Abstract
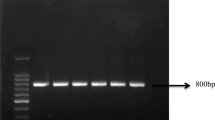
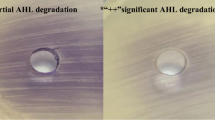
Quorum sensing (QS) disruption is considered as a potential alternative strategy to combat bacterial diseases in aquaculture. In this study, we isolated and identified bacteria degrading QS molecules from pond sediment and fish intestine. A total of 132 strains were obtained in the enrichment culture, of which two strains were identified as Enterobacter sp. f003 and Staphylococcus sp. sw120, being isolated from the fish intestine and pond sediment, respectively. We found that strains f003 and sw120 could degrade acyl-homoserine lactones (AHLs) and cause no hemolysis of sheep red blood cells. The AHL lactonase ( aiiA ) homologous gene in the two strains was detected in PCR amplification and the high-degrading activity to N-hexanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (C6-HSL) and AHLs secreted from pathogenic Aeromonas hydrophila was assessed. Meanwhile, the artificial infection of cyprinid C arassius auratus gibelio with intraperitoneal injection showed that the two strains were avirulent. Therefore, the obtained indigenous bacteria are candidate probiotics against pathogenic A. hydrophila in aquaculture.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austin B, Austin D A. 2012. Bacterial Fish Pathogens. Springer, Heidelberg, Germany, https://doi.org/10.1007/978–94–007–4884–2.
Bergey D H, Holt J G, Krieg N R, Sneath P H A, Staley J T. 1994. Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology, Williams and Wilkins. Baltimore Maryland 527.
Boyen F, Eeckhaut V, Van Immerseel F, Pasmans F, Ducatelle R, Haesebrouck F. 2009. Quorum sensing in veterinary pathogens: mechanisms, clinical importance and future perspectives. Veterinary Microbiology, 135 (3): 187–195, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2008.12.025.
Bruhn J B, Dalsgaard I, Nielsen K F, Buchholtz C, Larsen J L, Gram L. 2005. Quorum sensing signal molecules (acylated homoserine lactones) in gram–negative fish pathogenic bacteria. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 65 (1): 43–52, https://doi.org/10.3354/dao065043.
Cao Y N, He S X, Zhou Z G, Zhang M C, Mao W, Zhang H T, Yao B. 2012. Orally administered thermostable N–acyl homoserine lactonase from Bacillus sp. strain AI96 attenuates Aeromonas hydrophila infection in zebrafish. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 78 (6): 1 899–1 908, https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.06139–11.
Chan K G, Yin W F, Sam C K, Koh C L. 2009. A novel medium for the isolation of N–acylhomoserine lactone–degrading bacteria. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 36 (2): 247–251, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295–008–0491–x.
Chong T M, Koh C L, Sam C K, Choo Y M, Yin W F, Chan K G. 2012. Characterization of quorum sensing and quorum quenching soil bacteria isolated from Malaysian tropical montane forest. Sensors, 12 (4): 4 846–4 859, https://doi. org/10.3390/s120404846.
Chu W, Lu F, Zhu W, Kang C. 2011. Isolation and characterization of new potential probiotic bacteria based on quorum–sensing system. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 110 (1): 202–208, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365–2672.2010.04872.x. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2004.06.031.
De Kievit T R, Iglewski B H. 2000. Bacterial quorum sensing in pathogenic relationships. Infection and Immunity, 68 (9): 4 839–4 849, https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.68.9.4839–4849.2000.
Defoirdt T, Boon N, Bossier P, Verstraete W. 2004. Disruption of bacterial quorum sensing: an unexplored strategy to fight infections in aquaculture. Aquaculture, 240 (1): 69–88.
Dewhirst F E, Chien C C, Paster B J, Ericson R L, Orcutt R P, Schauer D B, Fox J G. 1999. Phylogeny of the defined murine microbiota: altered Schaedler flora. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 65 (8): 3 287–3 292.
Dong Y H, Wang L H, Xu J L, Zhang H B, Zhang X F, Zhang L H. 2001. Quenching quorum–sensing–dependent bacterial infection by an N–acyl homoserine lactonase. Nature, 411 (6839): 813–817, https://doi.org/10.1038/35081101.
Dong Y H, Xu J L, Li X Z, Zhang L H. 2000. AiiA, an enzyme that inactivates the acylhomoserine lactone quorumsensing signal and attenuates the virulence of Erwinia carotovora. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97 (7): 3 526–3 531, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.060023897.
Garde C, Bjarnsholt T, Givskov M, Jakobsen T H, Hentzer M, Claussen A, Sneppen K, Ferkinghoff–Borg J, Sams T. 2010. Quorum sensing regulation in Aeromonas hydrophila. Journal of Molecular Biology, 396 (4): 849–857, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2010.01.002.
Ghani N A, Norizan S N, Chan X Y, Yin W F, Chan K G. 2014. Labrenzia sp. BM1: a quorum quenching bacterium that degrades N–acyl homoserine lactones via lactonase activity. Sensors, 14 (7): 11 760–11 769, https://doi.org/10. 3390/s140711760.
Hossain M J, Sun D W, McGarey D J, Wrenn S, Alexander L M, Martino M E, Xing Y, Terhune J S, Liles M R. 2014. An asian origin of virulent Aeromonas hydrophila responsible for disease epidemics in united states–farmed catfish. mBio, 5 (3): e00848–14, https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00848–14.
Huang J H, Shi Y H, Zeng G M, Gu Y L, Chen G Q, Shi L X, Hu Y, Tang B, Zhou J X. 2016. Acyl–homoserine lactone–based quorum sensing and quorum quenching hold promise to determine the performance of biological wastewater treatments: an overview. Chemosphere, 157: 137–151, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.05.032.
Huma N, Shankar P, Kushwah J, Bhushan A, Joshi J, Mukherjee T, Raju S C, Purohit H J, Kalia V C. 2011. Diversity and polymorphism in AHL–lactonase gene (aiiA) of Bacillus. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 21 (10): 1 001–1 011, https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1105.05056.
Karber G. 1931. Determination of LD50. Arches of Experimental Pathology and Pharmacology, 62: 480–483.
Khajanchi B K, Sha J, Kozlova E V, Erova T E, Suarez G, Sierra J C, Popov V L, Horneman A J, Chopra A K. 2009. N–acylhomoserine lactones involved in quorum sensing control the type VI secretion system, biofilm formation, protease production, and in vivo virulence in a clinical isolate of Aeromonas hydrophila. Microbiology, 155 (11): 3 518–3 531, https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.031575–0.
Lau Y Y, Sulaiman J, Chen J W, Yin W F, Chan K G. 2013. Quorum sensing activity of Enterobacter asburiae isolated from lettuce leaves. Sensors, 13 (10): 14 189–14 199, https://doi.org/10.3390/s131014189.
Lynch M J, Swift S, Kirke D F, Keevil C W, Dodd C E, Williams P. 2002. The regulation of biofilm development by quorum sensing in Aeromonas hydrophila. Enviro n mental Microbi o logy, 4 (1): 18–28, https://doi. org/10.1046/j.1462–2920.2002.00264.x.
McClean K H, Winson M K, Fish L, Taylor A, Chhabra S R, Camara M, Daykin M, Lamb J H, Swift S, Bycroft B W, Stewart G S A B, Williams P. 1997. Quorum sensing and Chromobacterium violaceum: exploitation of violacein production and inhibition for the detection of N–acylhomoserine lactones. Microbiology, 143 (12): 3 703–3 711, https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287–143–12–3703.
Norizan S N M, Yin W F, Chan K G. 2013. Caffeine as a potential quorum sensing inhibitor. Sensors, 13 (4): 5 117–5 129, https://doi.org/10.3390/s130405117.
Pande G S J, Natrah F M I, Flandez A V B, Kumar U, Niu Y F, Bossier P, Defoirdt T. 2015. Isolation of AHL–degrading bacteria from micro–algal cultures and their impact on algal growth and on virulence of Vibrio campbellii to prawn larvae. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 99 (24): 10 805–10 813, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253–015–6918–1.
Smith R S, Iglewski B H. 2003. P. aeruginosa quorum–sensing systems and virulence. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 6 (1): 56–60, https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369–5274(03)00008–0.
Swift S, Karlyshev A V, Fish L, Durant E L, Winson M K, Chhabra S R, Williams P, Macintyre S, Stewart G S. 1997. Quorum sensing in Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas salmonicida: identification of the LuxRI homologs AhyRI and AsaRI and their cognate N–acylhomoserine lactone signal molecules. Journal of Bacteriology, 179 (17): 5 271–5 281, https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.179.17.5271–5281.1997.
Takayama Y, Kato N. 2016. Switch of SpnR function from activating to inhibiting quorum sensing by its exogenous addition. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 477 (4): 993–997, https://doi.org/10. 1016/j.bbrc.2016.07.017.
Tang K H, Zhang X H. 2014. Quorum quenching agents: resources for antivirulence therapy. Marine Drugs, 12 (6): 3 245–3 282, https://doi.org/10.3390/md12063245.
Torres M, Rubio–Portillo E, Antón J, Ramos–Esplá A A, Quesada E, Llamas I. 2016. Selection of the N–Acylhomoserine Lactone–degrading bacterium Alteromonas stellipolaris PQQ–42 and of its potential for biocontrol in aquaculture. Frontiers in Microbiology, 7: 646, https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00646.
Wang N N, Wu Y F, Pang M D, Liu J, Lu C P, Liu Y J. 2015. Protective efficacy of recombinant hemolysin co–regulated protein (Hcp) of Aeromonas hydrophila in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 46 (2): 297–304, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2015.06.019.
Waters C M, Bassler B L. 2005. Quorum sensing: cell–to–cell communication in bacteria. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology, 2 1: 319–346, https://doi. org/10.1146/annurev.cellbio.21.012704.131001.
Weisburg W G, Barns S M, Pelletier D A, Lane D J. 1991. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. Journal of Bacteriology, 173 (2): 697–703, https://doi. org/10.1128/jb.173.2.697–703.1991.
Zhao J, Chen M, Quan C S, Fan S D. 2015. Mechanisms of quorum sensing and strategies for quorum sensing disruption in aquaculture pathogens. Journal of Fish Diseases, 38 (9): 771–786, https://doi.org/10.1111/jfd.12299.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supported by the Central Public-Interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, CAFS (Nos. 2017HY-ZD1008, 2017JBFR03) and the Earmarked Fund for China Agriculture Research System (No. CARS-45)
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Xi, B., Qin, T. et al. Isolation and characterization of AHL-degrading bacteria from fish and pond sediment. J. Ocean. Limnol. 37, 1460–1467 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-019-8137-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-019-8137-6