Abstract
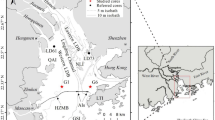
With available survey data and 237 surface sediment samples, the modern sedimentation in Qingdao bays is studied. The research result shows that the east area is shallower (16.4 m) than that in the west (45.8 m). The geography was formed by a symmetric wave in a sequence of bank — offshore depression — platform — tidal channel — platform — offshore depression — foreshore from south to north. Flood sedimentary systems were formed from inlet of the Jiaozhou Bay in the west to the barrier bar in the east. Lateral sedimentation includes mainly tidal current ridges in two tidal channels. Gravel sandy sediments formed by wave lie in midland of from seashore to wave base. Dynamic functions are mainly tide and wave. Tidal current moves sediment in vertical and horizontal directions, sorting sediments and providing materials for coastwise beaches. The sources of sediment are mainly from eroded headland rocks. In general, grain sizes in this area from the inlet of the Jiaozhou Bay in the west (120°17′) to the barrier bar outside in the east (120°35′) are coarse-fine-coarse, forming gravel-gravelly sand (G-S), sand (S), gravel clay silt (G-YT), clay silt (YT), gravelly silty sand (G-TS), silty sand (TS), gravelly sandy silt (G-ST), and sandy silt (ST) in turn.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Z X, Dong H P, Zhao D Z. et al. 2006. Movements of sediments in the Qingdao City Coast. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 26(5): 45–53. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Fitygerald D M, Nummedal D. 1983. Response characteristics of an ebb-dominated tidal inlet channel. J. Sed. Petrol., 53: 833–845.
Folk R M, Ward W C. 1957. Brazos river bar: A study in significance of grain size parameters. J. Sed. Petrol., 27(1) 3–26.
Hayes, M O. 1980. General morphology and sediment patter in tidal inlet. Sed. Geol., 23: 139–156.
Friedman G M, Sanders J E. 1978. Principles of Sedimentology. New York, John Wiley and Sons, p. 498–531.
Liu Z X, Xia D X. 2004. Tidal Sediments in China Offshore Areas. China Ocean Press, 65–66, Beijing. (in Chinese)
Moslow T F. 1985. Recognition and characteristics of Holocene tidal inlet sequences. Marine Geology, 63: 129–151.
Wang Y P, Gao S, Jia J J. 2000. Distribution and movement of sediments on the Jiaozhou Bay and the adjacent area. Acta Geographica Sinica, 55(4): 449–457. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang Y P, Gao S. 1999. A preliminary study on suspended sediment concentration measurements using an ADCP mounted on a moving vessel. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 30(6): 758–763. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang Y P, Gao S, Jia J J. 2000. Sediment distribution and transport patter in Jiaozhou Bay an adjoining areas. ACTA Geographical Sinica, 55(4): 449–457. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang Y P, Gao S. 2001. Studies on sediment dynamics and related research fields of Jiaozhou Bay: a review. Marine Sciences, 25(2): 26–28. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xia D X, Liu Z X. 1984. Formation mechanism and developmental conditions of tidal ridges. ACTA Oceanologyca Sinica, 6(3): 361–367. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yu H J, Xu X Y, Li P et al. 2003. Environments for beaches and seafloor sediments of Fushan, Huiquan and Laoshan Bays in Qingdao, Coastal Engineering, 22(3): 12–18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang M H. 2000. Distributions and seasonal variation of suspended matter in Jiaozhou Bay seawater. Studies Marine Sinica, 42: 49–54. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao L, Wei H, Zhao J Z. 2002. Numerical study on water exchange in Jiaozhou Bay. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 33(1): 23–28. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Scientific Foundation of China (No. 40506013).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Huang, P., Huang, H. et al. Characteristics of modern sedimentation in Qingdao bays. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 27, 683–696 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-009-9124-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-009-9124-0