Abstract
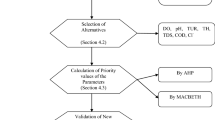
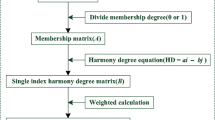
The relative importance of each pollution factor in analytical hierarchy process (AHP) method comes from pooling expert opinions in general. Because expert opinions are based on information and judgment criteria, determining their weight may lead to uncertainty — Therefore, an improved AHP method had been developed. The process of the improved AHP method involved four key procedures. The weights of pollution factors were completely related to the objective monitoring data through the standardization of these procedures. The environmental comprehensive quality of water and sediment of Xuanwu Lake, Nanjing, China had been evaluated. The environmental quality comprehensive indices (EQCI) of the water in 1991–1995 and 1996–2000 were 3.32 and 1.85, respectively, indicating that the water quality improved. The EQCI of the sediment in 1995 and 2000 indicates that the sediment contamination decreased from 1995 to 2000. Such results agreed with the fact that the lake had been under comprehensive control. However, with the classical AHP method, the EQCI of the sediment in the northwestern part of the lake may have indicated that sediment contamination increased from 1995 to 2000. The discrepancy may have resulted from the judgment difference of the experts. The improved AHP method can avoid arbitrariness of subjective judgment and can reflect the real influential factors of environment pollution in different periods or regions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jonathan G. T. and D. R. Stephen, 2003. Use of the Delphi method resolving complex water resources issues. Journal of the American Water Resources Association. 39(1): 183–789.
Miller, A., 1984. Professional collaboration in environmental management: the effectiveness of expert groups. Journal of Environmental Management. 19: 365–388.
Miller, A. and W. Cuff, 1986. The Delphi approach to the mediation of environmental disputes. Environmental Management 19: 321–330.
Saaty, T. L., 1980. The analytical Hierarchy Process. McGraw Hill, New York.
Silvia, F. and A. W. Daniel, 2000. Use of water quality indices to verify the impact of Cordoba City (Argentina) on Suquia River. Water Resource 34(11): 2 915–2 926.
State General Administration of the People’s Republic of China for Quality Supervision and Inspection and Quarantine, State Environmental Protection Administration of China, 2002. State standard of People’s Republic of China: Environmental quality standard for surface water (GB3838-2002). Standards Press of China, Beijing, China. 1–10. (in Chinese)
Villa, F., M. Geroni and A. Mazza, 1996. A GIS-based method for multi-objective evaluation of Park vegetation. Landscape and Urban Planning 35: 230–212.
Xia, Z. L., S. Z. Li, T. F. Li and Y. Ba, 1987. Background value of soil elements and methods of investigation. China Meteorological Press. Beijing, China. 295. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation: National Natural Science Foundation of China, No.40771186.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Zhang, H., Gao, X. et al. Improved AHP method and its application in lake environmental comprehensive quality evaluation—a case study of Xuanwu Lake, Nanjing, China. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 25, 427–433 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-007-0427-8
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-007-0427-8