Abstract
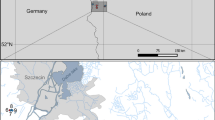
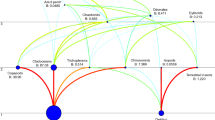
The seasonal variations in biomass, abundance, and species composition of plankton in relation to hydrography were studied in the saline Bange Lake, northern Tibet, China. Sampling was carried out between one to three times per month from May 2001 to July 2002. Salinity ranged from 14 to 146. The air and water temperature exhibited a clear seasonal pattern, and mean annual temperatures were approximately 4.8°C and 7.3°C, respectively. The lowest water temperature occurred in winter from December to March at -2°C and the highest in June and July at 17.7°C. Forty-one phytoplankton taxa, 21 zooplankton, and 5 benthic or facultative zooplankton were identified. The predominant phytoplankton species were Gloeothece linearis, Oscillatoria tenuis, Gloeocapsa punctata, Ctenocladus circinnatus, Dunaliella salina, and Spirulina major. The predominant zooplankton species included Holophrya actra, Brachionus plicatilis, Daphniopsis tibetana, Cletocamptus dertersi, and Arctodiaptomus salinus. The mean annual total phytoplankton density and biomass for the entire lake were 4.52×107 cells/L and 1.60 mg/L, respectively. The annual mean zooplankton abundance was 52, 162, 322, and 57, 144 ind./L, in the three sublakes. The annual mean total zooplankton biomass in Lakes 1–3 was 1.23, 9.98, and 2.13 mg/L, respectively. The annual mean tychoplankton abundances in Bg1, 2, and 3 were 47, 67, and 654 ind./L. The annual mean tychoplankton biomass was 2.36, 0.16, and 2.03 mg/L, respectively. The zooplankton biomass (including tychoplankton) in the lake was 9.11 mg/L. The total number of plankton species in the salt lake was significantly negatively correlated with salinity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso M. 1990. Anostraca, Cladocera and Copepoda of Spanish saline lakes. Hydrobiologia, 197 (1): 221–231.
An Y X, He Z H. 1991. Toxicity of four heavy metals in marine water to Moina mongolic a. Journal of Fisheries of China, 15 (4): 273–282. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Beadle L C. 1981. The Inland Waters of Tropical Africa. 2 nd edn. Langman, London, UK.
Chen Z M. 1981. Approaches to the changes of ecological environment of lakes in Xizang based on the upheaval of the Qinghai-Xizang plateau. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 12 (5): 402–411. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Colburn E A. 1988. Factors influencing species diversity in saline waters of Death Valley, USA. Hydrobiologia, 158 (1): 215–226.
Ehrlich A, Dor I. 1985. Photosynthetic microorganisms of the Gavish Sabkha. In: Friedman G M, Krumbein W E eds. Hypersaline Ecosystems: The Gavish Sabkha. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg. p.296–321.
Fott B. 1971. Algenkunde. 2 nd edn. VEB Gustav Fischer Verlag, Jena. 581p.
Geddes M C, de Deckker P, Williams W D, Morton D W, Topping M. 1981. On the chemistry and biota of some saline lakes in Western Australia. Hydrobiologia, 81-82 (1): 201–222.
Gong X J. 1983. Rotifera of Tibetan Plateau. In: Jiang X Z, Shen Y F, Gong X J eds. Aquatic Invertebrates of the Tibetan Plateau. Series of the Scientific Expedition to Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Science Press, Beijing, China. (in Chinese)
Green J, Mengestou S. 1991. Specific diversity and community structure of Rotifera in a salinity series of Ethiopian inland waters. Hydrobiologia, 209 (2): 95–106.
Hammer U T, Shamess J, Haynes R C. 1983. The distribution and abundance of algae in saline lakes of Saskatchewan, Canada. Hydrobiologia, 105 (1):1–26.
Hammer U T, Sheard J S, Kranabetter J. 1990. Distribution and abundance of littoral benthic fauna in Canadian prairie saline lakes. Hydrobiologia, 197 (1):173–192.
Hammer U T. 1986. Saline Lakes Ecosystems of the World. Junk, Dordrecht.
He Z H, Jiang H, Bi F S. 1996. Further research on the hydrochemistry and hydrobiologia of Dali Lake. Journal of Dalian Fisheries University, 11 (2): 1–13. (in Chinese with English abstract)
He Z H, Qin J G, Wang H Q, Wang Z H, Xia X. 1989. Studies on the saline and hypersaline zooplanktons from Jinnan and Yinchuan regions. Acta Hydrobiologi c a Sinica, 13 (1): 24–37. (in Chinese with English abstract)
He Z H, Qin J G, Wang Y, Jiang H, Zhao W. 2001. Biology of Moina mongolica (Moinidae, Cladocera) and perspective as live food for marine fish larvae: review. Hydrobiologia, 457 (1-3): 25–37.
He Z H, Qin K J, Wang Y, Zhao W. 1993. Biological resources in inland saline waters from Southern Shanxi, China. Part I. Lake Xiao chi. Journal of Dalian Fisheries University, 8 (4): 1–16. (in Chinese with English abstract)
He Z H, Qin K J, Wang Y, Zhao W. 1994. Biological resources in inland saline waters from Southern Shanxi, China. Part II. Lake Bei Mentan. Journal of Dalian Fisheries University, 9 (2): 1–16. (in Chinese with English abstract)
He Z H, Xie Z H, Lei Y Z. 1981. Studies on the hydrochemistry and hydrobiologia of Da-Li Lake. Acta Hydrobiologi c a Sinica, 7(3-341): 357. (in Chinese with English abstract)
He Z H, Xie Z H, Lei Y Z. 1984. Preliminary studies on the hydrochemistry and hydrobiologia of Wuliangsuhai Lake. Journal of Dalian Fisheries University, (1): 41–56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hu H J, Wei Y X. 1981. The characteristics of the green algal flora of Xizang and the unheaval of the plateau in relation to certain endemic species. In: Anon. ed. Geological and Ecological Studies of Qing-Xiang Plateau. Proceedings of Symposium on Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau (Beijing, China). Science Press, Beijing, Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, Inc., NY.
Huang X F, Chen W M, Cai Q M. 1999. Survey, Observation and Analysis of Lake Ecology. Standards Press of China Beijing. (in Chinese)
Jakher G R, Bhargava S C, Sinha R K. 1990. Comparative limnology of Sambhar and Didwana lakes (Rajasthan, NW India). Hydrobiologia, 197 (1): 245–256.
Jiang X Z, Du N S. 1979. Fauna Sinica. Crustacea: Freshwater Cladocera. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese)
Jiang X Z, Shen Y F, Gong X J. 1983. Aquatic Invertebrates of the Tibetan Plateau. Series of the Scientific Expedition to Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese)
Koste W. 1978. Rotatoria. Die Radertiere Mitteleuropas. 2 nd edn. Gebruder Borntraeger, Berlin and Stuttgart, 673p.
Lei Y Z, Dong S L, Shen C G. 1985. Study on the toxicity of carbonate-alkaline to fishes. Journal of Fisheries of China, 9 (2): 171–183. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Leibold M A, Chase J M, Shurin J B, Downing A L. 1997. Species turnover and the regulation of trophic structure. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 28: 467–494.
Li X Y, Wei Y X, Xin S Z, Hu H J. 1992. The Algae of the Xizang Plateau. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese)
Li Y Y. 1981. The blue-green algae of Xizang Plateau. In: Anon ed. Geological and ecological Studies of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Gorden & Breach, New York. p.1 131–1 134.
Ma Z Z. 1995. Preliminary studies on algae in salt pans and saline lakes of Northern China. Oceanologia e t Limnologia Sinica, 26 (3): 317–322. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Paine R T. 1980. Food webs: Linkage, interaction strength and community infrastructure. Journal of Animal Ecology, 49 (3): 666–685.
Ren M L, Quo Y, Wang J L, Su R, Li H, Ren B. 1996. Survey of Artemia Ecology and Resources in Inland Salt Lakes in Northwest China. Heilongjiang Science and Technology Press, Harbin. (in Chinese)
Servant-Vildary S, Roux M. 1990. Multivariate analysis of diatoms and water chemistry in Bolivian saline lakes. Hydrobiologia, 197 (1): 267–290.
Shen J R. 1979. Fauna Sinica, Crustacea Freshwater Copepoda. Science Press, Beijing, China. (in Chinese)
Shen Y F. 1983. Protozoa of the Tibetan Plateau. In: Jiang X Z, Shen Y F, Gong X J eds. Aquatic Invertebrates of the Tibetan Plateau. Series of the Scientific Expedition to Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Science Press, Beijing, China. (in Chinese)
Stephens D W. 1990. Changes in lake levels, salinity and the biological community of Great Salt Lake (Utah, USA), 1847-1987. Hydrobiologia, 197 (1): 139–146.
Vargas C A, Escribano R, Poulet S. 2006. Phytoplankton food quality determines time windows for successful zooplankton reproductive pulses. Ecology, 87 (12): 2 992–2 999.
Wang J J. 1977. Protozoa from some districes of Tibetan Plateau. A c ta Zoologica Sinica, 23 (2): 131–160. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang J L, Zheng Y M, Xing D J. 1975. Investigation report of Qinghai Lake naked carps bait. In: Qinghai Biological Research Institute ed. Fish Fauna and Biology of Naked Carps in Qinghai Lake. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese)
Wetzel R G. 1983. Limnology. 2 nd edn. Saunders, Philadelphia. p.1–300.
Williams W D. 1991. Chinese and Mongolian saline lakes: a limnological overview. Hydrobiologia, 210: 39–66.
Williams W D, Boulton A J, Taaffe R G. 1990. Salinity as a determinant of salt lake fauna: a question of scale. Hydrobiologia, 197 (1): 257–266.
Williams W D. 1983. Life in Inland Waters. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Victoria, Australia.
Wood R B, Talling J F. 1988. Chemical and algal relationships in a salinity series of Ethiopian inland waters. Hydrobiologia, 158 (1): 29–67.
Xu M Q, Cao H, Jia Q X, Gao Y R, Chen S G. 2002. Preliminary study of plankton community diversity of the Gahai Salt Lake in the Qaidam Basin of the Qinghai Tibet Plateau. Biodiversity Science, 10 (1): 38–43. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yu S S, Tang Y. 1981. The hydrochemical characteristics of the saline lakes on the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Ocean ologia et Limnol ogia Sin ica, 12 (6): 498–511. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao W, He Z H. 1993. Rotifera from inland saline waters in northern China. Journal of Dalian Fisheries University, 8 (2-3): 20–31. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao W, He Z H. 1995. Protozoa from inland saline waters in North China. Acta Hydrobiologi c a Sinica, 19 (3): 193–202. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao W, He Z H. 1999. Biological and ecological features of inland saline waters in North Hebei, China. International Journal of Salt Lake Research, 8 (3): 267–285.
Zhao W, Jiang H, He Z H. 1996. Planktonic Crustaceans of inland saline waters in Sanbei District, Northern China. Journal of Dalian Fisheries University, 11 (1): 1–13. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao W, Sun Z H, Huang Q, Xia Y J, Liu C Y, Wang Y Y. 1993. A Study on the plankton of inland saline water in northwest Jilin. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 15 (2): 65–71, 84. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao W, Wang Q H, Zheng M P, Zhao Y Y, Wang H L. 2002. A preliminary study on the biology of Daphniopsis t e b i tana Sars. Journal of Dalian Fisheries University, 17 (3): 209–214. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao W, Ying X W, Peng Z et al. 2010b. Ecology of Inland Saline Lakes in China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese)
Zhao W, Zhao Y Y, Wang Q H, Zheng M P, Zhang P, He Z H. 2010a. Spatial and temporal patterns of plankton assemblage structure in a high altitude saline lake, Namuka Co in Northern Tibet, China. CLEAN -Soil, Air, Water, 38 (10): 960–968.
Zhao W, Zheng M P, Xu X Z et al. 2005. Biological and ecological features of saline lakes in northern Tibet, China. Hydrobiologia, 541 (1): 189–203.
Zhao W. 1992a. A review on the Cladocera in inland saline waters. Journal of Dalian Fisheries University, 6 (2): 31–41. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao W. 1992b. A Study on the phytoplankton from inland saline waters in northern China. Journal of Dalian Fisheries University, 7 (2-3): 49–64. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zheng M P, Xiang J, Wei X J, Zheng Y. 1989. Saline Lakes on the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau. Beijing Scientific and Technical Publishing House, Beijing, China. (in Chinese)
Zheng M P. 1995. On “Saline lake agriculture”. Acta Geosi ci enti a Sinica, (4): 404–418. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhu H Z, Chen J Y. 2000. Bacillariophyta of the Xizang Plateau. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the China Geological Survey (Resources No. [2002]004), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30371112), the Liaoning Science and Technology Foundation (Nos. 002119, 20022100), the Special Program for Key Basic Research of Ministry of Science and Technology, China (No. 2014FY210700)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, W., Zhao, Y., Wang, Q. et al. The community structure and seasonal dynamics of plankton in Bange Lake, northern Tibet, China. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 34, 1143–1157 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-016-5131-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-016-5131-0