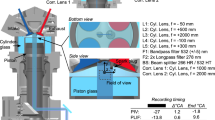
Abstract.
Spatially and spectrally resolved in-cylinder absorption measurements were performed in spark-ignited internal combustion engines and in Diesel engines. With UV-broadband illumination it was shown that the UV attenuation occurs throughout the burned gas area with roughly homogeneous absorption cross-sections. Model calculations based on the absorption properties of CO2 at elevated temperatures show that this species gives the main contribution to in-cylinder UV absorption.
A previously suggested technique of assessing UV absorption using O2 laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) as probe light is successfully applied to in-cylinder measurements of the light absorption inside a fired heavy-duty Diesel engine. Even in this environment, the comparison with model calculations shows that CO2 is the main contributor to UV light absorption. Since the O2-LIF absorption technique is based on the identical geometry used for LIF concentration measurements, the results can directly be used for correcting LIF signal data such as that obtained from NO imaging.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 20 April 2001 / Published online: 18 July 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hildenbrand, F., Schulz, C. Measurements and simulation of in-cylinder UV-absorption in spark ignition and Diesel engines . Appl Phys B 73, 173–180 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003400100620
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003400100620