Abstract
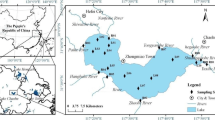
This study was conducted to evaluate the distribution characteristics of phosphorus and its species in 14 sediments samples collected from Lake Hongfeng based on sequential extraction. Lake Hongfeng, a major drinking-water source for Guiyang City in southwestern China, is one of the largest artificial reservoirs located in a typical karstic area of the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau. The results of this study indicate that the average percentages of DP, Al-P, Fe-P, Ca-P and OP in the lake sediments were 0.52, 6.59, 6.09, 42.85 and 40.27, respectively. The concentrations of organic phosphorus (OP) were lower than those of inorganic phosphorus (IP), which consisted mainly of calcium-bound phosphorus (Ca-P). The high concentrations of Ca-P may temporarily control the release of phosphorus from the sediments because it is a relatively stable, inert, and non-bioavailable phosphorus fraction. However, a large number of phosphate solubilizing bacteria can transform insoluble phosphate into bioavailable forms. Moreover, the concentrations of total phosphorus (TP) in the lake sediments were high; thus, the potential for the release of phosphorus from the sediments to the water column and phosphorus bioavailability were still significant. Further statistical analyses of the results revealed significant correlations between phosphorus species in sediments from the lake with two extractable principal component species (PCs) and five selectable cluster levels allowing interpretation of possible origins of phosphorus loading and the release of phosphorus. Furthermore, available remediation measures were briefly assessed for the lake with consideration of its distinctive environmental features.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ádám K, Krogstad T, Suliman F R D, Jenssen P D. 2005. Phosphorous sorption by filtralite P-small scale box experiment. J. Environ. Sci. Health, 40: 1 239–1 250.
An K G, Park S S. 2002. In situ experimental evidence of phosphorus limitation on algal growth in a lake ecosystem. J. Environ. Sci. Health, A37(5): 913–924.
Beauchemin S, Hesterberg D, Chou J, Beauchemin M, Simard R R, Sayers D E. 2003. Speciation of phosphorus in phosphorus-enriched agricultural soils using x-ray absorption near-edge structure spectroscopy and chemical fractionation. J. Environ. Qual., 32: 1 809–1 819.
Chinault S L, O’Connor G A. 2008. Phosphorus release from a biosolids-amended sandy spodosol. J. Environ. Qual., 37: 937–943.
Conley D J, Paerl H W, Howarth R W, Boesch D F, Seitzinger S P, Havens K E, Lancelot C, Likens G E. 2009. Controlling eutrophication: nitrogen and phosphorus. Science, 323: 1 014–1 015.
Deng J J, Huang X F, Hu J W, Li C X, Yi Y, Long J. 2009. Distribution of several microorganisms and activity of alkaline phosphatase in sediments from Baihua Lake. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng., 4: 711–716.
Fisher M M, Reddy K R. 2001. Phosphorus flux from wetland soils affected by long-term nutrient loading. J. Environ. Qual., 30: 261–271.
Haggard B E, Moore P A Jr, DeLaune P B. 2005. Phosphorus flux from bottom sediments in Lake Eucha, Oklahoma. J. Environ. Qual., 34: 724–728.
He T R, Feng X B, Li Z G, Qiu G L, Bai W Y, Liang L, Lu J L. 2006. Buildup of methyl mercury in a seasonal anoxic reservoir and impact on downstream. J. Lake Sci., 18(6): 565–571. (in Chinese)
Huang Q H, Wang D H, Wang C X, Ma M, Wang Z J. 2003. Relation between phosphorus forms in the sediments and lake eutrophication. China Environmental Science, 23(6): 583–586. (in Chinese)
Huang Q H, Wang Z J, Wang D H, Wang C X, Ma M, Jin X C. 2005. Origins and mobility of phosphorus forms in the sediments of Lakes Taihu and Chaohu, China. J. Environ. Sci. Health, A40: 91–102.
Huang X F, Hu J W, Li C X, Deng J J, Long J, Qin F X. 2009. Heavy metals pollution and potential ecological risk assessment of sediments from Baihua Lake, Guizhou, P.R. China. International Journal of Environmental Health Research, 19: 405–419.
Jiang C H, Deng J J, Hu J W, Huang X F, Li C X. 2008. Phosphorus speciation in sediments from Baihua and Aha Lakes. In: Qian X H, Qu J P eds. Abstracts of the 12th Asian Pacific Confederation of Chemical Engineering Congress (ISBN 978-7-5611-4285-1). Dalian University of Technology Press, Dalian, China. Vol. 2, 30p.
Jin X C, Tu Q Y. 1990. Criterion for Investigation of Eutrophication of Lakes. Chinese Environmental Science Press, Beijing, China. p. 218–229. (in Chinese)
Kinaci C, Inanc B, Aydin A F, Yuksel E, Sevimli M F, Arikan O, Topacik D. 2004. Quality of the bottom sediment prior to dredging in the Golden Horn of Istanbul. J. Environ. Sci. Health, A39(2): 365–374.
Kotut K, Ballot A, Krienitz L. 2006. Toxic cyanobacteria and their toxins in standing waters of Kenya: implications for water resource use. J. Wat. Health, 4(2): 233–245.
Kruopiene J. 2007. Distribution of heavy metals in sediments of the Nemunas River (Lithuania). Polish J. of Environ. Stud., 16(5): 715–722.
Lee G, Faure G, Bigham J M, Williams D J. 2008. Metal release from bottom sediments of Ocoee Lake No. 3, a primary catchment area for the Ducktown Mining district. J. Environ. Qual., 37: 344–352.
Liu A J, Kong F X, Wang D. 2006. Water quality risk assessment for sediment dredging operations, Wulihu in Taihu Lake. Environmental Science, 27(10): 1 946–1 952. (in Chinese)
Liu F, Qin F X, Hu J W, Huang X F, Jiang C H, Li C X. 2009. Acid volatile sulfide and bioavailability of heavy metals in sediments from Hongfeng Lake. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 29(10): 2 215–2 223.
Li X G, Song J M, Yuan H M, Dai J C, Li N. 2007. Biogeochemical characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus in Jiaozhou Bay sediments. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol., 25(2): 157–165.
Milenkovic N, Damjanovic M, Ristic M. 2005. Study of heavy metal pollution in sediments from the iron gate (Danube River), Serbia and Montenegro. Polish J. Environ. Studies, 14: 781–787.
Moosmann L, Gächter R, Müller B, Wüest A. 2006. Is phosphorus retention in autochthonous lake sediments controlled by oxygen or phosphorus? Limnol. Oceanogr., 51(1, part 2): 763–771.
Nathalie K, Dupouyet S, Bonin G. 2002. Environmental risks of applying sewage sludge compost to vineyards: carbon, heavy metals, nitrogen, and phosphorus accumulation. J. Environ. Qual., 31(5): 1 522–1 527.
Paerl H W, Valdes L M, Joyner A R, Piehler M F. 2004. Solving problems resulting from solutions: evolution of a dual nutrient management strategy for the eutrophying Neuse River Estuary, North Carolina. Environ. Sci. Technol., 38(11): 3 068–3 073.
Pardo P, López-Sánchez J F, Rauret G. 2003. Relationships between phosphorus fractionation and major components in sediments using the SMT harmonized extraction procedure. Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 376: 248–254.
Penn C J, Bryant R B. 2008. Phosphorus solubility in response to acidification of dairy manure amended soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J., 72: 238–243.
Ruban V, López-Sánchez J F, Pardo P, Rauret G, Muntau H, Quevauviller Ph. 2001. Harmonized protocol and certified reference material for the determination of extractable contents of phosphorus in freshwater sediments-a synthesis of recent works. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem., 370: 224–228.
Song J M, Luo Y X, Lv X X, Li P C. 2003. Forms of phosphorus and silicon in the natural grain size surface sediments of the southern Bohai Sea. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol., 21(3): 286–292.
Spivakov B YA, Maryutina T A, Muntau H. 1999. Phosphorus speciation in water and sediments. Pure Appl. Chem., 71: 2161–2176.
Surridge B W J, Heathwaite A L, Baird A J. 2007. The release of phosphorus to porewater and surface water from river riparian sediments. J. Environ. Qual., 36: 1 534–1 544.
Su Y P, Zheng D X, Zhuang Y T, Li G., Lin W Z, Xue L Q. 2005. Phosphorus fractionations in sediments from eutrophicated lakes in Fujian Province. Journal of Agro-Environmental Science, 24(2): 362–365. (in Chinese)
Wan G J. 2009. Environmental process of the deep-water lakes and approach to the protection of water resources on the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau. Engineering Sciences, 11(5): 60–71. (in Chinese)
Wang Y C, Wan G J, Wang S L, Li S H, Huang R G. 2000. Forms of phosphorus in sediments of Lake Baihua and Lake Hongfeng, Guizhou. Acta Mineralogica Sinica., 20(3): 273–278. (in Chinese)
Wang Y C, Ma M, Wan G J, Liu C Q, Yin C Q. 2004. The phosphorus forms and depositional history in sediments of Lake Hongfeng, Guizhou Province. J. Lake Sci., 16(1): 21–27. (in Chinese)
Xiao H Y, Liu C Q, Wang S L, Li S L. 2003. Organic degradation by nitrification and denitrification before diagenesis in the Hongfeng Lake, SW China. Geochimica., 32(4): 375–381. (in Chinese)
Yu H Q, Fang T, Xia S B, Ao H Y. 2007. Seasonal and vertical distribution of nitrogen and phosphorus in the sediment under different ecological restoration measures in the West Lake Wuli, Lake Taihu. J. Lake Sci., 19(6): 683–689. (in Chinese)
Zhang W. 1999. Eutrophication and Environmental Characteristic about Lakes Hongfeng and Baihua. Guiyang Science and Technology Press, Guiyang, China. P. 5–23. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 20967003)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, C., Hu, J., Huang, X. et al. Phosphorus speciation in sediments of Lake Hongfeng, China. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 29, 53–62 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-011-9047-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-011-9047-4