Abstract
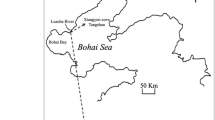
An artificial oyster shell reef was deployed in Rongcheng Bay, East China. However, the effects of this reef on the surrounding macrobenthic communities were unknown. We compared sedimentary factors, macrobenthic biomass, abundance, and community composition and ecological indicators between the reef and non-reef areas over a one year period. The mean values for chlorophyll a (Chl a), total organic matter (TOM), total organic carbon (TOC), and total nitrogen (TN) content in surface sediments in the reef area were slightly higher than those in the non-reef area. The Chl a levels differed significantly between the two areas, but the TOM, TOC, and TN were not significantly different. The abundance of crustaceans was significantly different between the two areas, but the abundance and biomass of polychaetes, echinoderms, mollusk did not differ significantly. The permutational multivariate analysis of variance (PERMANOVA) revealed that the macrobenthic community differed significantly through time and analysis of similarity multivariate analyses (ANOSIM) revealed that the macrobenthic community differed significantly in some months. The ecological indicators revealed that the environmental quality of the reef area was slightly better than that of the non-reef area. Overall, our results suggest that the artificial oyster shell reef may change the macrobenthic community and the quality of the environment. Despite the lack of an effect in the short term, long-term monitoring is still needed to evaluate the effects of artificial oyster shell reefs on macrobenthic communities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Airoldi L, Abbiati M, Beck M W, Hawkins S J, Jonsson P R, Martin D, Moschella P S, Sundelof A, Thompson R C, Aberg P. 2005. An ecological perspective on the deployment and design of low-crested and other hard coastal defence structures. Coastal Engineering, 52(10–11): 1 073–1 087.
Ambrose R, Anderson T. 1990. Influence of an artificial reef on the surrounding infaunal community. Marine Biology, 107(1): 41–52.
Anderson M J. 2001. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecology, 26(1): 32–46.
Anderson M, Gorley R, Clarke K. 2008. PERMANOVA+ for PRIMER: Guide to Software and Statistical Methods. PRIMER-E Ltd, Plymouth. 214p.
Anderson S C, Flemming J M, Watson R, Lotze H K. 2010. Serial exploitation of global sea cucumber fisheries. Fish and Fisheries, 12(3): 317–339.
Arkema K, Reed D, Schroeter S. 2009. Direct and indirect effects of giant kelp determine benthic community structure and dynamics. Ecology, 90(11): 3 126–3 137.
Baine M. 2001. Artificial reefs: a review of their design, application, management and performance. Ocean & Coastal Management, 44(3–4): 241–259.
Bertasi F, Colangelo M A, Abbiati M, Ceccherelli V U. 2007. Effects of an artificial protection structure on the sandy shore macrofaunal community: the special case of Lido di Dante (Northern Adriatic Sea). Hydrobiologia, 586(1): 277–290.
Bohnsack J, Sutherland D. 1985. Artificial reef research: a review with recommendations for future priorities. Bulletin of Marine Science, 37(1): 11–39.
Borja A, Dauer D, Díaz R, RJ L, Muxika I, Rodruez J, Schaffner L. 2008. Assessing estuarine benthic quality conditions in Chesapeake Bay: a comparison of three indices. Ecological Indicators, 8(4): 395–403.
Borja A, Franco J, Pérez V. 2000. A marine biotic index to establish the ecological quality of soft-bottom benthos within European estuarine and coastal environments. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 40(12): 1 100–1 114.
Borja A, Josefson A B, Miles A, Muxika I, Olsgard F, Phillips G, Rodriguez J, Rygg B. 2007. An approach to the intercalibration of benthic ecological status assessment in the North Atlantic ecoregion, according to the European Water Framework Directive. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 55(1–6): 42–52.
Bortone S A. 2006. A perspective of artificial reef research: the past, present, and future. Bulletin of Marine Science, 78(1): 1–8.
Buschmann A H, Briganti F, Retamales C A. 1997. Intertidal cultivation of Gracilaria chilensis (Rhodophyta) in southern Chile: long term invertebrate abundance patterns. Aquaculture, 156(3–4): 269–278.
Clarke K R, Gorley R N. 2006. RIMER v6: User Manual Tutorial. PRIMER-E Ltd., Plymouth. 190p.
Clarke K R, Warwick R M. 2001. Changes in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation (2nd edition). PRIMER-E Ltd, Plymouth. 172p.
Cotano U, Villate F. 2006. Anthropogenic influence on the organic fraction of sediments in two contrasting estuaries: a biochemical approach. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 52(4): 404–414.
Dauvin J-C. 2007. Paradox of estuarine quality: Benthic indicators and indices, consensus or debate for the future. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 55(1–6): 271–281.
Davis N, VanBlaricom G, Dayton P. 1982. Man-made structures on marine sediments: effects on adjacent benthic communities. Marine Biology, 70(3): 295–303.
Dewsbury B M, Fourqurean J W. 2010. Artificial reefs concentrate nutrients and alter benthic community structure in an oligotrophic, subtropical estuary. Bulletin of Marine Science, 86(4): 813–829.
Fabi G, Luccarini F, Panfili M, Solustri C, Spagnolo A. 2002. Effects of an artificial reef on the surrounding soft-bottom community (central Adriatic Sea). ICES Journal of Marine Science, 59(suppl.): S343–S349.
Falcão M, Santos M, Vicente M, Monteiro C. 2007. Biogeochemical processes and nutrient cycling within an artificial reef off Southern Portugal. Marine Environmental Research, 63(5): 429–444.
Fukunaga A, Bailey-Brock J H. 2008. Benthic infaunal communities around two artificial reefs in Mamala Bay, Oahu, Hawaii. Marine Environmental Research, 65(3): 250–263.
Gao Q F, Wang Y, Dong S, Sun Z, Wang F. 2011. Absorption of different food sources by sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus (Selenka) (Echinodermata: Holothuroidea): evidence from carbon stable isotope. Aquaculture, 319(1–2): 272–276.
Holm-Hansen O, Riemann B. 1978. Chlorophyll a determination: improvements in methodology. Oikos, 30(3): 438–447.
Hu L, Guo Z, Feng J, Yang Z, Fang M. 2009. Distributions and sources of bulk organic matter and aliphatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments of the Bohai Sea, China. Marine Chemistry, 113(3–4): 197–211.
Jespersen A, Christoffersen K. 1987. Measurements of chlorophyll-a from phytoplankton using ethanol as extraction solvent. Archiv. Fur. Hydrobiologie, 109(3): 445–454.
Krumhansl K, Scheibling R. 2011. Detrital production in Nova Scotian kelp beds: patterns and processes. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 421: 67–82.
Langhamer O. 2010. Effects of wave energy converters on the surrounding soft-bottom macrofauna (west coast of Sweden). Marine Environmental Research, 69(5): 374–381.
Langlois T J, Anderson M J, Babcock R C. 2006. Inconsistent effects of reefs on different size classes of macrofauna in adjacent sand habitats. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 334(2): 269–282.
Lee H W, Bailey-Brock J H, McGurr M M. 2006. Temporal changes in the polychaete infaunal community surrounding a Hawaiian mariculture operation. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 307: 175–185.
Littler M M, Littler D S, Brooks B L. 2010. The effects of nitrogen and phosphorus enrichment on algal community development: Artificial mini-reefs on the Belize Barrier Reef sedimentary lagoon. Harmful Algae, 9(3): 255–263.
Luczak C, Janquin M A, Kupka A. 1997. Simple standard procedure for the routine determination of organic matter in marine sediment. Hydrobiologia, 345(1): 87–94.
Margalef R. 1968. Perspectives in Ecological Theory. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. 111p.
Marques J C, Salas F, PatrÍcio J, Teixeira H, Neto J M. 2009. Ecological Indicators for Coastal and Estuarine Environmental Assessment: A User Guide. Wit Pr/Computational Mechanics, Southampton. 183p.
Martins G M, Amaral A F, Wallenstein F M, Neto A I. 2009. Influence of a breakwater on nearby rocky intertidal community structure. Marine Environmental Research, 67(4–5): 237–245.
Muxika I, Borja A, Bald J. 2007. Using historical data, expert judgement and multivariate analysis in assessing reference conditions and benthic ecological status, according to the European Water Framework Directive. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 55(1–6): 16–29.
Quiroga E, Ortiz P, Gerdes D, Reid B, Villagran S, Quiñones R. 2012. Organic enrichment and structure of macrobenthic communities in the glacial Baker Fjord, Northern Patagonia, Chile. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 92(01): 73–83.
Shannon C E, Weaver W. 1963. Mathematical Theory of Communication. University Illinois Press, Urbana. 114p.
Steimle F, Foster K, Kropp R, Conlin B. 2002. Benthic macrofauna productivity enhancement by an artificial reef in Delaware Bay, USA. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 59(suppl.): S100–S105.
Teixeira H, Borja A, Weisberg S B, Ranasinghe J A, Cadien D B, Dauer D M, Dauvin J-C, Degraer S, Diaz R J, Gremare A, Karakassis I, Llanso R J, Lovell L L, Marques J C, Montagne D E, Occhipinti-Ambrogi A, Rosenberg R, Sarda R, Schaffner L C, Velarde R G. 2010. Assessing coastal benthic macrofauna community condition using best professional judgement—developing consensus across North America and Europe. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 60(4): 589–600.
Terlizzi A, Bevilacqua S, Scuderi D, Fiorentino D, Guarnieri G, Giangrande A, Licciano M, Felline S, Fraschetti S. 2008. Effects of offshore platforms on soft-bottom macrobenthic assemblages: a case study in a Mediterranean gas field. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 56(7): 1 303–1 309.
Ugland K I, Bjorgesaeter A, Bakke T, Fredheim B, Gray J S. 2008. Assessment of environmental stress with a biological index based on opportunistic species. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 366(1–2): 169–174.
Verissimo H, Neto J M, Teixeira H, Franco J N, Fath B D, Marques J C, Patricio J. 2012. Ability of benthic indicators to assess ecological quality in estuaries following management. Ecological Indicators, 19: 130–143.
Wilding T A, Sayer M D J. 2002. Evaluating artificial reef performance: approaches to pre-and post-deployment research. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 59(suppl.): S222–S230.
Wilding T A. 2006. The benthic impacts of the Loch Linnhe artificial reef. Hydrobiologia, 555(1): 345–353.
Yuan X, Yang H, Wang L, Zhou Y, Gabr H R. 2009. Bioenergetic responses of sub-adult sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus (Selenka) (Echinodermata: Holothuroidea) to temperature with special discussion regarding its southernmost distribution limit in China. Journal of Thermal Biology, 34(6): 315–319.
Zhang J, Fang J, Wang W, Du M, Gao Y, Zhang M. 2012. Growth and loss of mariculture kelp Saccharina japonica in Sungo Bay, China. Journal of Applied Phycology, 2012(24): 1–8.
Zhang J, Hansen P K, Fang J, Wang W, Jiang Z. 2009. Assessment of the local environmental impact of intensive marine shellfish and seaweed farming—application of the MOM system in the Sungo Bay, China. Aquaculture, 287(3–4): 304–310.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Marine Public Welfare Research Project (Nos. 200805069, 201305043), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41106134), and National Key Technology Research and Development Program (Nos. 2011BAD13B02, 2010BAC68B01).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Q., Zhang, L., Zhang, T. et al. Effects of an artificial oyster shell reef on macrobenthic communities in Rongcheng Bay, East China. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 32, 99–110 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-014-2308-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-014-2308-2