Abstract
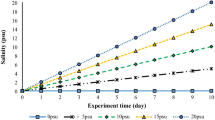
Effect of salinity on survival, feeding behavior and growth of juvenile swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus was investigated under 5 salinity levels of 5, 10, 20, 30 and 40. The results show that the crab juveniles fed 2 or 3 times at the salinity 20 and 30, each lasted for about 25 minutes, for a total feeding time of 73.2±22.65 minutes per day. At these salinities, there were significantly higher in the frequency of feeding and in total feeding time than those at lower salinities of 5 and 10. All crab juveniles moulted when reared at a salinity of 20 during the 5 days duration of the experiment, which is significantly higher than those at other salinities. All juveniles survived at salinity 20, and the survivorship was not significantly different from that at 30, but was significantly higher than those at other salinities. The crab juveniles reared at a salinity of 20 had the highest value of food ration of 0.190 8±0.011 3 g/gBW, average body weight gain of 0.796±0.128 g, gain rate of 87%–96%, and food conversion ratio of 1.20±0.09. There was no significant difference in the values found between 20 and 30 but these values were significantly lower than that at the other salinities (P >0.05). Highest activities of digestive enzymes (Amylase, Protease, Lipase) and lowest activities of protective enzymes (SOD, PO, CAT) were also obtained on crab juveniles reared at salinity of 20.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anger K. 1991. Effects of temperature and salinity on the larval development of the Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis (Decapoda: Grapsidae). Marine Ecology Progress Series, 72(1/2): 103–110.
Ashley P J. 2007. Fish welfare: current issues in aquaculture. Applied Animal Behavior Science, 104(3): 199–235.
Baylon J C. 2009. Appropriate food type, feeding schedule and Artemia density for the zoea larvae of the mud crab Scylla tranquebarica (Crustacea: Decapoda: Portunidae). Aquaculture, 288: 190–198.
Baylon J, Suzuki H. 2007. Effects of changes in salinity and temperature on survival and development of larvae and juveniles of the crucifix crab Charybdis feriatus (Crustacea: Decapoda: Portunidae). Aquaculture, 269: 390–401.
Bryars S R, Havenhand J N. 2006. Effects of constant and varying temperatures on the development of blue swimmer crab (Portunus pelagicus) larvae: laboratory observations and field predictions for temperate coastal waters. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 329(2): 218–229.
Chang E S. 1995. Physiological and biochemical changes during the molt cycle in decapod crustaceans: an overview. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 193(1–2): 1–14.
Chen C, Chen Z, Hu J. 2003. Study on halotolerance of phyllosoma larva of Chinese spiny lobster (Panulirus stimpsoni Holthuis). Acta Oceanologia Sinica, 25(2): 25–28.
Cui Z, Song C, Liu Y, Wang C L. 2012. Crustins from eyestalk cDNA library of swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus: molecular characterization, genomic organization and expression analysis. Fish Shellfish Immunol., 33(4): 937–45.
Ding S, Wang F, Guo B, Dong S L. 2008. Effects of salinity fluctuation on the molt, growth, and energy budget of juvenile Fenneropenaeus chinensis. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecolog., 19(2): 419–423. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ding X, He Z, Qiu X. 2010. A study on digestive enzyme activities and their effects by compound feed during different growth stages of Portunus trituberculatus. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 22(2): 492–497. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Fisher M R. 1999. Effect of temperature and salinity on size at maturity of female blue crabs. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society, 128(3): 499–506.
Gao B, Liu P, Li J. 2007. Analysis of morphological variations among four wild populations of Portunus trituberculatus. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 14(2): 223–228. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hamasaki K. 2003. Effects of temperature on the egg incubation period, survival and developmental period of larvae of the mud crab Scylla serrata (Forskl) (Brachyura: Portunidae) reared in the laboratory. Aquaculture, 219: 561–572.
Liao Y, Xiao Z, Yuan Y. 2008. Temperature tolerance of larva and juvenile of Portunus trituberculatus. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 32(4): 535–541.
Liu Y, Shi G, Cui Z. 2014. PtSerpin from the swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus, a putative regulator of prophenoloxidase activation with antibacterial activity. Fish Shellfish Immunol., 35(1): 167–173.
Nurdiani R, Zeng C S. 2007. Effects of temperature and salinity on the survival and development of mud crab, Scylla serrata (Forssk l), larvae. Aquaculture Research, 38(14): 1 529–1 538.
Qiao Z, Wang C, Fang W. 2012. Technical Guide for Safely Farming of Sea Crabs. Agricuture Press, Beijing, China. p.3–5. (in Chinese)
Romano N, Zeng C S. 2006. The effects of salinity on the survival growth and haemolymph osmolality of early juvenile blue swimmer crabs, Portunus pelagicus. Aquaculture, 260: 151–162.
Ruscoe I M, Shelley C C, Williams G R. 2004. The combined effects of temperature and salinity on growth and survival of juvenile mud crabs (Scylla serrata Forskl). Aquaculture, 238(1/4): 239–247.
Stickle W B, Wyler H J, Dietz T H. 2007. Effects of salinity on the juvenile crab physiology and agonistic interactions between two species of blue crabs, Callinectes sapidus and C. similes from coastal Louisiana. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 352: 361–370.
Wang C, Jiang L, Wang R. 2010. Effect of abrupt and gradual changes in salinity on development and feeding in juvenile swimming crab (Portunus trituberculatus). Fisheries Science, (29): 510–514. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wu X G, Cheng Y X, Sui L Y. 2007. Effect of dietary supplementation of phospholipids and highly unsaturated fatty acids on re-productive performance and offspring quality of Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis, female broodstock. Aquaculture, 273: 602–613.
Xia J, Zhou Q, Ri H. 2012. The problems and solutions of ecology polyculture with Penaeus japonicus and Portunus trituberculatus. Hebei Fisher., 4: 19–20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu Y, Dai G, Lu H. 2011. Observation and analysis of daily rhythm and preferred holdfast behavior of the seahorse, Hippocampus kuda. Journal of Ningbo University (NSEE), 24(1): 1–4. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ye J. 2007. Overwintering techniques for Portunus trituberculatus under high density. China Fisher., 3: 54–55. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang D, Li A. 1992. Study on salinity and adapt to survive the lower salinity Portunus trituberculatus Zoea. Marine Sciences, (1): 8–10. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang G, Fei Z, Yin Q. 2011. Contrast test of crab pond covered raise Procambarus clarkii. Journal of Aquaculture, 6: 10–12. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Science and Technology Innovation Team of Marine Crab Industry in Ningbo City (No. 2011B81003), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41276123), the National Spark Plan Program of China (No. 2012GA701048), the Key Project of Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (No. 212070), and the K C Wong Magana Fund in Ningbo University
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shentu, J., Xu, Y. & Ding, Z. Effects of salinity on survival, feeding behavior and growth of the juvenile swimming crab, Portunus trituberculatus (Miers, 1876). Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 33, 679–684 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-015-4218-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-015-4218-3