Abstract
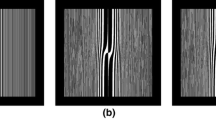
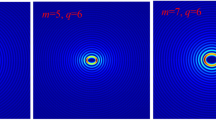
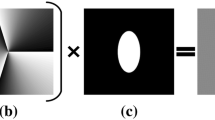
An elliptic spiral forked plate (ESFP) is proposed to generate two off-axis elliptic optical vortices, whose topological charges are identified by the numbers of lines in the vortices. Moreover, the number of lines minus one is equal to the absolute value of the topological charge. a and c are the vertical ellipticity factors, which adjust the lengths of the vertical axes for the elliptical vortices generated by φ and ϕ, respectively. b and d are the horizontal ellipticity factors, which adjust the lengths of the horizontal axes for the elliptical vortices generated by φ and ϕ, respectively. φ and ϕ present the elliptic spiral phase plates for the elliptic forked grating and elliptic spiral zone plate, respectively. When ellipticity factors (a, b, c, d) satisfy a = c = 1 and b = d = 0.5, the topological charge identification is the most obvious. At this time, the elliptic vortices are vertical. On the contrary, i.e., a = c = 0.5 and b = d = 1, the elliptic vortices are horizontal. The elliptical vortex can rotate by adjusting the horizontal modulation parameter g. For the vertical and horizontal elliptical vortices, the slopes of the long axes are equal to − 1/g and g, respectively. The ESFP consists of the elliptic forked grating and elliptic spiral zone plate with the topological charges l1 and l2 respectively. The left and right elliptic vortices have the topological charges of l2 – l1 and l2 + l1, respectively. The method of constructing the ESFP is illustrated. It is proved in the simulations and experiments that the topological charges of the two elliptic vortices can be identified by the numbers of the lines. The proposed zone plate is used for optical trapping, optical communication and optical imaging.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
X.H. Zhang, T. Xia, S.B. Cheng, S.H. Tao, Free-space information transfer using the elliptic vortex beam with fractional topological charge. Opt. Commun. 431, 238–244 (2019)
Z. Ji, H. Zang, C. Fan, J. Wang, C. Zheng, L. Wei, C. Wang, L. Cao, Fractal spiral zone plates. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 35, 726–731 (2018)
J. Pu, P.H. Jones, Devil’s lens optical tweezers. Opt. Express 23, 8190–8199 (2015)
N.R. Heckenberg, R. McDuff, C.P. Smith, H. Rubinsztein-Dunlop, M.J. Wegener, Laser beams with phase singularities. Opt. Quant. Electron. 24, S951–S962 (1992)
V. Lerner, D. Shwa, Y. Drori, N. Katz, Shaping Laguerre-Gaussian laser modes with binary gratings using a digital micromirror device. Opt. Lett. 37, 4826–4828 (2012)
T. Lei, M. Zhang, Y. Li, P. Jia, G.N. Liu, X. Xu, Z. Li, C. Min, J. Lin, C. Yu, H. Niu, X. Yuan, Massive individual orbital angular momentum channels for multiplexing enabled by Dammann gratings. Light: Sci. Appl. 4, e257 (2015)
N.L. Kazanskiy, S.N. Khonina, S.V. Karpeev, A.P. Porfirev, Diffractive optical elements for multiplexing structured laser beams. Quantum Electron. 50, 629–635 (2020)
I. Moreno, J.A. Davis, B.M.L. Pascoguin, M.J. Mitry, D.M. Cottrell, Vortex sensing diffraction gratings. Opt. Lett. 34, 2927–2929 (2009)
N. Zhang, J.A. Davis, I. Moreno, J. Lin, K.-J. Moh, D.M. Cottrell, X. Yuan, Analysis of fractional vortex beams using a vortex grating spectrum analyzer. Appl. Opt. 49, 2456–2462 (2010)
S.N. Khonina, A.V. Ustinov, Binary multi-order diffraction optical elements with variable fill factor for the formation and detection of optical vortices of arbitrary order. Appl. Opt. 58, 8227–8236 (2019)
L. Rayleigh, Laboratory notebook entry of April 11, 1871, “Quoted in RW Wood, ” physical optics. Macmillan, New York 37, 38 (1934)
R.W. Wood, LIII. Phase-reversal zone-plates, and diffraction-telescopes. Lond. Edinburgh Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 45, 511–522 (1898)
C. Allain, M. Cloitre, Spatial spectrum of a general family of self-similar arrays. Phys. Rev. A 36, 5751–5757 (1987)
S.N. Khonina, S.G. Volotovskiy, Fractal cylindrical fracxicon. Opt. Memory Neural Netw. 27, 1–9 (2018)
S.N. Khonina, A.V. Ustinov, R.V. Skidanov, A.P. Porfirev, Local foci of a parabolic binary diffraction lens. Appl. Opt. 54, 5680–5685 (2015)
N.R. Heckenberg, R. Mcduff, C.P. Smith, A.G. White, Generation of optical phase singularities by computer-generated holograms. Opt. Lett. 17, 221 (1992)
Z. Jaroszewicz, A. Kolodziejczyk, D. Mouriz, C. Gomez-Reino, Spiral zone plates with arbitrary diameter of the dark spot in the centre of their focal point. Opt. Commun. 114, 1–8 (1995)
L. Wei, Y. Gao, X. Wen, Z. Zhao, L. Cao, Y. Gu, Fractional spiral zone plates. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 30, 233–237 (2013)
T. Xia, S. Cheng, S. Tao, An annular beam with segmented phase gradients generated by a modified spiral zone plate. J. Opt. 21, 115602 (2019)
A. Sabatyan, Z. Behjat, Radial phase modulated spiral zone plate for generation and manipulation of optical perfect vortex. Opt. Quant. Electron. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-017-1211-4
S.H. Tao, X.C. Yuan, J. Lin, R.E. Burge, Sequence of focused optical vortices generated by a spiral fractal zone plate. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 416–458 (2006)
A. Calatayud, V. Ferrando, L. Remón, W.D. Furlan, J.A. Monsoriu, Twin axial vortices generated by Fibonacci lenses. Opt. Express 21, 10234–10239 (2013)
T. Xia, S. Cheng, S. Tao, Two pairs of twin foci with the golden mean generated by a modified Fibonacci zone plate. J. Opt. 21, 035602 (2019)
V.V. Kotlyar, A.A. Kovalev, A.P. Porfirev, Elliptic Gaussian optical vortices. Phys. Rev. A 95, 8 (2017)
V.V. Kotlyar, A.A. Kovalev, A.P. Porfirev, Elliptic perfect optical vortices. Optik 156, 49–59 (2018)
X.H. Liu, J.X. Pu, Investigation on the scintillation reduction of elliptical vortex beams propagating in atmospheric turbulence. Opt. Express 19, 26444–26450 (2011)
R. Chakraborty, A. Ghosh, Generation of an elliptic hollow beam using Mathieu and Bessel functions. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 23, 2278–2282 (2006)
G. Liang, W.J. Cheng, Q. Wang, Rotations of elliptic vortex beams in media with and without anisotropy. J. Opt. 21, 8 (2019)
Y.X. Liu, J.X. Pu, Measuring the orbital angular momentum of elliptical vortex beams by using a slit hexagon aperture. Opt. Commun. 284, 2424–2429 (2011)
Y. Liang, E. Wang, H. Li, C. Xie, Tailoring focused optical vortices by using spiral forked plates. Opt. Lett. 44, 935–938 (2019)
H. Ebrahimi, A. Sabatyan, Multi-region spiral photon sieve to produce tailorable multiple vortex. Opt. Laser Technol. 126, 106137 (2020)
P. García-Martínez, M.M. Sánchez-López, J.A. Davis et al., Generation of Bessel beam arrays through Dammann gratings[J]. Appl. Opt. 51(9), 1375–1381 (2012)
J. Zhou, W. Zhang, L. Chen, Experimental detection of high-order or fractional orbital angular momentum of light based on a robust mode converter[J]. Appl. Phys. Lett. 108(11), 111108 (2016)
Funding
The research was financially supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Central South University, China (Grant No. 2020zzts043), and the Central South University of College Students’ Innovation and Entrepreneurship Project (20210010020032, 20210010020015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest related to this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, T., Huang, X., Zhao, H. et al. Two off-axis elliptic optical vortices generated by an elliptic spiral forked plate. Appl. Phys. B 128, 176 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-022-07895-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-022-07895-8