Abstract
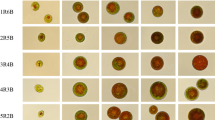
Cells of Haematococcus pluvialis Flot. et Will were collected in four different growth phases. We quantified the initial and total enzyme activity of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase (Rubisco) in crude extracts, and the relative expression of large-subunit ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate caboxylase / oxygenase (rbcL) mRNA. We measured the ratio of photosynthetic rate to respiration rate (P/R), maximal effective quantum yield of photosystem II (F v/F m), electron transport rate (ETR), actual photochemical efficiency of PSII in the light (PSII), and non-photochemical quenching (NPQ). Green vegetative cells were found to be in the most active state, with a relatively higher P/R ratio. These cells also displayed the lowest NPQ and the highest F v/F m, ETR, and PSII, indicating the most effective PSII. However, both Rubisco activity and rbcL mRNA expression were the lowest measured. In orange resting cysts with relatively lower P/R and NPQ, Rubisco activity and rbcL expression reached a peak, while F v/F m, ETR, and ΦPSII were the lowest measured. Taking into account the methods of astaxanthin induction used in industry, we suggest that Rubisco may participate in astaxanthin accumulation in H. pluvialis. A continuous and sufficient supply of a carbon source such as CO2 may therefore aid the large scale production of astaxanthin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berman-Frank I, Dubinsky Z. 1999. Balanced growth in aquatic plants: myth or reality? BioScience, 49: 29–37.
Birnboim H C, Doly J. 1979. A rapid alkaline procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res., 7: 1 513–1 523.
Boussiba S, Vonshak A. 1991. Astaxanthin accumulation in the green alga Haematococcus pluvialis. Plant Cell Physiol., 32: 1 077–1 082.
Boussiba S. 2000. Carotenogenesis in the green alga Haematococcus pluvialis: Cellular physiology and stress response. Physiol. Plantarum, 108: 111–117.
Brown M R, Dunstan G A, Norwood S J, Miller K A. 1996. Effects of harvest stage and light on the biochemical composition of the diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana. J. Phycol., 32: 64–73.
Cleveland J S, Perry M J. 1987. Quantum yield, relative specific absorption and fluorescence in nitrogen-limited Chaetoceros gracilis. Mar. Biol., 94: 489–497.
Cunningham F X, Gantt E. 1998. Genes and enzymes of carotenoid biosynthesis in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol., 49: 557–583.
Dennis D, Blakeley S T. 2000. Energy-conserving reactions of glycolysis. In: Buchanan B, Gruissem W, Jones R eds. Biochemistry & Molecular Biology of Plants. Science Press, Beijing. p.667.
Domínguez-Bocanegra A R, Legarreta I G, Jeronimo F M, Campocosio A T. 2004. Influence of environmental and nutritional factors in the production of astaxanthin from Haematococcus pluvialis. Bioresour. Technol., 92: 209–214.
Enríquez S, Merino M, Iglesias-Prieto R. 2002. Variations in the photosynthetic performance along the leaves of the tropical seagrass Thalassia testudinum. Mar. Biol., 140: 891–900.
Fábregas J, Domínguez A, Álvareza D C, Lamela T, Otero A. 1998. Induction of astaxanthin accumulation by nitrogen and magnesium deficiencies in Haematococcus pluvialis. Biotechnol. Lett., 20: 623–626.
Ferreira I D, Rosário V E D, Cravo P V L. 2006. Real-time quantitative PCR with SYBR Green I detection for estimating copy numbers of nine drug resistance candidate genes in Plasmodium falciparum. Malaria. Journal, 5: 1.
Forster R M, Schubert H. 1997. Wavelength dependence of photoinhibition in the green alga Chlorella vulgaris. Photosynthetica, 33: 541–552.
Gerard V A, Driscoll T. 1996. A spectrophotometric assay for Rubisco activity: application to the kelp Laminaria saccharina and implications for radiometric assays. J. Phycol., 32: 880–884.
Guerin M, Huntley M E, Olaizola M. 2003. Haematococcus astaxanthin; applications for human health and nutrition. Trends Biotechnol., 21: 210–216.
Gu W L, An G H, Johnson E A. 1997. Ethanol increases carotenoid production in Phaffia rhodozyma. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 19: 114–117.
Guillard R R L. 1975. Culture of phytoplankton for feeding marine invertebrates. In: Smith W L, Chanley M H eds. Culture of marine invertebrate animals. Plenum Press, New York. p.26–60.
Gygi S P, Rochon Y, Franza B R, Aebersold R. 1999. Correlation between protein and mRNA abundance in yeast. Mol. Cell Biol., 19: 1 720–1 730.
Hagen C, Grünewald K, Schmidt S, Müller J. 2000. Accumulation of secondary carotenoids in flagellates of Haematococcus pluvialis (Chlorophyta) is accompanied by an increase in per unit chlorophyll productivity of photosynthesis. Eur. J. Phycol., 35: 75–82.
Herrmann H, Häder D P, Köfferlein M, Seidlitz H K, Ghetti F. 1996. Effects of UV radiation on photosynthesis of phytoplankton exposed to solar simulator light. J. Photoch. Photobio. B, 34: 21–28.
Humphrey G F. 1975. The photosynthesis: respiration ratio of some unicellular marine algae. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 18: 111–119.
Kang C D, Lee J S, Park T H, Sim S J 2005. Comparison of heterotrophic and photoautotrophic induction on astaxanthin production by Haematococcus pluvialis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 68: 237–241.
Kang C D, Lee J S, Park T H, Sim S J. 2007. Complementary limiting factors of astaxanthin synthesis during photoautotrophic induction of Haematococcus pluvialis: C/N ratio and light intensity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 74: 987–994.
Katsuda T, Shimahara K, Shiraishi H, Yamagami K, Ranjbar R, Katoh S. 2006. Effect of flashing light from blue light emitting diodes on cell growth and astaxanthin production of Haematococcus pluvialis. J. Biosci. Bioeng., 102: 442–446.
Kobayashi M, Kakizono T, Nagai S. 1993. Enhanced carotenoid biosynthesis by oxidative stress in acetate induced cyst cells of a green unicellular alga, Haematococcus pluvialis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 59: 867–873.
Kobayashi M, Sakamoto Y. 1999. Singlet oxygen quenching ability of astaxanthin esters from the green alga Haematococcus pluvialis. Biotechnol. Lett., 21: 265–269.
Liang Y, Beardall J, Heraud P. 2006. Effects of nitrogen source and UV radiation on the growth, chlorophyll fluorescence and fatty acid composition of Phaeodactylum tricornutum and Chaetoceros muelleri (Bacillariophyceae). J. Photoch. Photobio. B, 2: 161–172.
Lichtenthaler H K. 1999. The 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol., 50: 47–66.
Lorenz R T, Cysewski G R. 2000. Commercial potential for Haematococcus microalgae as a natural source of astaxanthin. Trends Biotechnol., 18: 160–167.
Linden H. 1999. Carotenoid hydroxylase from Haematococcus pluvialis: cDNA sequence, regulation and functional complementation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1446: 203–212.
Malkin R, Niyogi K. 2000a. Overview of photosynthesis. In: Buchanan B, Gruissem W, Jones R eds. Biochemistry & Molecular Biology of Plants. Science Press, Beijing. p.570.
Malkin R, Niyogi K. 2000b. Light absorption and energy conversion. In: Buchanan B, Gruissem W, Jones R eds. Biochemistry & Molecular Biology of Plants. Science Press, Beijing. p.579.
Margalith P Z. 1999. Production of ketocarotenoids by microalgae. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 51: 431–438.
Mcallister C D, Shaw N, Strickland J D. 1964. Marine phytoplankton photosynthesis as a function of light intensity: A comparison of methods. J. Fish Res. Bd. Can., 21: 159–181.
Melis A, Melnicki M R. 2006. Integrated biological hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energ., 31: 1 563–1 573.
Merino M, Enríĺquez S, Strasser R J, Iglesias-Prieto R. 1995. Spatial and diurnal variations in photosynthetic activity of the tropical seagrass Thalassia testudinum. In: Mathis P ed. Photosynthesis: from Light to Biosphere. Kluwer Academic Publishers, The Netherlands, Vol. 5. p.889–892.
Mouget J L, Beeson R C, Legendre L, Noüe J D L. 1993. Inadequacy of Rubisco initial and total activities to account for observed rates of photosynthetic carbon dioxide assimilation by Scenedesmus orecnis. Eur. J. Phycol., 28: 99–106.
Nilawati J, Greenberg B M, Smith R E H. 1997. Influence of ultraviolet radiation on growth and photosynthesis of two cold ocean diatoms. J. Phycol., 33: 215–224.
Ralph P J, Macinnis-Ng C M O, Frankart C. 2005. Fluorescence imaging application: effect of leaf age on seagrass photokinetics. Aqu. at Bot., 81: 69–84.
Pichard S L, Campbell L, Kang J B, Tabita F R, Paul J H. 1996. Regulation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase gene expression in natural phytoplankton communities. I. Diel rhythms. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 139: 257–265.
Ryther J H. 1954. The ratio of photosynthesis to respiration in marine plankton algae and its effect on the measurement of productivity. Deep Sea Res., 2: 134–139.
Schwender J, Goffman F, Ohlrogge J B, Shachar-Hill Y. 2004. Rubisco without the Calvin cycle improves the carbon efficiency of developing green seeds. Nature, 432: 779–782.
Somerville C, Browse J, Jaworski J G, Ohlrogge J B. 2000. Fatty acid biosynthesis. In: Buchanan B, Gruissem W, Jones R eds. Biochemistry & Molecular Biology of Plants. Science Press, Beijing. p.467.
Spreitzer R J. 1993. Genetic dissection of Rubisco structure and function. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol., 44: 411–434.
Sukenik A, Carmeli Y. 1990. Lipid synthesis and fatty acid composition in Nannochloropsis sp. (Eustigmatophyceae) growth in a light-dark cycle. J. Phycol., 26: 463–469.
Tabita F R. 1988. Molecular and cellular regulation of autotrophic carbon dioxide fixation in microorganisms. Microbiol. Rev., 52: 155–189.
Tan S, Cunningham F X, Youmans M, Grabowski B, Sun Z, Gantt E. 1995. Cytochrome f loss in astaxanthin accumulating red cells of Haematococcus pluvialis (Chlorophyceae): Comparison of photosynthetic activity, photosynthetic enzymes and thylakoid membrane polypeptides in red and green cells. J. Phycol., 31: 897–905.
Torzillo G, Goksan T, Faraloni C, Kopecky J, Masojídek J. 2003. Interplay between photochemical activities and pigment composition in an outdoor culture of Haematococcus pluvialis during the shift from the green to red stage. J. Appl. Phycol., 15: 127–136.
Torzillo G, Goksan T, Isik O, Gokpinar S. 2005. Photon irradiance required to support optimal growth and interrelations between irradiance and pigment composition in the green alga Haematococcus pluvialis. Eur. J. Phycol., 40: 233–240.
Wang B, Zarka A, Trebst A, Boussiba S. 2003. Astaxanthin accumulation in Haematococcus pluvialis (Chlorophyceae) as an active photoprotective process under high irradiance. J. Phycol., 39: 1 116–1 124.
Wang S B, Hu Q, Sommerfeld M, Chen F. 2004. Cell wall proteomics of the green alga Haematococcus pluvialis (Chlorophyceae). Proteomics, 4: 692–708.
Wawrik B, Paul J H, Tabita F R. 2002. Real-time PCR quantification of rbcL (Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase) mRNA in diatoms and pelagophytes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 68: 3 771–3 779.
Woodrow I E, Berry J A. 1988. Enzymatic regulation of photosynthetic CO2, fixation in C3 plants. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol., 39: 533–594.
Xu H H, Tabita F R. 1996. Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase gene expression and diversity of Lake Erie planktonic microorganisms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 62: 1 913–1 921.
Yong Y Y R, Lee Y K. 1991. Do carotenoids play a photoprotective role in the cytoplasm of Haematococcus lacustris (Chlorophyta)? J. Phycol., 30: 257–261.
Yuan J P, Chen F. 1999. Hydrolysis kinetics of astaxanthin esters and stability of astaxanthin of Haematococcus pluvialis during saponification. J. Agric. Food Chem., 47: 31–35.
Yuan J P, Chen F. 2000. Purification of trans-astaxanthin from a high-yielding astaxanthin ester-producing strain of the microalga Haematococcus pluvialis. Food Chem., 68: 443–448.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Basic Projects for Science and Technology (No. SQ2012FY4910019-1), the Project of Science and Technology for Supporting Tianjin Development (No. 10ZCKFSH0070), and the Project for Developing Marine Economy by Science and Technology in Tianjin (KX2010-0005)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Wang, G. & Niu, J. Variation in Rubisco and other photosynthetic parameters in the life cycle of Haematococcus pluvialis . Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 30, 136–145 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-012-1060-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-012-1060-8