Abstract
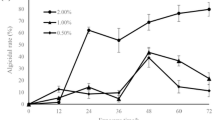
Red tide occurrs frequently and causes significant damage to the environment and human health. As a result, development of new efficient and environment friendly red-tide microalgae inhibitors has gained increasing attention in recent times. Algicolous endophytic fungi with unique habitats are promising sources for active agents owing to their abundant secondary metabolites and distinguished activities. In this study, the algicidal activities of 49 marine macroalgal-derived endophytic fungi against phytoplankton Alexandrium tamarense, Prorocentrum donghaiense, Heterosigma akashiwo, and Chattonella marina were examined using 96-well microplate. Four fungal strains, including Aspergillus wentii (pt-1), A. ustus (cf-42), and A. versicolor (dl-29, pt-20), exhibited potent algicidal activities. A total of 32 pure compounds isolated from these fungi were noted to possess different degrees of algicidal activities. Of those, 11 compounds comprising five anthraquinones, two terpenoids, and four steroids showed high 24-h inhibition rates for the four red tide algae, with EC 50(24 h) values ranging from 0.01 to 14.29 μg/mL. Among them, compound 1 (1,5-dihydroxy-3-methoxy-7-methylanthraquinone) presented the strongest activity against H. akashiwo, and could decrease its chlorophyll a (Chl a ) and superoxide dismutase contents and increase the soluble protein, malondialdehyde, and peroxidase contents. These results suggested that the identified anti-algal compound might inhibit the growth of red tide algae by weakening photosynthesis (reducing Chl a content), destroying cell membrane, and damaging the antioxidant system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cantrell C L, Schrader K K, Mamonov L K, Sitpaeva G T, Kustova T S, Dunbar C, Wedge D E. 2005. Isolation and identification of antifungal and antialgal alkaloids from Haplophyllum sieversii. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 53 (20): 7 741–7 748.
Chen C, Imamura N, Nishijima M, Adachi K, Sakai M, Sano H. 1996. Halymecins, new antimicroalgal substances produced by fungi isolated from marine algae. The J ournal of Antibiot ics, 49 (10): 998–1 005.
Cui C M, Li X M, Li C S, Proksch P, Wang B G. 2010. Cytoglobosins A–G, cytochalasans from a marine–derived endophytic fungus, Chaetomium globosum QEN–14. Journal of Natural Products, 73 (4): 729–733.
Ji N Y, Wang B G. 2016. Mycochemistry of marine algicolous fungi. Fungal Divers ity, 80 (1): 301–342.
Jin Q, Dong S L. 2003. Comparative studies on the allelopathic effects of two different strains of Ulva pertusa on Heterosigma akashiwo and Alexandrium tamarense. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology A nd Ecology, 293 (1): 41–55.
Krohn K, Dai J Q, Flörke U, Aust H J, Dräger S, Schulz B. 2005. Botryane metabolites from the fungus Geniculosporium sp. isolated from the marine red alga Polysiphonia. Journal of Natural Products, 68 (3): 400–405.
Liu X H, Miao F P, Li X D, Yin X L, Ji N Y. 2012. A new sesquiterpene from an endophytic Aspergillus versicolor strain. Nat ural Prod uct Commun ication, 7 (7): 819–820.
Liu X H, Miao F P, Liang X R, Ji N Y. 2014. Ergosteroid derivatives from an algicolous strain of Aspergillus ustus. Nat ural Prod uct Res earch, 28 (15): 1 182–1 186.
Liu X H, Miao F P, Qiao M F, Cichewicz R H, Ji N Y. 2013. Terretonin, ophiobolin, and drimane terpenes with absolute configurations from an algicolous Aspergillus ustus. RSC Adv ances, 3 (2): 588–595.
Liu X H. 2012. Secondary metabolites from three Codium fragile–endophytic fungi and their bioactivities. Shandong Agricultural University, Taian, China. p.34–37. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Miao F P, Li X D, Liu X H, Cichewicz R H, Ji N Y. 2012. Secondary metabolites from an algicolous Aspergillus versicolor strain. Mar ine Drugs, 10 (1): 131–139.
Miazek K, Remacle C, Richel A, Goffin D. 2014. Effect of lignocellulose related compounds on microalgae growth and product biosynthesis: a review. Energies, 7 (7): 4 446–4 481.
Murray–Gulde C L, Heatley J E, Schwartzman A L, Rodgers J H Jr. 2002. Algicidal effectiveness of clearigate, cutrineplus, and copper sulfate and margins of safety associated with their use. Archives of E nvironmental Contamination and T oxicology, 43 (1): 19–27.
Osterhage C, Kaminsky R, König G M, Wright A D. 2000. Ascosalipyrrolidinone A, an antimicrobial alkaloid, from the obligate marine fungus Ascochyta salicorniae. J ournal of Org anic Chem istry, 65 (20): 6 412–6 417.
Qian H F, Xu X Y, Chen W, Jiang H, Jin Y X, Liu W P, Fu Z W. 2009. Allelochemical stress causes oxidative damage and inhibition of photosynthesis in Chlorella vulgaris. Chemosphere, 75 (3): 368–375.
Rateb M E, Ebel R. 2011. Secondary metabolites of fungi from marine habitats. Nat ural Prod uct Rep orts, 28 (2): 290–344.
Schrader K K, De Regt M Q, Tucker C S, Duke S O. 1997. A rapid bioassay for selective algicides. Weed Technology, 11 (4): 767–774.
Shapiro H M. 2008. Flow cytometry of bacterial membrane potential and permeability. In: Champney W S ed. New Antibiotic Targets. Humana Press, Totowa, New Jersey. p.175–186.
Song X X, Yu Z M, Gao Y H. 2003. Removal of different species of red tide organisms with an effective claycomplex system. Chinese J ournal of Applied E cology, 14 (7): 1 165–1 168. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Sun K L, Wang Y, Fu P, Liu P P, Zhu W M. 2013a. Studies on the secondary metabolites of Eurotium herbariorum HT–2 symbiotic with Enteromorpha prolifera. Chinese J ournal of Marine Drugs, 32 (1): 37–45. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Sun R R, Miao F P, Zhang J, Wang G, Yin X L, Ji N Y. 2013b. Three new xanthone derivatives from an algicolous isolate of Aspergillus wentii. Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry, 51 (1): 65–68.
Wang F, Li H J, Lan W J. 2011. The metabolites of the marine fungus Penicillium sp. Associated with soft coral Sarcophyton tortuosum. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 50 (6): 72–77. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wintermans J F G M, De Mots A. 1965. Spectrophotometric characteristics of chlorophylls a and b and their pheophytins in ethanol. Biochim ica et Biophys ica Acta ( BBA )–Biophysics including Photosynthesis, 109 (2): 448–453.
Zhang S L, Zhang B, Dai W, Zhang X M. 2011. Oxidative damage and antioxidant responses in Microcystis aeruginosa exposed to the allelochemical berberine isolated from golden thread. Journal of Plant Physiology, 168 (7): 639–643.
Zhou M J, Zhu M Y. 2006. Progress of the project “Ecology and oceanography of harmful algal blooms in China”. Advances in Earth Science, 21 (7): 673–679. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41106137, 31670355), the Yantai Program for Science and Technique Development (Nos. 2015ZH089, 2015ZH076), the Natural Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of Shandong Province (No. JQ201712), the Key Cutting-Edge Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. QYZDB-SSW-DQC013), and the Open Fund of Key Laboratory of Experimental Marine Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. KF2017NO4)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miao, F., Zuo, J., Liu, X. et al. Algicidal activities of secondary metabolites of marine macroalgal-derived endophytic fungi. J. Ocean. Limnol. 37, 112–121 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-019-7393-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-019-7393-9