and trapping fluxes, consequently increasing PSII photochemistry. The enhanced antioxidant catalase enzyme activity, protein content, and greater accumulation of proline contents due to bacterial inoculation have more significant effect on improving PSII machinery. This study reveals that weeds rhizosphere possesses novel Enterobacter spp. microbes, which can serve as potent biofertilizers, while reducing the application of chemical fertilizers without affecting normal plant growth.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data that support the findings of this study have been deposited in “GenBank” under the accession numbers MT796341 and MT796342.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Abbas SZ, Rafatullah M, Ismail N, Lalung J (2014) Isolation, identification, characterization, and evaluation of cadmium removal capacity of Enterobacter species. J Basic Microbiol 54(12):1279–1287
Abo-Aba S, Soliman E, Nivien AA (2006) Enhanced production of extra cellular alkaline protease in Bacillus circulance through plasmid transfer. Res J Agric Biol Sci 16:526–530
Aebi H (1984) [13] Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Akhtar MS, Azam T (2014) Effects of PGPR and antagonistic fungi on the growth, enzyme activity and fusarium root-rot of pea. Arch Phytopathol Plant Prot 47(2):138–148
Anbi AA, Mirshekari B, Eivazi A, Yarnia M, Behrouzyar EK (2020) PGPRs affected photosynthetic capacity and nutrient uptake in different Salvia species. J Plant Nutr 43(1):108–121
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta Vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24(1):1
Baber M, Fatima M, Abbas R, Mansoor M, Naz S, Hanif M, Naqqash T (2018) Weed rhizosphere: a source of novel plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR). Int J Biosci (IJB) 13:224–234
Bates L, Waldren R, Teare I (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39(1):205–207
Bhandari D, Sen D (1979) Agro-ecosystem analysis of the Indian arid zone I. Indigofera cordifolia heyne ex roth as a weed. Agro-Ecosystems 5(3):257–262
Blackburn F (1984) Sugarcane. Longman, New York
Bouyoucos GJ (1962) Hydrometer method improved for making particle size analyses of soils 1. Agron J 54(5):464–465
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254
Bremner JM, Mulvaney CS (1982) Nitrogen-total. In: Page AL, Miller RH (eds) Methods of soil analysis: part 2. American Society of Agronomy, Soil Science Society of America, Madison, pp 595–624
Bukhat S, Manzoor H, Zafar ZU, Azeem F, Rasul S (2019) Salicylic acid induced photosynthetic adaptability of raphanus sativus to salt stress is associated with antioxidant capacity. J Plant Growth Regul 39:809
Çakmakçı R, Erat M, Erdoğan Ü, Dönmez MF (2007) The influence of plant growth–promoting rhizobacteria on growth and enzyme activities in wheat and spinach plants. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 170(2):288–295
Cessna S, Demmig-Adams B, Adams WW III (2010) Exploring photosynthesis and plant stress using inexpensive chlorophyll fluorometers. J Nat Resour Life Sci Educ 39(1):22–30
d Steel RG, Torrie JH (1986) Principles and procedures of statistics: a biometrical approach. McGraw-Hill, New York
Deepa C, Dastager SG, Pandey A (2010) Isolation and characterization of plant growth promoting bacteria from non-rhizospheric soil and their effect on cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.) seedling growth. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 26(7):1233–1240
Ejaz S, Batool S, Anjum MA, Naz S, Qayyum MF, Naqqash T, Shah KH, Ali S (2020) Effects of inoculation of root-associative Azospirillum and Agrobacterium strains on growth, yield and quality of pea (Pisum sativum L.) grown under different nitrogen and phosphorus regimes. Sci Hortic 270:109401
Fickett ND, Boerboom CM, Stoltenberg DE (2013) Predicted corn yield loss due to weed competition prior to postemergence herbicide application on Wisconsin farms. Weed Technol 27(1):54–62
Galloway JN, Townsend AR, Erisman JW, Bekunda M, Cai Z, Freney JR, Martinelli LA, Seitzinger SP, Sutton MA (2008) Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 320(5878):889–892
Grimont F, Grimont PA (2006) The genus enterobacter. Prokaryotes 6:197–214
Halford C, Hamill AS, Zhang J, Doucet C (2001) Critical period of weed control in no-till soybean (Glycine max) and corn (Zea mays). Weed Technol 15(4):737–744
Hanif K, Hameed S, Imran A, Naqqash T, Shahid M, Van Elsas JD (2015) Isolation and characterization of a β-propeller gene containing phosphobacterium Bacillus subtilis strain KPS-11 for growth promotion of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Front Microbiol 6:583
Kadir J, Charudattan R, Berger R (2000) Effects of some epidemiological factors on levels of disease caused by Dactylaria higginsii on Cyperus rotundus. Weed Sci 48:61–68
Karthikeyan B, Sakthivel U, Narayanan JS (2013) Role of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria for commercially grown medicinal plants. In: Maheshwari DK, Saraf M (eds) Bacteria in agrobiology: crop productivity. Springer, Berlin, pp 65–76
Kim K, Jang Y-J, Lee S-M, Oh B-T, Chae J-C, Lee K-J (2014) Alleviation of salt stress by Enterobacter sp. EJ01 in tomato and Arabidopsis is accompanied by up-regulation of conserved salinity responsive factors in plants. Mol Cells 37(2):109
Kravchenko L, Azarova T, Makarova N, Tikhonovich I (2004) The effect of tryptophan present in plant root exudates on the phytostimulating activity of rhizobacteria. Microbiology 73(2):156–158
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA, X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35:1547–1549
Laidlaw M, Louden M, Bean T, Thompson E (2017) Reducing weed risks from fodder. Herbarium Queensland, Toowong
Lastochkina O, Pusenkova L, Yuldashev R, Babaev M, Garipova S, Dy B, Khairullin R, Aliniaeifard S (2017) Effects of Bacillus subtilis on some physiological and biochemical parameters of Triticum aestivum L. (wheat) under salinity. Plant Physiol Biochem 121:80–88
Lastochkina O, Aliniaeifard S, Seifikalhor M, Yuldashev R, Pusenkova L, Garipova S (2019) Plant growth-promoting bacteria: biotic strategy to Cope with abiotic stresses in wheat. In: Hasanuzzaman M, Nahar K (eds) Wheat production in changing environments. Springer, Singapore, pp 579–614
Lastochkina O, Garshina D, Allagulova C, Fedorova K, Koryakov I, Vladimirova A (2020a) Application of endophytic Bacillus subtilis and salicylic acid to improve wheat growth and tolerance under combined drought and Fusarium root rot stresses. Agronomy 10(9):1343
Lastochkina O, Garshina D, Ivanov S, Yuldashev R, Khafizova R, Allagulova C, Fedorova K, Avalbaev A, Maslennikova D, Bosacchi M (2020b) Seed priming with endophytic Bacillus subtilis modulates physiological responses of two different Triticum aestivum L. Cultivars under Drought Stress. Plants 9(12):1810
Lastochkina O, Garshina D, Allagulova C, Pusenkova L, Garipova S, Maslennikova D, Fedorova K, Shpirnaya I, Ibragimov A, Koryakov I (2021) Potential aspects of plant growth promoting bacteria to improve horticultural crop production. Int J Hortic Sci Technol 8(2):103–122
Lati RN, Filin S, Eizenberg H (2011) Temperature-and radiation-based models for predicting spatial growth of purple nutsedge (Cyperus rotundus). Weed Sci 59(4):476–482
Li W, Zhang S, Shan L (2007) Responsibility of non-stomatal limitations for the reduction of photosynthesis—response of photosynthesis and antioxidant enzyme characteristics in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) seedlings to water stress and rehydration. Front Agric China 1(3):255
Li L, Zhengyi L, Chunjing H, Xincheng Z, Siping C, Litao Y, Yangrui L, Qianli A (2012) Plant growth-promoting nitrogen-fixing enterobaeteria are in association with sugarcane plants growing in Guangxi. China 27(4):391–398
Macedo-Raygoza GM, Valdez-Salas B, Prado FM, Prieto KR, Yamaguchi LF, Kato MJ, Canto-Canché BB, Carrillo-Beltrán M, Di Mascio P, White JF (2019) Enterobacter cloacae, an endophyte that establishes a nutrient-transfer symbiosis with banana plants and protects against the black Sigatoka pathogen. Front Microbiol 10:804
Majeed A, Abbasi MK, Hameed S, Imran A, Rahim N (2015) Isolation and characterization of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria from wheat rhizosphere and their effect on plant growth promotion. Front Microbiol 6:198
Majeed A, Abbasi MK, Hameed S, Imran A, Naqqash T, Hanif MK (2018) Isolation and characterization of sunflower associated bacterial strain with broad spectrum plant growth promoting traits. Microbiol Res 216:56
Marques AP, Pires C, Moreira H, Rangel AO, Castro PM (2010) Assessment of the plant growth promotion abilities of six bacterial isolates using Zea mays as indicator plant. Soil Biol Biochem 42(8):1229–1235
McLean E (1982) Soil pH and lime requirement. In: Page AL (ed) Methods of soil analysis, 2nd edn. ASA and SSSA, Madison, WI, pp 199–224
Mehnaz S, Kowalik T, Reynolds B, Lazarovits G (2010) Growth promoting effects of corn (Zea mays) bacterial isolates under greenhouse and field conditions. Soil Biol Biochem 42(10):1848–1856
Melis A (1999) Photosystem-II damage and repair cycle in chloroplasts: what modulates the rate of photodamage in vivo? Trends Plant Sci 4(4):130–135
Metwali EM, Abdelmoneim TS, Bakheit MA, Kadasa NM (2015) Alleviation of salinity stress in faba bean (Vicia faba L.) plants by inoculation with plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR). Plant Omics 8(5):449
Montanez A, Blanco AR, Barlocco C, Beracochea M, Sicardi M (2012) Characterization of cultivable putative endophytic plant growth promoting bacteria associated with maize cultivars (Zea mays L.) and their inoculation effects in vitro. Appl Soil Ecol 58:21–28
Naqqash T, Hameed S, Imran A, Hanif MK, Majeed A, van Elsas JD (2016) Differential response of potato toward inoculation with taxonomically diverse plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Front Plant Sci 7:144
Naqqash T, Imran A, Hameed S, Shahid M, Majeed A, Iqbal J, Hanif MK, Ejaz S, Malik KA (2020) First Report of diazotrophic Brevundimonas spp. as growth enhancer and root colonizer of potato. Sci Rep 10(1):1–14
Naveed M, Mitter B, Reichenauer TG, Wieczorek K, Sessitsch A (2014) Increased drought stress resilience of maize through endophytic colonization by Burkholderia phytofirmans PsJN and Enterobacter sp. FD17. Environ Exp Bot 97:30–39
Nei M, Kumar S (2000) Molecular evolution and phylogenetics. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Nelson DR, Mele PM (2007) Subtle changes in rhizosphere microbial community structure in response to increased boron and sodium chloride concentrations. Soil Biol Biochem 39(1):340–351
Norris RF, Kogan M (2000) Interactions between weeds, arthropod pests, and their natural enemies in managed ecosystems. Weed Sci 48(1):94–158
Okon Y, Albrecht SL, Burris R (1977) Methods for growing Spirillum lipoferum and for counting it in pure culture and in association with plants. Appl Environ Microbiol 33(1):85–88
Olanrewaju OS, Glick BR, Babalola OO (2017) Mechanisms of action of plant growth promoting bacteria. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 33(11):197
Olsen SR (1954) Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate, vol 939. US Department of Agriculture, Washington, DC
Peerzada AM (2017) Biology, agricultural impact, and management of Cyperus rotundus L.: the world’s most tenacious weed. Acta Physiol Plant 39(12):270
Pérez-Montaño F, Alías-Villegas C, Bellogín R, Del Cerro P, Espuny M, Jiménez-Guerrero I, López-Baena FJ, Ollero F, Cubo T (2014) Plant growth promotion in cereal and leguminous agricultural important plants: from microorganism capacities to crop production. Microbiol Res 169(5–6):325–336
Peterson L (1977) A field guide to edible wild plants of eastern and central North America, vol 23. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, Boston
Pikovskaya R (1948) Mobilization of phosphorus in soil in connection with the vital activity of some microbial species. Mikrobiologiya 17:362–370
Reddy AR, Chaitanya KV, Vivekanandan M (2004) Drought-induced responses of photosynthesis and antioxidant metabolism in higher plants. J Plant Physiol 161(11):1189–1202
Rendic S (1975) Resolution of (+/-)-alpha-(3-benzoylphenyl)-propionic acid (Ketoprofen) and diastereomer interactions of its enantiomers with some biological systems. Chimia 29:170–172
Rhoades J, Manteghi NA, Shouse P, Alves W (1989) Estimating soil salinity from saturated soil-paste electrical conductivity. Soil Sci Soc Am J 53(2):428–433
Richards LA (1954) Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. Soil Sci 78(2):154
Rørth M, Jensen P (1967) Determination of catalase activity by means of the Clark oxygen electrode. Biochim Biophys Acta 139(1):171–173
Sachdev DP, Chaudhari HG, Kasture VM, Dhavale DD, Chopade BA (2009) Isolation and characterization of indole acetic acid (IAA) producing Klebsiella pneumoniae strains from rhizosphere of wheat (Triticum aestivum) and their effect on plant growth. Indian J Exp Biol 47:993–1000
Santi C, Bogusz D, Franche C (2013) Biological nitrogen fixation in non-legume plants. Ann Bot 111(5):743–767
Sarathambal C, Ilamurugu K (2014) Phosphate solubilising diazotrophic bacteria associated with rhizosphere of weedy grasses. Indian J Weed Sci 46(4):364–369
Schreiter S, Ding G-C, Heuer H, Neumann G, Sandmann M, Grosch R, Kropf S, Smalla K (2014) Effect of the soil type on the microbiome in the rhizosphere of field-grown lettuce. Front Microbiol 5:144
Shahzad SM, Khalid A, Arshad M, Tahir J, Mahmood T (2010) Improving nodulation, growth and yield of Cicer arietinum L. through bacterial ACC-deaminase induced changes in root architecture. Eur J Soil Biol 46(5):342–347
Sokhangoy SH, Ansari K, Eradatmand AD (2012) Effect of bio-fertilizers on performance of Dill (Anethum graveolens L.). Iran J Plant Physiol 4:552–547
Somasegaran P, Hoben HJ (2012) Handbook for rhizobia: methods in legume-Rhizobium technology. Springer, Berlin
Stepp JR (2004) The role of weeds as sources of pharmaceuticals. J Ethnopharmacol 92(2–3):163–166
Vincent JM (1970) A manual for the practical study of the root-nodule bacteria. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Hoboken
Wang X, Wang Y, Tian J, Lim BL, Yan X, Liao H (2009) Overexpressing AtPAP15 enhances phosphorus efficiency in soybean. Plant Physiol 151(1):233–240
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173(2):697–703
Wickens GE, Haq N, Day P, Day PR (1989) New crops for food and industry. Springer, Berlin
Yadav J, Verma JP, Tiwari KN (2010) Effect of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on seed germination and plant growth chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) under in vitro conditions. Biol Forum 2:15–18
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Dr. Habib-ur-Rehman Athar for providing necessary laboratory facilities at the Institute of Pure and Applied Biology to carry out present research work.
Funding
This study was partially funded by Deputy Director, Higher Education Commission, Islamabad, Pakistan under Startup Research Grant Program—R & D via Grant Number 21- 1627/SRGP/R&D/HEC/2017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: MB and TN; Data acquisition: MS and MT; Data analysis: MF and Saif ur Rehman; Critical revision of the manuscript: GS and MA; Writing and approval of the final submitted version: TN and SB.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest and competing interest.
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
All authors have approved the manuscript for submission and publication.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Vijay Pratap Singh.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naqqash, T., Fatima, M., Saif-ur-Rehman et al. Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria Significantly Improves Growth Attributes and Photosynthetic Machinery in Wheat. J Plant Growth Regul 41, 3372–3386 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-021-10519-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-021-10519-8