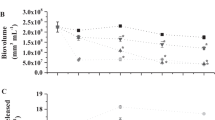
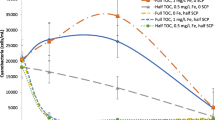
Abstract
Cyanobacteria can accumulate as a heavy biomass on the leeward side of large eutrophic lakes, posing a potential threat to public health. The mitigating capacity of three flocculants and their potential impacts on the major environmental features of water and sediments was evaluated. Results indicate that polyaluminum chloride (PAC) and ferric chloride (FeCl3) are efficient flocculants that can rapidly mitigate cyanobacterial blooms with chlorophyll-a concentrations higher than 1 500 µg/L within 15 min. In comparison, cationic starch with chitosan could only treat cyanobacterial blooms in chlorophyll-a concentrations of less than 200 µg/L. The addition of FeCl3 caused a decline in the pH value, while dissolved oxygen in the water column dropped to 2 mg/L during cationic starch with chitosan treatment for a high cyanobacterial biomass group. Thus, a combination of flocculants and oxygenators should be considered when treating high-concentration cyanobacterial blooms for emergency purposes. Additionally, the cell lysis of cyanobacteria caused by cationic starch with chitosan can result in an increase in total dissolved phosphorus and total dissolved nitrogen. Furthermore, the high accumulation of nutrients in sediments after the settling of cyanobacteria can cause high internal phosphorus pollution. The increase in the total organic carbon of the sediments can threaten lake restoration achieved by planting submerged macrophytes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on request.
References
Aktas T S, Takeda F, Maruo C et al. 2013. Comparison of four kinds of coagulants for the removal of picophytoplankton. Desalination and Water Treatment, 51(16–18): 3547–3557, https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2012.750777.
Barko J W, Adams M S, Clesceri N L. 1986. Environmental factors and their consideration in the management of submersed aquatic vegetation: a review. Journal of Aquatic Plant Management, 24: 1–10.
Barko J W, Gunnison D, Carpenter S R. 1991. Sediment interactions with submersed macrophyte growth and community dynamics. Aquatic Botany, 41 (1-3): 41–65, https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3770(91)90038-7.
Bishop W M, Richardson R J, Willis B E. 2018. Comparison of partitioning and efficacy between copper algaecide formulations: refining the critical burden concept. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 229(9): 300, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3958-z.
Caille N, Tiffreau C, Leyval C et al. 2003. Solubility of metals in an anoxic sediment during prolonged aeration. Science of the Total Environment, 301(1–3): 239–250, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00289-9.
G. Dennis Cooke, Eugene B. Welch, Spencer A. Peterson, et al. 1994. Restoration and management of lakes and reservoirs (2nd edn). 9(2): 131–132, https://doi.org/10.1002/rrr.3450090207.
Huang J C, Zhang Y J, Huang Q et al. 2018. When and where to reduce nutrient for controlling harmful algal blooms in large eutrophic Lake Chaohu, China? Ecological Indicators, 89: 808–817, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.01.056.
Huo X C, Chang D W, Tseng J H et al. 2015. Exposure of Microcystis aeruginosa to hydrogen peroxide under light: kinetic modeling of cell rupture and simultaneous microcystin degradation. Environmental Science & Technology, 49(9): 5502–5510, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b00170.
Jiang Y, Liu Y, Shi D T et al. 2020. Membrane fouling in a powdered activated carbon-membrane bioreactor (PAC-MBR) for micro-polluted water purification: fouling characteristics and the roles of PAC. Journal of Cleaner Production, 277: 122341, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122341.
Jin X C, Xu Q J, Huang C Z. 2005. Current status and future tendency of lake eutrophication in China. Science in China Series C: Life Sciences, 48(2): 948–954, https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03187133.
Jin X G, Bi L, Lyu T et al. 2019. Amphoteric starch-based bicomponent modified soil for mitigation of harmful algal blooms (HABs) with broad salinity tolerance: flocculation, algal regrowth, and ecological safety. Water Research, 165: 115005, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.115005.
Kiørboe T. 1980. Distribution and production of submerged macrophytes in tipper grund (ringkobing fjord, Denmark), and the impact of waterfowl grazing. Journal of Applied Ecology, 17(3): 675–687, https://doi.org/10.2307/2402646.
Knuckey R M, Brown M R, Robert R et al. 2006. Production of microalgal concentrates by flocculation and their assessment as aquaculture feeds. Aquacultural Engineering, 35(3): 300–313, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaeng.2006.04.001.
Li H, Pan G. 2015. Simultaneous removal of harmful algal blooms and microcystins using microorganism- and chitosan-modified local soil. Environmental Science & Technology, 49(10): 6249–6256, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b00840.
Li P N, Zhang L Z, Wang W W et al. 2011. Rapid catalytic microwave method to damage Microcystis aeruginosa with FeCl3-loaded active carbon. Environmental Science & Technology, 45(10): 4521–4526, https://doi.org/4521-4526.10.1021/es200057g.
Li X Q, Pei H Y, Hu W R et al. 2015. The fate of Microcystis aeruginosa cells during the ferric chloride coagulation and flocs storage processes. Environmental Technology, 36(7): 920–928, https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2014.966768.
Liu C, Shao S G, Shen Q S et al. 2015. Use of multi-objective dredging for remediation of contaminated sediments: a case study of a typical heavily polluted confluence area in China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(22): 17839–17849, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4978-5.
Liu M X, Shi X L, Chen C et al. 2017. Responses of Microcystis colonies of different sizes to hydrogen peroxide stress. Toxins, 9(10): 306, https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9100306.
Lürling M, Mucci M. 2020. Mitigating eutrophication nuisance: in-lake measures are becoming inevitable in eutrophic waters in the Netherlands. Hydrobiologia, 847(21): 4447–4467, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-020-04297-9.
Ma X X, Wang Y N, Feng S Q et al. 2015. Comparison of four flocculants for removing algae in Dianchi Lake. Environmental Earth Sciences, 74(5): 3795–3804, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4903-4.
Matthijs H C P, Visser P M, Reeze B et al. 2012. Selective suppression of harmful cyanobacteria in an entire lake with hydrogen peroxide. Water Research, 46(5): 1460–1472, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.11.016.
Meyers P A. 1994. Preservation of elemental and isotopic source identification of sedimentary organic matter. Chemical Geology, 114(3–4): 289–302, https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(94)90059-0.
Park J, Son Y, Lee W H. 2019. Variation of efficiencies and limits of ultrasonication for practical algal bloom control in fields. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 55: 8–17, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.03.007.
Stroom J M, Kardinaal W E A. 2016. How to combat cyanobacterial blooms: strategy toward preventive lake restoration and reactive control measures. Aquatic Ecology, 50(3): 541–576, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-016-9593-0.
Tang Y, Zhang H, Liu X N et al. 2011. Flocculation of harmful algal blooms by modified attapulgite and its safety evaluation. Water Research, 45(9): 2855–2862, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.03.003.
Truttmann L, Su Y X, Lee S et al. 2020. Gravity-driven membrane (GDM) filtration of algae-polluted surface water. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 36: 101257, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101257.
Ulrich A E, Malley D F, Watts P D. 2016. Lake Winnipeg basin: advocacy, challenges and progress for sustainable phosphorus and eutrophication control. Science of the Total Environment, 542: 1030–1039, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.09.106.
Visser P M, Ibelings B W, Bormans M et al. 2016. Artificial mixing to control cyanobacterial blooms: a review. Aquatic Ecology, 50(3): 423–441, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-015-9537-0.
Waajen G, van Oosterhout F, Douglas G et al. 2016. Geoengineering experiments in two urban ponds to control eutrophication. Water Research, 97: 69–82, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.11.070.
Waajen, G., F. van Oosterhout & G. Douglas, 2016. Management of eutrophication in Lake De Kuil (The Netherlands) using combined flocculant: lanthanum modified bentonite treatment. Water Research 97: 83–95, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.11.034.
Wan C, Alam A, Zhao X Q et al. 2015. Current progress and future prospect of microalgal biomass harvest using various flocculation technologies. Bioresource Technology, 184: 251–257, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.11.081.
Watson S B, Miller C, Arhonditsis G et al. 2016. The reeutrophication of Lake Erie: harmful algal blooms and hypoxia. Harmful Algae, 56: 44–66, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2016.04.010.
Wu Z S, Lai X J, Li K Y. 2021. Water quality assessment of rivers in Lake Chaohu basin (China) using water quality index. Ecological Indicators, 121: 107021, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.107021.
Yang C Y, Hou X P, Wu D H et al. 2020. The characteristics and algicidal mechanisms of cyanobactericidal bacteria, a review. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 36(12): 188, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-020-02965-5.
Yang M, Yu JW, Li ZL et al. 2008. Taihu Lake not to blame for Wuxi’s Woes. Science, 319: 157–159, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.319.5860.158a.
Zhang Z Y, Fan X J, Peijnenburg W J G M et al. 2021. Alteration of dominant cyanobacteria in different bloom periods caused by abiotic factors and species interactions. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 99: 1–9, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2020.06.001.
Zhong J C, You B S, Fan C X et al. 2008. Influence of sediment dredging on chemical forms and release of phosphorus. Pedosphere, 18(1): 34–44, https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(07)60100-3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Nos. 32071573, 41877544), the Science and Technology Service Network Initiative of Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. KFJ-STS-QYZD-2021-01-002), and the Science and Technology Achievement Transformation Foundation of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (No. 2021CG0013)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, K., Jiang, L., Yang, J. et al. Comparison of three flocculants for heavy cyanobacterial bloom mitigation and subsequent environmental impact. J. Ocean. Limnol. 40, 1764–1773 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-022-1351-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-022-1351-7