Abstract
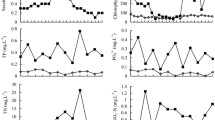
Rotifer community structure was investigated in Yangcheng Lake in 2008. Dominant species and species diversity indices were determined and Q B/T was used to assess water quality. The annual average density and biomass of the rotifers in Yangcheng Lake was 2 894 ± 1 006 ind./L and 12.47 ± 10.28 mg/L, respectively. The highest densities were observed in the western portion of the lake in March, but the highest biomass occurred in inflowing creeks in September. Within a year of monitoring in Yangcheng Lake, 93 species were identified and the dominant species were found to be Polyarthra trigla, Brachionus angularis, Keratella cochlearis, Keratella valga, Brachionus calyciflorus, and Filinia major. Of the species recorded, 75 were pollution indicator species. Density and biomass exhibited significant positive correlations with water temperature (R = 0.209, P = 0.003; R = 0.446, P = 0.000), but the peak density showed two lags in response to chl a. According to the Jaccard similarity index (S J), the greatest similarity among dominant species occurred between creeks and the eastern part of the lake. The annual average Shannon-Wiener diversity index H′, Margalef richness index D and Pielou evenness index J were 1.96 ± 0.34, 1.61 ± 0.50 and 0.77 ± 0.10, respectively. In all four areas of Yangcheng Lake, β-mesosaprobic species comprised the largest share of pollution indicator species. These data suggest that Yangcheng Lake is mesosaprobic.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arora H C. 1966. Rotifera as indicators of trophic nature of environments. Hydrobiologia, 27: 146–158.
Arora J, Mehra N K. 2003. Seasonal dynamics of rotifers in relation to physical and chemical conditions of the river Yamuna (Delhi), India. Hydrobiologia, 491: 101–109.
Arora J, Mehra N K. 2009. Seasonal dynamics of zooplankton in a shallow eutrophic, man-made hyposaline lake in Delhi (India): role of environmental factors. Hydrobiologia, 626: 27–40.
Beaver J, Havens K. 1996. Seasonal and spatial variation in zooplankton community structure and their relation to possible controlling variables in Lake Okeechobee. Freshwater Biology, 36(1): 45–56.
Bērzinš B, Pejler B. 1989b. Rotifer occurrence in relation to temperature. Hydrobiologia, 15: 223–231.
Bērzinš B. 1949. Zur Limnologie der Seen Südostlettlands. Schweiz. Z. Hydrol., 11: 583–607.
Castro B B, Antunes C S, Pereira R. 2005. Rotifer community structure in three shallow lakes: seasonal fluctuations and explanatory factors. Hydrobiologia, 543: 221–232.
Chen L J, Gu J, Peng Z R. 2008. The community structure of rotifer and ecological assessment of water quality of Lake Gehu. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 43(3): 7–16. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen L J, Gu J, Peng Z R. 2009. Community structure of rotifer in Mingzhu Lake of Chongming Island, Shanghai. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 20(12): 3 061. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Christofferson K, Riemann B, Klysner A. 1993. Potential role of fish predation and natural populations of zooplankton in structuring a plankton community in eutrophic lake water. Limnology and Oceanography, 38(3): 561–573.
Devetter M, Sed’a J. 2003. Rotifer fecundity in relation to components of a microbial food web in eutrophic reservoir. Hydrobiologia, 504: 167–175.
Dumont J H. 2007. Rotifers, the jelly plankton of freshwater. Hydrobiologia, 593: 59–66.
Galkovskaja G A. 1987. Planktonic rotifers and temperature. Hydrobiologia, 147: 307–317.
Guo K, Zhao W, Yin Sh. 2010. Relationship between eutrophication status of the water body and rotifer community structure in Guangting Reservoir, Beijing. Journal of Lake Science, 22(2): 256–264. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hu J X, Wu Sh G, Chen J Sh. 2007. Effect of eutrophication on rotifers in Chaohu Lake. Environmental Science and Technology, 30(12): 16–18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Huang X F. 1999. Survey, Observation and Analysis of Lake Ecology. China Standards Press, Beijing, China. p.72–79. (in Chinese)
Jeppesen E, Jensen P J, Sondergaard M, Lauridsen T. 1999. Trophic dynamics in turbid and clearwater lakes with special emphasis on the role of zooplankton for water clarity. Hydrobiologia, 408/409: 217–231.
Jin X C. 1990. Investigation of Lake Eutrophication. Chine Environmental Science Press, Beijing, China. p.282–283. (in Chinese)
Koste W. 1978. Rotatoria (Monogononta II. Tafelband). Gebruder Borntraeger, Berlin, Stuttgart, Germany. p.1–234.
Krebs C J. 1972. Ecology: The Experimental Analysis of Distribution and Abundance. Harper & Row, Publishers, New York. p. 455–457.
Li G G, Yu Z M. 2003. Community structure of rotifera and ecological assessment of water quality in Qiandao Lake. Journal of Lake Sciences, 15(2): 169–178. (in Chinese with English abstract)
May L. 1983. Rotifer occurrence in relation to water temperature in Leven, Scotland. Hydrobiologia, 104: 311–315.
May L, O’Hare M. 2005. Changes in rotifer species composition and abundance along a trophic gradient in Loch Lomond, Scotland, UK. Hydrobiologia, 546: 397–404.
Pace M L. 1986. An empirical analysis of zooplankton community size structure across lake trophic gradients. Limnology and Oceanography, 31(1): 45–55.
Pejler B. 1995. Relation to habitat in rotifers. Hydrobiologia, 313/314: 267–278.
Qian F P, Xi Y L, Wen X L. 2007. Eutrophication impact on community structure and species diversity of rotifers in five lakes of Anhui. Biodiversity Science, 15(4): 344–355. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Scheffer M. 1999. The effect of aquatic vegetation on turbidity: how important are the filter feeders. Hydrobiologia, 408/409: 307–316.
Segers H. 2006. Rotifera: Biology, Ecology and Systematic. Backbuys, Netherlands. 42p.
Segers H. 2007. Annotated checklist of the rotifers (Phylum Rotifera), with notes on nomenclature, taxonomy and distribution. Zootaxa, 1 564: 3–104.
Segers H. 2008. Global diversity of rotifers (Rotifera) in freshwater. Hydrobiologia, 595: 49–59.
Sellami I, Hamza A, Mhamdi M A. 2009. Abundance and biomass of rotifers in relation to the environmental factors in geothermal waters in Southern Tunisia. Journal of Thermal Biology, 34: 267–275.
Sládecek V. 1983. Rotifers as indicators of water quality. Hydrobiologia, 100: 169–201.
Temerova T A, Tolomeyev A P, Degermendzhy A G. 2002. Growth of dominant zooplankton species feeding on plankton microflora in Lake Shira. Aquatic Ecology, 36: 235–243.
ter Braak C J C. 1986. Canonical correspondence analysis: a new eigenvector technique for multivariate direct gradient analysis. Ecology, 67: 1 167–1 179, doi:10.2307/1938672.
Walz N, Elster H J, Mezger M. 1987. The development of the rotifer community structure in Lake Constance during its eutrophication. Hydrobiologia, 4: 452–487.
Wang L Q, Chen J L, Zheng X Y. 2008. Diversity and seasonal dynamics of rotifer in Dianshan Lake. Journal of Fisheries of China, 32(6): 906–913. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang X H, Wang T, Lin Q Q. 2009. Species composition and quantitative dynamics of rotifers in a pumped storage, eutrophic reservoir in South China. Journal of Lake Science, 21(1): 101–109. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wen X L, Xi Y L, Zhang L. 2006. Analysis of community structure of rotifer and ecological assessment of water quality in Lake Jinghu, Wuhu city. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 30(2): 152–157. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wen X L, Xi Y L, Qian F P. 2011. Comparative analysis of rotifer community structure in five subtropical shallow lakes in East China: role of physical and chemical conditions. Hydrobiologia, 661: 303–316.
Xie G L, Fu R SH, Liu J L. 2004. The community distribution of soil oribatida in Heze Peony Garden. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 24(4): 693–699. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xiong J L, Mei X G, Hu Ch L. 2003. Relationship between the trophication classification and the community structure of rotifers in four lakes. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 38(6): 8–13. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang G J, Pan H J, Liu Zh W. 2007. Comparative study on seasonal variations in rotifers of the waters with different trophic states in Lake Taihu. Journal of Lake Science, 19(6): 652–657. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang G J, Qin B Q, Gao G. 2008. Comparative study on seasonal variations of community structure of rotifer in different lake areas in Lake Taihu. Environmental Science, 29(10): 2 963–2 969. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang G J, Zhong Ch N. 2009. Comparative studies on seasonal variations of metazooplankton in waters with different eutrophic states in Lake Taihu. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 150: 445–453.
Yoshida T, Urabe J, Elser J J. 2003. Assessment of ‘topdown’ and ‘bottom-up’ forces as determinants of rotifer distribution among lakes in Ontario, Canada. Ecological Research, 18: 639–650.
Zhang Z S, Huang X F. 1991. Research Methods of Freshwater Plankton. Science Press, Beijing, China. p.257–258. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Scientific Special Fund of Commonweal Industry (Agriculture) of Finance Ministry (No. ayhyzx07-045), the Key Discipline Projects of Shanghai (No. S30701), and the Doctor Startup Projects of Shanghai Ocean University
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Liu, Q., Peng, Z. et al. Rotifer community structure and assessment of water quality in Yangcheng Lake. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 30, 47–58 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-012-0150-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-012-0150-y