Abstract
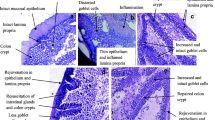
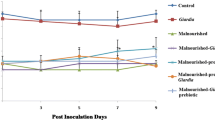
Oyster peptides were produced from Crassostrea hongkongensis and used as a new protein source for the preparation of an oyster peptide-based enteral nutrition formula (OPENF). Reserpineinduced malabsorption mice and cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppression mice were used in this study. OPENF powder is light yellow green and has a protein-fat-carbohydrate ratio of 16:9:75 with good solubility in water. A pilot study investigating immune functional impacts of the OPENF on mice show that the OPENF enhanced spleen lymphocyte proliferation and the activity of natural killer (NK) cells in BALB/c mice. Furthermore, OPENF can improve intestinal absorption, increase food utilization ratio, and maintain the normal physiological function of mice. These results suggest that oyster peptides could serve as a new protein source for use in enteral nutrition formula, but more importantly, also indicate that OPENF has an immunostimulating effect in mice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiking H. 2011. Future protein supply. Trends Food Sci. Tech., 22(2–3): 112–120.
Bao S, Fei J, Shen J, Gong S J, Fang H, Husband A J. 2006. Reserpine-induced model of stress suppresses mucosal immunity. Immunol. Cell Biol., 84(6): 537–542.
Cai D Z. 2005. Practical Nutrition. People’s Medical Publishing House, Beijing, China. p.485–487. (in Chinese)
Defer D, Bourgougnon N, Fleury Y. 2009. Screening for antibacterial and antiviral activities in three bivalve and two gastropod marine molluscs. Aquaculture, 293(1–2): 1–7.
Eberts T J, Sample R H, Glick M R, Ellis G H. 1979. A simplified, colorimetric micromethod for xylose in serum or urine, with pholroglucinol. Clin. Chem., 25(8): 1 440–1 443.
Hou H, Fan Y, Li B F, Xue C H, Yu G L. 2012. Preparation of immunomodulatory hydrolysates from Alaska pollock frame. J. Sci. Food Agr., 92(15): 3 029–3 038.
Kim E K, Kim Y S, Lee S J, Jeon Y J, Lee J D, Son T I, Ahn C B, Kim Y T, Moon S H, Jeon B T, Kim S W, Park P J. 2010. Anticancer effect of lipids partially purified from Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas on PC3 cells. J. Food Sci. Biotechnol., 19(1): 213–217.
Kim S K, Wijesekara I. 2010. Development and biological activities of marine-derived bioactive perptides: a review. J. Funct. Food, 2(1): 1–9.
Kirby D F, Delegge M H, Fleming C R. 1995. Americangastroenterological-association technical review on tubefeeding for enteral nutrition. Gastroenterology, 108(4): 1 282–1 301.
Kong X Z, Guo M M, Hua Y F, Cao D, Zhang C M. 2008. Enzymatic preparation of immunomodulatiing hydrolysates from soy proteins. Bioresource Technol., 99(18): 8 873–8 879.
Kume H, Okazaki K, Yamaji T, Sasaki H. 2012. A newly designed enteral formula containing whey peptides and fermented milk product protects mice against concanavalin A-induced by suppressing overproduction of inflammatory cytokines. Clin. Nutr., 31(2): 283–289.
Laura H. 2002. The history of internal nutrition therapy: from raw eggs and nasal tubes to purified amino acids and early postoperative jejuna delivery. Amer. Dietetic Assoc., 102(3): 399–404.
Li J S. 2003. Enteral nutrition-surgical approach of choice for clinical nutritional support. Par. Ent. Nutr., 10(3): 129–130.
Li J Y, Sun D. 2003. Experimental study of gut absorptive capacity after trauma detected by D-xylose content test with micromethod. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation, 32(4): 29–33. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Matarese L E, Gottschlich M M. 2003. Contemporary NutritionSupport Practice: A Clinical Guide. 2nd edn. Philadelphia: Saunders. 150p.
Matsumoto K, Ogikubo A, Yoshino T, Matsui T, Osajima Y. 1994. Separation and purification of angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptide in peptic hydrolyzate of oyster. Nippon Shokuhin Kogyo Gakkaishi, 41: 589–594.
Pomponi S A. 1999. The bioprocess-technological potential of the sea. J. Biotechnol., 70(1–3): 5–13.
Shen P P, Zhao S W, Zheng W J, Hua Z C, Shi Q, Liu Z T. 2003. Effects of cyanobacteria bloom extract on some parameters of immune function in mice. Toxicol. Lett., 143(1): 27–36.
Sun S F, Pan Q Z, Hui X, Zhang B L, Wu H M, Li H, Xu W, Zhang Q, Li J Y, Deng X M, Chen J W, Lian Z X, Li N. 2008. Stronger in vitro phagocytosis by monocytesmacrophages is indicative of greater pathogen clearance and antibody levels in vivo. Poultry. Sci., 87(9): 1 725–1 733.
Wang Y K, He H L, Wang G F, Wu H, Zhou B C, Chen X L, Zhang Y Z. 2010. Oyster (Crassostrea gigas) hydrolysates produced on a plant scale have antitumor activity and immunostimulating effects in BALB/c mice. Marine Drugs, 8(2): 255–268.
Wang X Q, Zhang X W. 2012. Optimal extraction and hydrolysis of Chlorella pyrenoidosa proteins. Bioresource Technol., 126: 307–313.
Wildhaber B E, Yang H, Spencer A U, Drongowski R A, Teitelbaum D H. 2005. Lack of enteral nutrition-effects on the intestinal immune system. J. Surg. Res., 123(1): 8–16.
Wohlt P D, Zheng L, Gunderson S, Balzar S A, Johnson B D, Fish J T. 2009. Recommendations for the use of medications with continuous enteral nutrition. Am. J. Health-Syst. Ph., 66(16): 1 458–1 467.
Yang Y, Li X H, Zhang X Z. 2007. Study on effects of superior fiber complexes on the digestion-absorbtion function of mice. Modern Preventive Medicine, 34(16): 3 036–3 039. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yoshikawa T, Naito Y, Masui K, Fujii T, Boku Y, Nakagawa S, Yoshida N, Kondo M. 1997. Free radical-scavenging activity of Crassostera gigas extract (JCOE). Biomedecine & Pharmacotherapy, 51(8): 328–332.
Yuan H, Song J, Li X, Li N, Dai J. 2006. Immunomodulation and antitumor activity of kappa-carrageenan oligosaccharides. Cancer Lett., 243(2): 228–234.
Zeng M H, Fang C Y, Wang S S, Zhu M, Xie L, Li R, Wang L, Wu X W, Chen S. 2006. A study of soluble HLA-G(1) protecting porcine endothelial cells against human natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Transpl. P., 38(10): 3 312–3 314.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Knowledge Innovation Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. KZCX2-EW-Q214), the Comprehensive Strategic Cooperation Programs between Guangdong Province and Chinese Academy of Sciences (Nos. 2011A090100008, 2009B091300018, 2010B090300027), and the Marine Fisheries Technology PromotionSpecial Program of Guangdong Province (No. A2009009-035(a))
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, B., Pan, J., Wu, Y. et al. Immune functional impacts of oyster peptide-based enteral nutrition formula (OPENF) on mice: a pilot study. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 31, 813–820 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-013-2311-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-013-2311-z