Abstract
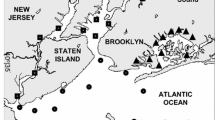
In-situ data from cruises in the Pearl River estuary and adjacent marine areas were collected during March to May 2001. The absorption coefficients of the water color components were studied in detail containing total suspended matter (TSM), chlorophyll-a (chl-a), colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM), and de-pigment particles. For absorption coefficient of TSM, ap, and that of de-pigment particles, ad, correlations of ap(440)-TSM, ad(440)-TSM, ap(440)-chl-a and ad-chl-a were done (the italicized term means the concentration). There was a good correlation between ap(440) and chl-a concentration. An empirical relationship model between aph(675) and chl-a was developed showing a strong correlation of 0.93. Based on the two models the chl-a and aph(λ) were correlated. The values of calculated empirical spectral slope for CDOM absorption coefficients and that of de-pigment particles, 0.017 0 and 0.011 6 respectively, both are within a relative standard error of 10.0%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, Y. H., J. E. Moon and S. Gallegos, 2001. Development of suspended particulate matter algorithms for ocean color remote sensing. Korean Journal of Remote Sensing 17(4): 285–295.
Boynton, G. C. and H. R. Gordon, 2002. Irradiance inversion algorithm for absorption and backscattering profiles in natural waters: improvement for clear waters. Applied Optics 41(12): 2 224–2 227.
Bricaud, A., A. Morel, M. Babin, K. Allali and H. Claustre, 1998. Variations of light absorption by suspended particles with chlorophyll-a concentration in oceanic (case 1) waters: Analysis and implications for bio-optical models. J. Geophys. Res. 103(C13): 31 033–31 044.
Cao, W. X., Y. Z. Yang, X. Q. Xu, L. M. Huang and J. L. Zhang, 2003. Absorption spectrums of suspended particles and regional model in Pearl River estuary. Chinese Science Bulletin 48(17): 1 876–1 882.
Cao, W. X., Y. Z. Yang, S. Liu et al., 2005. Absorption coefficients of phytoplankton in relation to chlorophyll and remote sensing reflectance in the coastal waters of Southern China. Progress in Natural Science 15(4): 342–350.
Carder, K. L., F. R. Chen, Z. P. Lee et al., 1999. Semianalytic moderate resolution imaging spectrometer algorithms for chlorophyll a and absorption with bio-optical domains based on nitrate-depletion temperatures. J. Geophys. Res. 104(C3): 5 403–5 421.
Chen, C. Q., Y. Li and J. M. Pan, 2004. Distributions of colored dissolved organic matter and dissolved organic carbon in the Pearl River estuary, China. Continental Shelf Res. 24: 1 845–1 865.
Gallegos, C. L. and P. J. Neale, 2002. Partitioning spectral absorption in case 2 waters: discrimination of dissolved and particulate components. Applied Optics 41(21): 4 220–4 233.
Gordon, H. R. and A. Y. Morel, 1983. Remote assessment of ocean color for interpretation of satellite visible imagery. A Review (Springer-Verlag, New York, 1983).
Hakim, A. H. and N. J. McCormick, 2003. Ocean opties estimation for absorption, backscattering, and phase function parameters. Applied Optics 42(6): 931–938.
Hong, H. S., J. Y. Wu and S. L. Shang, 2005. Absorpion and fluorescence of Chromophoric dissolved organic matter in the Pearl River estuary, South China. Marine Chemistry 97: 78–89.
Hooker, S. B., G. Zibordi, J. F. Berthon et al., 2003. NASA SeaWiFS Postlauch Technical Report Series. 23: Tower-Perturbation Measurements in Above-Water Radiometry. NASA Tech. Memo. 2003/206892, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland, 20771.
Leathers, R. A., C. S. Roesler and N. J. McCormick, 1999. Ocean inherent optical property determination from in-water light field measurements. Applied Optics 38(24): 5 096–5 103.
Lee, Z. P., K. L. Carder, C. D. Mobley et al., 1998. Hyperspectral remote sensing for shallow waters, 1 A Semianalytical model. Applied Optics 37: 6 329–6 338.
Lee, Z. P., K. L. Carder and R. A. Arnone, 2002. Deriving inherent optical properties from water color: a multiband quasi-analytical algorithm for optically deep waters. Applied Optics 41(27): 5 755–5 772.
Morel, A. and L. Prieur, 1977. Analysis of variations in ocean color. Limnol. Oceanogr. 22: 709–22.
Qian, H., and S. Liang, 1999. Study on the red tide in the Pearl River estuary and its near waters. Mar. Environ. 18: 69–74. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Sathyendranath, S., 2003. Remote sensing of ocean color in coastal and other optically-complex waters[EB/OL]. IOCCG Project Office. http://www.ioccg.org .
Tassan, S., 1994. Local algorithms using SeaWiFS data for the retrieval of phytoplankton, pigments,suspended sediment, and yellow substance in coastal waters. Applied Optics 33(12): 2 369–2 378.
Wang, G. F., W. X. Cao, D. Z. Xu, S. Liu and J. L. Zhang, 2005. Variations in specific absorption coefficients of phytoplankton in northern South China Sea. Journal of Tropical Oceanonography 24(5): 1–9.
Zhou, H. L. and J. H. Zhu, 2005. The analysis of water color element absorb spectral characteristic in Qinghai Lake. Ocean Technology 24(2): 55–58.
Zhu, J. H. and T. J. Li, 2004a. Relationship research of phytoplankton pigments absorption and chlorophyll a concentration in the East China Sea and Yellow Sea. Ocean Technology 23(4): 117–122.
Zhu, J. H. and T. J. Li, 2004b. Spectral mode research about absorption coefficient of the de-pigment particles and yellow substance in Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Ocean Technology 23(2): 7–13.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National 973 Project (No. 2001CB409708).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xi, H., Qiu, Z., He, Y. et al. The absorption of water color components and spectral modes in the Pearl River estuary. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 25, 359–366 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-007-0359-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-007-0359-3