Abstract
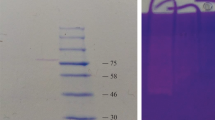
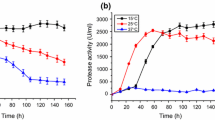
A crude protease produced from Planomicrobium sp. L-2 is described, and its effectiveness as an additive in liquid detergent evaluated. We isolate the protease-producing Planomicrobium sp. L-2 from the gastrointestinal tract of Octopus variabilis. At least three caseinolytic protease clear bands were observed in zymogram analysis. The crude alkaline protease was highly tolerant of a pH range from 7.0 to 9.0, and temperatures to 50°C after incubation for 1 h. Proteolytic enzymes were stable towards three surfactants (5% Tween 80, 1% Triton X-100 and 0.05% SDS) and an oxidizing agent (1% hydrogen peroxide), in addition to being highly stable and compatible with popular commercial laundry powered detergent brands available in China. Our study demonstrates the potential these proteases have for development into novel classes of detergent additive. This study also suggests that the gastrointestinal tract of Octopus variabilis may be a rich source of commercially valuable strains of enzyme.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banik R M, Prakash M. 2004. Laundry detergent compatibility of the alkaline protease from Bacillus cereus. Microbiol. Res., 159 (2): 135–140.
Bradford M M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem., 72 (1-2): 248–254.
Espósito T S, Amaral I P G, Buarque D S, Oliveira G B, Carvalho L B Jr, Bezerra R S. 2009. Fish processing waste as a source of alkaline proteases for laundry detergent. Food Chem., 112 (1): 125–130.
Ghosh S. 2008. Interaction of trypsin with sodium dodecyl sulfate in aqueous medium: a conformational view. Colloids Surf., 66 (2): 178–186.
Gupta R, Beg Q, Lorenz P. 2002. Bacterial alkaline proteases: molecular approaches and industrial applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 59 (1): 15–32.
Jaouadi B, Ellouz-Chaabouni S, Rhimi M, Bejar S. 2008. Biochemical and molecular characterization of a detergent-stable serine alkaline protease from Bacillus pumilus CBS with high catalytic efficiency. Biochimie., 90 (9): 1 291–1 305.
Jasvir S, Gill N, Devasahayam G, Sahoo D K. 1999. Studies on alkaline protease produced by Bacillus sp. NG312. App. Biochem. Biotechnol., 76 (1): 57–63.
Ktari N, Khaled H B, Younes I, Bkhairia I, Mhamdi S, Hamza I, Nasri M. 2014. Zebra blenny (Salaria basilisca) viscera as a source of solvent-stable proteases: characteristics, potential application in the deproteinization of shrimp wastes and evaluation in liquid laundry commercial detergents. J. Food Sci. Technol., 51 (11): 3 094–3 103.
Lata C, Negi D S, Mehrotra V. 2014. Potential of microbial proteases. Indian Streams Res. J., 4 (2), http://dx.doi.org/ 10.9780/22307850.
Li J, Peng Y, Wang X H, Chi Z M. 2010. Optimum production and characterization of an acid protease from marine yeast Metschnikowia reukaufii W6b. J. Ocean Uni v. China., 9 (4): 359–364.
Moradian F, Khajeh K, Naderi-Manesh H, Sadeghizadeh M. 2009. Isolation, purification and characterization of a surfactants-, laundry detergents-and organic solventsresistant alkaline protease from Bacillus sp. HR-08. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol., 159 (1): 33–45.
Moreira K A, Albuquerque B F, Teixeira M F S, Porto A L F, Lima F J L. 2002. Application of protease from Nocardiopsis sp. as a laundry detergent additive. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 18 (4): 307–312.
Ren P, Wang Y, Jin Y L, Piao M Z. 2012. Extraction, purification and characterization of protease from digestive tract of Octopus vulgaris. Food Sci., 33 (7): 168–171. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Sellami-Kamoun A, Haddar A, Ali N E-H, Ghorbel-Frikha B, Kanoun S, Nasri M. 2008. Stability of thermostable alkaline protease from Bacillus licheniformis RP1 in commercial solid laundry detergent formulations. Microbiol. Res., 163 (3): 299–306.
Shimogaki H, Takeuchi K, Nishino T, Odhera M, Kudo T, Ohba K, Iwama M, Irie M. 1991. Purification and properties of a novel surface-active agent-and alkalineresistant protease from Bacillus sp. Y. Agric. Biol. Chem., 55 (9): 2 251–2 258.
Sinha R, Srivastava A K, Khare S K. 2014. Efficient proteolysis and application of an alkaline protease from halophilic Bacillus sp. EMB9. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol., 44 (7): 680–696.
Temiz H, Ustun N S, Turhan S, Aykut U. 2013. Partial purification and characterization of alkaline proteases from the Black Sea anchovy (Engraulis encrasicholus) digestive tract. Afr. J. Biotechnol., 12 (1): 56–63.
Venugopal M, Saramma A V. 2007. An alkaline protease from Bacillus circulans BM15, newly isolated from a mangrove station: characterization and application in laundry detergent formulations. Indian J. Microbiol., 47 (4): 298–303.
Zhong J X, Li L B, Ning Y. 2009. A review on the biocharacteristics and reproduction of octopus. J. F ujian F isheries, (4): 76–79. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2011CM023) and the High-Level Personnel Research Foundation of Qingdao Agricultural University (No. 631431)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, Y., Wang, Y., Xiao, L. et al. Characterization of proteases from Planomicrobium sp. L-2 isolated from the gastrointestinal tract of Octopus variabilis (Sasaki). Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 34, 559–566 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-016-5040-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-016-5040-2