Abstract
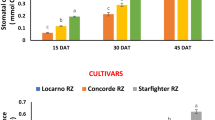
Different fertilization methods will affect rice yield and its growth. To address the influence of different fertilization methods on yield, photosynthetic intensity, and nitrogen synthetase enzymatic activities for hill direct-seeded rice, the field trials were conducted using two different rice varieties Yuxiangyouzhan and Wufengyou 615 in 2018 and 2019. There were four fertilizer application treatments at the rate of 150 kg N ha−1 in hill direct-seeded rice: All the fertilizer deep application as a disposable basal fertilizer by machine (T1); deep application of mechanized decrement fertilizers, i.e. 50% of all fertilizers into 10 cm depth of soil as basal by machine, whilst 25% of fertilizers at tillering stage and 25% of the fertilizer in the panicle initiation (PI) stage were artificially sown on the soil surface (T2), respectively; farmers’ manually traditional surface broadcast, i.e. 40% of the fertilizers as the basal fertilizer, whilst 30% of fertilizers was applied at tillering and PI stage (T3), respectively, and the control treatment is no fertilization (T0). The result showed that grain yield of Yuxiangyouzhan and Wufengyou 615 for T2 was increased by 25.79 and 11.98%, compared with T3, respectively. The rate of photosynthetic, water use efficiency and stomatal conductance for T2 treatment was 35.86, 27.32, and 56.87% higher than that for T0 treatment, respectively. It was also found that T2 had the highest chlorophyll and carotenoids during the heading stage (HS). We also observed that glutamine systhetase (GS) and glutamate synhthase (GOGAT) activities of T2 were higher than T3 at mid-tillering stage for both rice varieties, respectively. Among all treatments at the HS, Wufengyou 615 had the largest leaf area index and total above-ground biomass. Hence, the present study revealed that 50% of total amount of fertilization as basal fertilization deep placement with the rest of fertilization as topdressing more benefited the rice growth and produced more grain yield.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandaogo A, Bidjokazo F, Youl S, Safo E, Abaidoo R, Andrews O (2014) Effect of fertilizer deep placement with urea supergranule on nitrogen use efficiency of irrigated rice in Sourou Valley (Burkina Faso). Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 102:79–89
Cao XC, Zhong C, Zhu CQ, Zhu LF, Zhang JH, Wu LH, Jin QY (2018) Ammonium uptake and metabolism alleviate PEG-induced water stress in rice seedlings. Plant Physio Biochem 132:128–137
Cardona T, Shao S, Nixon PJ (2018) Enhancing photosynthesis in plants: the light reactions. Essays Biochem 62:85–94
Chen S, Yin M, Zheng X, Liu SW, Chu G, Xu CM, Wang DY, Zhang XF (2019) Effect of dense planting of hybrid rice on grain yield and solar radiation use in Southeastern China. Agron J 11:1229–1238
Du B, Luo HW, He LX, Zhang LH, Liu YF, Mo ZW, Pan SG, Tian H, Duan MY, Tang XR (2019) Rice seed priming with sodium selenate: effects on germination, seedling growth, and biochemical attributes. Sci Rep 9:4311
Evans John R, Clarke VC (2019) The nitrogen cost of photosynthesis. J Exp Bot 70(1):7–15
Fu XM, Gui RF, Li W, Gao ZF, Umair A (2020) Nitrogen and α-ketoglutaric acid application modulate grain yield, aroma, nutrient uptake and physiological attributes in fragrant rice. J Plant Growth Regul. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10215-z
Guan CY (2011) Modern crop cultivation. Chinese higher education press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Hitchcock A, Jackson PJ, Chidgey JW, Dickman MJ, Hunter CN, Canniffe DP (2016) Biosynthesis of chlorophyll a in a purple bacterial phototroph and assembly into a plant chlorophyll-protein complex. ACS Synth Biol 5:948–954
Hou WF, Tränkner M, Lu JW, Yan JY, Huang SY, Ren T, Cong RH, Li XK (2019a) Interactive effects of nitrogen and potassium on photosynthesis and photosynthetic nitrogen allocation of rice leaves. BMC Plant Biol 19:302
Hou WF, Xue XX, Li XK, Khan MR, Yan JY, Ren T, Cong RH, Lu JW (2019b) Interactive effects of nitrogen and potassium on: grain yield, nitrogen uptake and nitrogen use efficiency of rice in low potassium fertility in China. Field Crops Res 236:14–23
Islam SMM, Gaihre YK, Shah AL, Singh U, Sarkar MIU, Satter MA, Sanabria J, Biswas JC (2016) Rice yields and nitrogen use efficiency with different fertilizers and water management under intensive lowland rice cropping systems in Bangladesh. Nutr Cycling Agroecosyst 106:143–156
Li HS (2006) Principles and techniques of plant physiology and biochemistry. Higher education press, Beijing, China (in Chinese)
Li SY, Jiang HL, Wang JJ, Wang YD, Pan SG, Tian H, Duan MY, Wang SL, Tang XR, Mo ZW (2019) Responses of plant growth, physiological, gas exchange parameters of super and non-super rice to rhizosphere temperature at the tillering stage. Sci Rep 9:10618
Liu K, Deng J, Lu J, Wang X, Lu B, Tian X, Zhang Y (2019a) High nitrogen levels alleviate yield loss of super hybrid rice caused by high temperatures during the flowering stage. Front Plant Sci 10:357
Liu K, Yang R, Lu J, Wang XY, Lu BL, Tian XH, Zhang YB (2019b) Radiation use efficiency and source-sink changes of super hybrid rice under shade stress during grain-filling stage. Agron J 111:1–11
Liu TQ, Fan DJ, Zhang XX, Chen J, Li CF, Cao CG (2015) Deep placement of nitrogen fertilizers reduces ammonia volatilization and increases nitrogen utilization efficiency in no-tillage paddy fields in central China. Field Crops Res 184:80–90
Liu WF, Yang H, Liu JG, Azevedo LB, Wang XY, Xu ZX, Abbaspour KC, Schulin R (2016a) Global assessment of nitrogen losses and trade-offs with yields from major crop cultivations. Sci Total Environ 572:526–537
Liu XW, Wang HY, Zhou JM, Hu FQ, Zhu DJ, Chen ZM, Liu YZ (2016b) Effect of N fertilization pattern on rice yield, N use efficiency and fertilizer-N fate in the Yangtze river basin, China. PLoS ONE 11:e0166002
Luo XW, Jiang EC, Wang ZM, Tang XR, Liu JH, Chen WT (2008) Precision rice hill-drop drilling machine. Trans CSAE 24:52–56 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Nowicka B, Ciura J, Szymańska R, Kruk J (2018) Improving photosynthesis, plant productivity and abiotic stress tolerance–current trends and future perspectives. J Plant Physiol 231:415–433
Ort DR, Merchant SS, Alric J, Barkan A, Blankenship RE, Bock R (2015) Redesigning photosynthesis to sustainably meet global food and bioenergy demand. Proc Natl Acad Sci 112:8529–8853
Pan SG, Liu HD, Mo ZW, Bob P, Duan MY, Tian H, Hu SJ, Tang XR (2016) Effects of nitrogen and shading on root morphologies, nutrient accumulation, and photosynthetic parameters in different rice genotypes. Sci Rep 6:32148
Pan S, Wen XC, Wang ZM, Ashraf U, Tian H, Duan MY, Mo ZW, Fan FS, Tang XR (2017) Benefits of mechanized deep placement of nitrogen fertilizer in direct-seeded rice in South China. Field Crops Res 203:139–149
Peterhansel C, Krause K, Braun HP, Espie GS, Fernie AR, Hanson DT (2013) Engineering photorespiration: current state and future possibilities. Plant Biol 15:754–758
Rogers CW, Norman RJ, Siebenmorgen TJ, Grigg BC (2016) Rough rice and milling yields as affected by nitrogen, harvest moisture, and cultivar. Agron J 108:813–821
Sinclair TR, Purcell LC, Sneller CH (2004) Crop transformation and the challenge to increase yield potential. Trends Plant Sci 9:70–75
Tayefeh M, Sadeghi SM, Noorhosseini SA, Bacenetti J, Damalas CA (2018) Environmental impact of rice production based on nitrogen fertilizer use. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:15885–15895
Vibhu Kapoor U, Singh SKP, Magre H, Shrivastava LK (2008) Rice growth, grain yield, and floodwater nutrient dynamics as affected by nutrient placement method and rate. Agron J 100:526–536
Wang DY, Xu CM, Yan JX, Zhang XG, Chen S, Chauhan BS, Wang L, Zhang XF (2017) 15N tracer-based analysis of genotypic differences in the uptake and partitioning of N applied at different growth stages in transplanted rice. Field Crops Res 211:27–36
Wu M, Li GL, Li WT, Liu J, Liu M, Jiang CY, Li ZP (2017) Nitrogen fertilizer deep placement for increased grain yield and nitrogen recovery efficiency in rice grown in Subtropical China. Front Plant Sci 8:1227
Ye M, Peng SB, Li Y (2019) Intraspecific variation in photosynthetic nitrogen-use efficiency is positively related to photosynthetic rate in rice (Oryza sativa L.) plants. Photosynthetica 57(1):311–319
Zhang Y, Liu H, Guo Z (2018) Direct-seeded rice increases nitrogen runoff losses in Southeastern China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 251:149–157
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by the Key R&D Program of Guangdong Province (Grant No. 2019B020221003), Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (Grant No. 2021A1515011255) and Guangzhou Science and Technology Project (Grant No. 202103000075).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SG and XR initiated and designed the study, ZZ, YF, YY, UA, LL, MH, ZW, MY and ZM took part in the experiment, ZZ analysis of the experimental data and wrote the manuscript, SG and ZM provide experimental suggestions and edited manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Mikihisa Umehara.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Wang, Y., Chen, Y. et al. Effects of Different Fertilization Methods on Grain Yield, Photosynthetic Characteristics and Nitrogen Synthetase Enzymatic Activities of Direct-seeded Rice in South China. J Plant Growth Regul 41, 1642–1653 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-021-10404-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-021-10404-4