Abstract
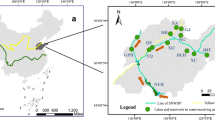
Dajingshan, Fenghuangshan and Meixi reservoirs are located in Zhuhai, a coastal city in southern China, and they function to supply drinking water to Zhuhai and Macau. For effectively supplying waster, they are hydrologically connected and Dajingshan Reservoir first receives the water pumped from the river at Guangchang Pumping Station, and then feeds Fenghuangshan Reservoir, and the two well-connected reservoirs are mesotrophic. Meixi Reservoir is a small and oligotrophic water body and feeds Dajingshan Reservoir only in wet seasons when overflow occurs. Particulate organic matter (POM) was collected from three hydrologically connected water supply reservoirs, and seasonal variations of POM were ascertained from stable carbon and nitrogen isotopes in wet and dry seasons, and the effects of pumping water and reservoir connectivity on POM variations and composition were demonstrated by the relationships of the stable isotope ratios of POM. Seasonality and similarity of stable carbon and nitrogen isotopes of POM varied with hydrodynamics, connectivity and trophic states of the four studied water bodies. The two well-connected reservoirs displayed more similar seasonality for δ13CPOM than those between the river station and the two reservoirs. However, the opposite seasonality appeared for δ15NPOM between the above waters and indicates different processes affecting the stable carbon and nitrogen isotopes of POM. δ13CPOM and δ15NPOM changed little between wet and dry seasons in Meixi Reservoir-a low productive and rain-driven system, suggesting little POM response to environmental changes in that water system. As expected, connectivity enhanced the similarity of the stable isotope ratios of POM between the water bodies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Public Health Association (APHA), American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation. 1995. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, Washington, D.C.
Cole J J, Carpenter S R, Kitchell J, Pace M L, Solomon C T, Weidel B. 2011. Strong evidence for terrestrial support of zooplankton in small lakes based on stable isotopes of carbon, nitrogen, and hydrogen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 108(5):1975–1980.
Grey J, Jones R I, Sleep D. 2000. Stable isotope analysis of the origins of zooplankton carbon in lakes of differing trophic state. Oecologia, 123 (2): 232–240.
Grey J, Jones R I, Sleep D. 2001. Seasonal changes in the importance of the source of organic matter to the diet of zooplankton in Loch Ness, as indicated by stable isotope analysis. Limnol. Oceanogr., 46 (3): 505–513.
Grey J, Jones R I. 1999. Carbon stable isotopes reveal complex trophic interactions in lake plankton. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom., 13(13):1311–1314.
Gu B H, Chapma A D, Schelske C L. 2006. Factors controlling seasonal variations in stable isotope composition of particulate organic matter in a soft water eutrophic lake. Limnol. Oceanogr., 51(6):2837–2848.
Gu B H, Schelske C L, Waters M N. 2011. Patterns and controls of seasonal variability of carbon stable isotopes of particulate organic matter in lakes. Oecologia, 165(4):1083–1094.
Gu B H, Schelske C L. 2010. Patterns and controls of nitrogen stable isotopes of particulate organic matter in subtropical lakes. Ann. Limnol. Int. J. Lim nol., 46 (1): 1–7.
Gu B H, Schelske L. 1996. Temporal and spatial variations in phytoplankton carbon isotopes in a polymictic subtropical lake. J. Plankton Res., 18(11):2081–2092.
Gu B. 2009. Variations and controls of nitrogen stable isotopes in particulate organic matter of lakes. Oecologia, 160 (3): 421–431.
Hadas O, Altabet M A, Agnihotri R. 2009. Seasonally varying nitrogen isotope biogeochemistry of particulate organic matter in Lake Kinneret, Israel. Limnol. Oceanogr., 54 (1): 75–85.
Han B P, Liu Z W. 2012. Tropical and Sub-tropical Reservoir Limnology in China: Theory and Practice. Springer, Netherlands. 369p.
Hollander D J, McKenzie J A. 1991. CO2 control on carbonisotope fractionation during aqueous photosynthesis: a paleo-pCO 2 barometer. Geology, 19 (9): 929–932.
Hou W, Gu B H, Lin Q Q, Gu J G, Han B P. 2013a. Stable isotope composition of suspended particulate organic matter in twenty reservoirs from Guangdong, southern China: implications for pelagic carbon and nitrogen cycling. Water Res., 47(11):3610–3623.
Hou W, Gu B H, Zhang H J, Gu J G, Han B P. 2013b. The relationship between carbon and nitrogen stable isotopes of zooplankton and select environmental variables in lowlatitude reservoirs. Limnology, 14 (1): 97–104.
Jones R I, Grey J, Sleep D, Quarmby C. 1998. An assessment, using stable isotopes, of the importance of allochthonous organic carbon sources to the pelagic food web in Loch Ness. Proc. Roy. Soc.
Lond. B, 265 (1391): 105–111.
Kendall C, Silval S R, Kelly V J. 2001. Carbon and nitrogen isotopic compositions of particulate organic matter in four large river systems across the United States. Hydrol. Process es, 15(7):1301–1346.
Kling G W, Fry B, O’Brien W J. 1992. Stable isotopes and planktonic trophic structure in arctic lakes. Ecology, 73 (2): 561–566.
Lee J Y, Kim J K, Owen J S, Choi Y, Shin K, Jung S, Kim B. 2013. Variation in carbon and nitrogen stable isotopes in POM and zooplankton in a deep reservoir and relationship to hydrological characteristics. J. Freshwater Ecol., 28 (1): 47–62.
Lehmann M F, Bernasconi S M, McKenzie J A, Barbieri A, Simona M, Veronesi M. 2004. Seasonal variation of the d 13 C and d 15 N of particulate and dissolved carbon and nitrogen in Lake Lugano: constraints on biogeochemical cycling in a eutrophic lake. Limnol. Oceanogr., 49 (2): 415–429.
Li Q H, Han B P. 2007. Structure and dynamics of phytoplankton community based CCA analysis in a pumped storage reservoir. Acta Ecol. Sinica, 27(6):2355–2364. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Lin S J, He L J, Huang P S, Han B P. 2005. Comparison and improvement on the extraction method for chlorophyll a in phytoplankton. Ecol. Sci., 24 (1): 9–11. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Lorenzen C J. 1967. Determination of chlorophyll and pheopigments: spectrophotometric equations. Limnol. Oceanogr., 12 (2): 343–346.
Pace M L, Cole J J, Carpenter S R, Kitchell J F, Hodgson J R, Van de Bogert M C, Bade D L, Kritzberg E S, Bastviken D. 2004. Whole-lake carbon-13 additions reveal terrestrial support of aquatic food webs. Nature, 427 (6971): 240–243.
Pisani O, Dodds W K, Jaffé R. 2016. Characterizing organic matter inputs to sediments of small, intermittent, prairie streams: a molecular marker and stable isotope approach. Aquat. Sci., 78 (2): 343–354.
Rožic P Ž, Dolenec T, Lojen S, Kniewald G, Dolenec M. 2015. Use of stable isotope composition variability of particulate organic matter to assess the anthropogenic organic matter in coastal environment (Istra Peninsula, Northern Adriatic). Environ. Earth Sci., 73(7):3109–3118.
Shotbolt L A, Thomas A D, Hutchinson S M. 2005. The use of reservoir sediments as environmental archives of catchment inputs and atmospheric pollution. Prog. Phys. Geog r., 29 (3): 337–361.
Syväranta J, Hämäläinen H, Jones R I. 2006. Within-lake variability in carbon and nitrogen stable isotope signatures. Freshw ater Biol., 51(6):1090–1102.
Wen M, Chen C M. 2005. Characteristics and estimation of water resources variation in resent 50-years in Zhuhai City. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 44 (S2): 272–275. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yoshioka T, Wada E, Hayashi H. 1994. A stable isotope study on seasonal food web dynamics in a eutrophic lake. Ecology, 75 (3): 835–846.
Zhang M, Lin Q Q, Xiao L J, Wang S, Qian X, Han B P. 2013. Effect of intensive epilimnetic withdrawal on phytoplankton community in a (sub) tropical deep reservoir. J. Limnol., 72 (3), http://dx.doi.org/10.4081/jlimnol.2013.e35.
Zohary T, Erez J, Gophen M, Berman-Frank I, Stiller M. 1994. Seasonality of stable carbon isotopes within the pelagic food web of Lake Kinneret. Limnol. Oceanogr., 39(5):1030–1043.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Henri Dumont from Gent University in Belgium for his reading and comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31170436) and the Science and Technology Project of Guangdong Province (No. 2013B080500022)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Peng, L., Gu, B. et al. Effect of trans-reservoir water supply on carbon and nitrogen stable isotope composition in hydrologically connected reservoirs in China. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 35, 1117–1126 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-017-5327-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-017-5327-y