Abstract
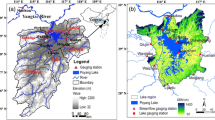
The Qaidam Basin (QB) is a concentrated distribution area and chemical industrial bases of salt lakes in China. Lakes in the QB have been expanding during the past 20 years. Rapid lake expansion resulted in some considerable scientific issues on the protection of salt lake resources and infrastructure, and monitoring of hydrological processes at the lake-basin scale. Although the spatial-temporal trends of lake changes on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau (QTP) have been well documented, the underlying influencing mechanism and hydrogeological implications of rapid lake changes in the QB are not well understood. Three lakes in the northern QB were selected to investigate lake water level fluctuations on different time scales based on extensive in-situ monitoring and satellite observations. The influencing mechanism and hydrogeological implications of rapid changes of terminal lakes were discussed in combination with the reported increasing precipitation rate and mass balance of glaciers in the northern QTP. Results reveal the following: (1) the fluctuation pattern of Sugan Lake was asynchronous and out of phase with that of Xiao Qaidam and Toson Lakes during the monitoring period; (2) Sugan Lake water rose gradually, and the rise interval was from late April to early July. In contrast, Xiao Qaidam and Toson Lakes took on a rapid and steep rise, and the rise intervalwas from late July to September; (3) the influencing mechanisms for rapid lake fluctuations are controlled by different factors: glacier and snow melting with increasing temperature for Sugan Lake and increasing precipitation for Xiao Qaidam and Toson Lakes; (4) in accordance with different intervals and influencing mechanisms of rapid lake expansions in the QB, hydrological risk precaution of lakes and corresponding river catchments was conducted in different parts of the basin. This study provided an important scientific basis for assessing the hydrological process and hydrological risk precaution, and protection of salt lake resources along with rapid lake expansions in the arid area.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
An Z S, Colman S M, Zhou W J et al. 2012. Interplay between the Westerlies and Asian monsoon recorded in Lake Qinghai sediments since 32 ka. Scientific Reports, 2(1): 619.
Bai W R, Yu D, Liu C H et al. 2019. Variation trend and cause analysis of water level and lake area of Qinghai Lake under the background of climate warming. Qinghai Science and Technology, 26(3): 72–78. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Biskop S, Maussion F, Krause P et al. 2016. Differences in the water-balance components of four lakes in the southern-central Tibetan Plateau. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 20(1): 209–225, https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-20-209-2016.
Chen B S, Pan A D, Yang M Z. 2010. Spatial and temporal characteristics and change trend of climatic elements of Qaidam Basin in recent 50 years. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 24(5): 117–123. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Dai S, Shen H Y, Li L et al. 2013. Analysis on climatic transition characteristic from warm-dry to warm-wet in Tsaidam Basin. Plateau Meteorology, 32(1): 211–220. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Du J N, Li Q J, Liu X S et al. 2020. Hydrological characteristics of Qinghai Lake, 1956–2017. Journal of Hydroecology, 41(4): 27–33. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Du Y E, Liu B K, He W G et al. 2018. Analysis on the variation and cause of the lake area in Qaidam Basin from 1976 to 2017. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 40(6): 1275–1284. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Duan S Q. 2018. Lake evolution in the Qaidam Basin during 1976–2015 and their changes in response to climate and anthropogenic factors. Journal of Lake Sciences, 30(1): 256–265, https://doi.org/10.18307/2018.0125. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Han N. 2019. Study on glacier variation and its effect on runoff in Sugan Lake Basin of Northwest China. China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Immerzeel W W, Lutz A F, Andrade M et al. 2020. Importance and vulnerability of the world’s water towers. Nature, 577(7790): 364–369, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1822-y.
Lei Y B, Yang K, Lei Y B. 2017. The cause of rapid lake expansion in the Tibetan Plateau: climate wetting or warming? Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews-Water, 4(6): e1236.
Lei Y B, Yang K, Wang B et al. 2014. Response of inland lake dynamics over the Tibetan Plateau to climate change. Climatic Change, 125(2): 281–290, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-014-1175-3.
Li Q K, Shan F S, Wang J P et al. 2022. The Variation of K Contents in Salt Lakes on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and its Influencing Factors. Journal of Salt Lake Research, 30(02):79–85. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li X D, Long D, Huang Q et al. 2019. High-temporal-resolution water level and storage change data sets for lakes on the Tibetan Plateau during 2000–2017 using multiple altimetric missions and Landsat-derived lake shoreline positions. Earth System Science Data, 11(4): 1603–1627.
Lu N. 2014. Changes of lake area in Qaidam basin and the influence factors. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 28(8): 83–87. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Lu N. 2015. RS-based monitoring of glacier change in Qaidam Basin. Yellow River, 37(2): 16–18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Luo S X, Song C Q, Zhan P F et al. 2021. Refined estimation of lake water level and storage changes on the Tibetan Plateau from ICESat/ICESat-2. CATENA, 200: 105177, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2021.105177.
Mao X C, Liu X, Dong Y et al. 2018. Research on the genesis of semi-submerged Yardang landform in the duck lake area of Qaidam Basin. Geological Review, 64(6): 1505–1518. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Qiao B J, Zhu L P. 2019. Difference and cause analysis of water storage changes for glacier-fed and non-glacierfed lakes on the Tibetan Plateau. Science of the Total Environment, 693: 133399.
Qiu J. 2008. China: the third pole. Nature, 454(7203): 393–396.
Song C Q, Huang B, Ke L H. 2013. Modeling and analysis of lake water storage changes on the Tibetan Plateau using multi-mission satellite data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 135: 25–35.
Song C Q, Huang B, Richards K et al. 2014. Accelerated lake expansion on the Tibetan Plateau in the 2000s: induced by glacial melting or other processes? Water Resources Research, 50(4): 3170–3186.
Tan Y. 2014. Water system, surface water resources and their characteristics in Qaidam Basin. Water Conservancy Science and Technology and Economy, 20(4): 51–54. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Tian H, Wei C, Ning S X et al. 2018. Study on the change of area of Dabson Lake and its influencing factors. Henan Science and Technology, (29): 89–91. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Treichler D, Kääb A, Salzmann N et al. 2019. Recent glacier and lake changes in High Mountain Asia and their relation to precipitation changes. The Cryosphere, 13(11): 2977–3005.
Tuo J B. 2019. Temporal and Spatial Evolution of NDVI in Qinghai Lake Basin and its Relationship with Environmental Factors. Qinghai Normal University, Xining. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang A, Zhao Y Y, Xu H et al. 2016. The characteristics of salt lake resources in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Journal of Salt Lake Research, 24(3): 24–29. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang L, Chen W, Huang G et al. 2017. Changes of the transitional climate zone in East Asia: past and future. Climate Dynamics, 49(4): 1463–1477.
Wang L, Liu H, Zhong X Y et al. 2022. Domino effect of a natural cascade alpine lake system on the Third Pole. PNAS Nexus, 1(3): pgac053.
Wang L, Yao T D, Chai C H et al. 2021. TP-River: monitoring and Quantifying total river runoff from the third pole. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 102(5): E948–E965.
Wang N L, Yao T D, Xu B Q et al. 2019. Spatiotemporal pattern, trend, and influence of glacier change in Tibetan Plateau and surroundings under global warming. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 34(11): 1220–1232. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wei S R, Jin X M, Wang K L et al. 2017. Response of lake area variation to climate change in Qaidam Basin based on remote sensing. Earth Science Frontiers, 24(5): 427–433. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wu H B, Wang N L, Guo Z M. 2021. Application of ICESat-2/ATLAS altimetry data to the estimation of the Qinghai Lake water level. Journal of Water Resources & Water Engineering, 32(5): 11–18, 26. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wu J J. 2014. Analysis on the Changing and Reason of the Salt Lake Surface Water Area in the Qaidam Basin Since Recent 20 Years. Qinghai Institute of Salt Lakes, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xining. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu H J, Yang T B. 2013. Climate factors change and its impact on lake area and vegetation growth in the Qaidam Basin during 1981–2010. Progress in Geography, 32(6): 868–879. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu L J, Hu Z Y, Zhao Y N et al. 2019. Climate change characteristics in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau during 1961–2010. Plateau Meteorology, 38(5): 911–919. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang H A, An R Z. 1986. The distribution of existing glaciers in the Qaidam Basin. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 8(2): 171–175. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang K, Lu H, Yue S Y et al. 2018. Quantifying recent precipitation change and predicting lake expansion in the Inner Tibetan Plateau. Climatic Change, 147(1–2): 149–163.
Yang K, Wu H, Qin J et al. 2014. Recent climate changes over the Tibetan Plateau and their impacts on energy and water cycle: a review. Global and Planetary Change, 112: 79–91.
Yao F F, Wang J D, Yang K H et al. 2018. Lake storage variation on the endorheic Tibetan Plateau and its attribution to climate change since the new millennium. Environmental Research Letters, 13(6): 064011.
Yao T D, Bolch T, Chen D L et al. 2022. The imbalance of the Asian water tower. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 3(10): 618–632.
Yao T D, Xue Y K, Chen D L et al. 2019. Recent third pole’s rapid warming accompanies cryospheric melt and water cycle intensification and interactions between monsoon and environment: multidisciplinary approach with observations, modeling, and analysis. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 100(3): 423–444.
Zhang C, Han L, Chen L. 2010. Remote sensing monitoring and analysis of lake surface change in Qaidam Basin. Yellow River, 32(12): 54–55, 58. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang G Q, Luo W, Chen W F et al. 2019. A robust but variable lake expansion on the Tibetan Plateau. Science Bulletin, 64(18): 1306–1309.
Zhang P X. 1987. Salt Lakes in the Qaidam Basin. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese)
Zhang W X, Liu P X. 2019. Surface humid situation and its affecting factors in the Qaidam Basin from 1961 to 2017. Arid Zone Research, 36(6): 1391–1400. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zheng M P, Xiang J, Wei X J et al. 1989. Saline Lakes on the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau. Beijing Science and Technology Press, Beijing, China. 431p. (in Chinese)
Zhou S G, Yao X J, Zhang Y et al. 2021. A glacier vector dataset in the Qaidam Basin from 1977 to 2018. China Scientific Data, 6(2): 169–176. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhu L P, Wang J B, Ju J T et al. 2019. Climatic and lake environmental changes in the Serling Co region of Tibet over a variety of timescales. Science Bulletin, 64(7): 422–424.
Acknowledgment
We would like to thank Dr. Haicheng WEI, Yongsheng DU, and Zhanjie QIN from the Qinghai Institute of Salt Lakes, Chinese Academy of Scienses, for their helpful suggestions and field contributions about arrangement of monitoring requirements and scientific project. Similarly, we also thank the reviewers and editor-in-chief for their constructive comments to improve the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supported by the Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research Program (No. 2019QZKK0805), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U21A2018), and the Foundation of Department of Qinghai Science & Technology (No. 2020-ZJ-T06)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, Y., Fan, Q., Chen, T. et al. Influencing mechanism and hydrogeological implications of water level fluctuation of lakes in the northern Qaidam Basin, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Ocean. Limnol. 41, 1243–1257 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-022-2185-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-022-2185-z