Abstract
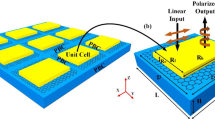
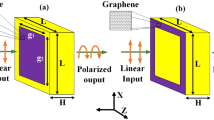
The mathematical and numerical analysis of the Graphene infrared tunable frequency selective surface (FSS) for far-infrared spectrum has been clarified. The proposed FSS shows different properties of transmittance, reflectance, polarization variation for the different range of fermi voltage which can be tuned by external biasing. Angular changes in the graphene plane demonstrate different frequency responses of reflected wave polarization. Proposed structures are also computed at normal as well as the complementary condition of the same design. The proposed structure also computed the variation in the many parameters with the rotation change of the frequency selective surface structure. It can observe more than 60% of the overall transmittance for the wide range of the frequency. The ultrathin and easy to fabricate structure opens up the door for various applications such as reflector, absorber, polarizer, a modulator for the THz regime.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The proposed work is numerically investigated by COMSOL simulation software.
References
S. Liu, T.J. Cui, Q. Xu, D. Bao, L. Du, X. Wan, W.X. Tang, C. Ouyang, X.Y. Zhou, H. Yuan, H.F. Ma, W.X. Jiang, J. Han, W. Zhang, Q. Cheng, Anisotropic coding metamaterials and their powerful manipulation of differently polarized terahertz waves. Light Sci. Appl. 5, e16076–e16076 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/lsa.2016.76
S.K. Patel, V. Sorathiya, S. Lavadiya, T.K. Nguyen, V. Dhasarathan, Polarization insensitive graphene-based tunable frequency selective surface for far-infrared frequency spectrum. Phys. E Low-Dimensional Syst. Nanostruct. 120, 114049 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2020.114049
S.K. Patel, V. Sorathiya, S. Lavadiya, Y. Luo, T.K. Nguyen, V. Dhasarathan, Numerical analysis of polarization-insensitive squared spiral-shaped graphene metasurface with negative refractive index. Appl. Phys. B Lasers Opt. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-020-07435-2
B. Wu, Y. Hu, Y.T. Zhao, W.B. Lu, W. Zhang, Large angle beam steering THz antenna using active frequency selective surface based on hybrid graphene-gold structure. Opt. Express. 26, 15353 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.26.015353
Y. Chen, J. Zhu, Y. Xie, N. Feng, Q.H. Liu, Smart inverse design of graphene-based photonic metamaterials by an adaptive artificial neural network. Nanoscale 11, 9749–9755 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c9nr01315f
H. Lu, D. Mao, C. Zeng, F. Xiao, D. Yang, T. Mei, J. Zhao, Plasmonic Fano spectral response from graphene metasurfaces in the MIR region. Opt. Mater. Express. 8, 1058 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1364/ome.8.001058
B. Wu, Y.J. Yang, H.L. Li, Y.T. Zhao, C. Fan, W.B. Lu, Low-loss dual-polarized frequency-selective rasorber with graphene-based planar resistor. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 68, 7439–7446 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TAP.2020.2998173
R. Mishra, R. Panwar, Investigation of graphene fractal frequency selective surface loaded terahertz absorber. Opt. Quantum Electron. 52, 1–13 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-020-02433-2
S.K. Patel, V. Sorathiya, T.K. Nguyen, V. Dhasarathan, Numerical investigation of tunable metasurface of graphene split-ring resonator for terahertz frequency with reflection controlling property. Phys. E Low-Dimensional Syst. Nanostruct. 118, 113910 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2019.113910
W.B. Lu, J.W. Wang, J. Zhang, Z.G. Liu, H. Chen, W.J. Song, Z.H. Jiang, Flexible and optically transparent microwave absorber with wide bandwidth based on graphene. Carbon N. Y. 152, 70–76 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.06.011
R. Yan, S. Arezoomandan, B. Sensale-Rodriguez, H.G. Xing, Exceptional terahertz wave modulation in graphene enhanced by frequency selective surfaces. ACS Photon. 3, 315–323 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsphotonics.5b00639
M. Qu, J. Song, L. Yao, S. Li, L. Deng, Y. Yang, Design of a graphene-based tunable frequency selective surface and its application for variable radiation pattern of a dipole at terahertz. Radio Sci. 53, 183–189 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/2017RS006401
C. Pei, L. Yang, G. Wang, Y. Wang, X. Jiang, Y. Hao, Y. Li, J. Yang, Broadband graphene/glass hybrid waveguide polarizer. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 27, 927–930 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/LPT.2015.2398452
J. Chen, N. Xu, A. Zhang, J. Guo, Using dispersion HIE-FDTD method to simulate the graphene-based polarizer. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 64, 3011–3017 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TAP.2016.2555325
R.E.P. De Oliveira, C.J.S. De Matos, Graphene based waveguide polarizers: in-depth physical analysis and relevant parameters. Sci. Rep. 5, 16949 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep16949
Y.V. Bludov, M.I. Vasilevskiy, N.M.R. Peres, Tunable graphene-based polarizer. J. Appl. Phys. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4759319
A.K. Geim, K.S. Novoselov, The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 6, 183–191 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1849
X. Li, L. Lin, L.S. Wu, W.Y. Yin, J.F. Mao, A bandpass graphene frequency selective surface with tunable polarization rotation for THz applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 65, 662–672 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TAP.2016.2633163
K. Sarabandi, N. Behdad, A frequency selective surface with miniaturized elements. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 55, 1239–1245 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/TAP.2007.895567
L. Martinez-Lopez, J. Rodriguez-Cuevas, J.I. Martinez-Lopez, A.E. Martynyuk, A multilayer circular polarizer based on bisected split-ring frequency selective surfaces. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 13, 153–156 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/LAWP.2014.2298393
M. Qu, M. Rao, S. Li, L. Deng, Tunable antenna radome based on graphene frequency selective surface. AIP Adv. 7, 095307 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5003020
V. Sorathiya, V. Dave, Numerical study of a high negative refractive index based tunable metamaterial structure by graphene split ring resonator for far infrared frequency. Opt. Commun. 456, 124581 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2019.124581
B. Li, Y.S. Zeng, B.J. Chen, C.H. Chan, Terahertz frequency-selective surface with polarization selection and conversion characteristics. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 9, 510–519 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TTHZ.2019.2928171
D.W. Wang, W.S. Zhao, H. Xie, J. Hu, L. Zhou, W. Chen, P. Gao, J. Ye, Y. Xu, H.S. Chen, E.P. Li, W.Y. Yin, Tunable THz multiband frequency-selective surface based on hybrid metal-graphene structures. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 16, 1132–1137 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNANO.2017.2749269
I. Epstein, D. Alcaraz, Z. Huang, V.V. Pusapati, J.P. Hugonin, A. Kumar, X.M. Deputy, T. Khodkov, T.G. Rappoport, J.Y. Hong, N.M.R. Peres, J. Kong, D.R. Smith, F.H.L. Koppens, Far-field excitation of single graphene plasmon cavities with ultracompressed mode volumes. Science 368, 1219–1223 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abb1570
S.K. Patel, V. Sorathiya, Z. Sbeah, S. Lavadiya, T.K. Nguyen, V. Dhasarathan, Graphene-based tunable infrared multi band absorber. Opt. Commun. 474, 126109 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2020.126109
J. Jiang, Q. Zhang, Q. Ma, S. Yan, F. Wu, X. He, Dynamically tunable electromagnetically induced reflection in terahertz complementary graphene metamaterials. Opt. Mater. Express. 5, 1962 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1364/ome.5.001962
S.K. Patel, V. Sorathiya, S. Lavadiya, L. Thomas, T.K. Nguyen, V. Dhasarathan, Multi-layered graphene silica-based tunable absorber for infrared wavelength based on circuit theory approach. Plasmonics 15, 1767–1779 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-020-01191-x
A. Pandya, V. Sorathiya, S. Lavadiya, Graphene-based nanophotonic devices, in Recent Advances in Nanophotonics—Fundamentals and Application. (IntechOpen, Rejika, 2020). https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.93853
E. Moreau, S. Godey, F.J. Ferrer, D. Vignaud, X. Wallart, J. Avila, M.C. Asensio, F. Bournel, J.J. Gallet, Graphene growth by molecular beam epitaxy on the carbon-face of SiC. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 241907 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3526720
K.S. Novoselov, D. Jiang, F. Schedin, T.J. Booth, V.V. Khotkevich, S.V. Morozov, A.K. Geim, Two-dimensional atomic crystals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 10451–10453 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0502848102
N. Petrone, C.R. Dean, I. Meric, A.M. Van Der Zande, P.Y. Huang, L. Wang, D. Muller, K.L. Shepard, J. Hone, Chemical vapor deposition-derived graphene with electrical performance of exfoliated graphene. Nano Lett. 12, 2751–2756 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl204481s
M.C. Sherrott, P.W.C. Hon, K.T. Fountaine, J.C. Garcia, S.M. Ponti, V.W. Brar, L.A. Sweatlock, H.A. Atwater, Experimental demonstration of >230° phase modulation in gate-tunable graphene-gold reconfigurable mid-infrared metasurfaces. Nano Lett. 17, 3027–3034 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b00359
L. Song, L. Ci, W. Gao, P.M. Ajayan, Transfer printing of graphene using gold film. ACS Nano 3, 1353–1356 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn9003082
T. Zou, B. Zhao, W. Xin, Y. Wang, B. Wang, X. Zheng, H. Xie, Z. Zhang, J. Yang, C.L. Guo, High-speed femtosecond laser plasmonic lithography and reduction of graphene oxide for anisotropic photoresponse. Light Sci. Appl. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-020-0311-2
G.B. Barin, Y. Song, I.D.F. Gimenez, A.G.S. Filho, L.S. Barreto, J. Kong, Optimized graphene transfer: influence of polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) layer concentration and baking time on grapheme final performance. Carbon N. Y. 84, 82–90 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2014.11.040
M.P. Lavin-Lopez, J.L. Valverde, A. Garrido, L. Sanchez-Silva, P. Martinez, A. Romero-Izquierdo, Novel etchings to transfer CVD-grown graphene from copper to arbitrary substrates. Chem. Phys. Lett. 614, 89–94 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2014.09.019
K. Chae, N.D. Cuong, S. Ryu, D. Il Yeom, Y.H. Ahn, S. Lee, J.Y. Park, Electrical properties of ion gels based on PVDF-HFP applicable as gate stacks for flexible devices. Curr. Appl. Phys. 18, 500–504 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2018.02.017
B.J. Kim, H. Jang, S.K. Lee, B.H. Hong, J.H. Ahn, J.H. Cho, High-performance flexible graphene field effect transistors with ion gel gate dielectrics. Nano Lett. 10, 3464–3466 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl101559n
J. Ding, B. Arigong, H. Ren, J. Shao, M. Zhou, Y. Lin, H. Zhang, Mid-infrared tunable dual-frequency cross polarization converters using graphene-based L-shaped nanoslot array. Plasmonics 10, 351–356 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-014-9816-y
D.R. Smith, S. Schultz, P. Markoš, C.M. Soukoulis, Determination of effective permittivity and permeability of metamaterials from reflection and transmission coefficients. Phys Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 65, 1–5 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.65.195104
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research, Taif University Researchers Supporting Project number (TURSP-2020/08), Taif University, Taif, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally to the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sorathiya, V., Lavadiya, S., Parmar, B. et al. Tunable frequency selective surface using crossed shaped graphene metasurface geometry for far infrared frequency spectrum. Appl. Phys. B 128, 169 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-022-07886-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-022-07886-9