Abstract
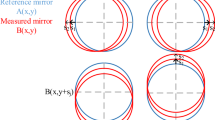
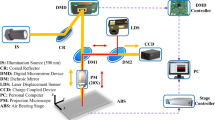
The accuracy of laser interferometry for measuring bearing balls is limited because it is challenging to realize null positioning of the ball being assessed. Even a slight alignment error causes the reflected wavefront to carry an uncertain aberration, which results in the surface error being obscured by the wavefront aberration. To effectively separate the surface error from the reflected wavefront, a virtual wavefront calibration method of ray tracing for alignment error compensation in the interferometric bearing ball measurement system is proposed. A virtual wavefront measurement model with variable alignment vector of the system is established based on the ray tracing principle and coordinate transform theory. According to the virtual wavefront, a calibration process is achieved in the virtual model with a known regularization and optimization method; as a result, no accurate adjustment mechanism is required to adjust the position of the bearing ball in the actual measurement system. Simulation and experiment results indicate that the proposed method is effective, and the repeatability of this measurement system is better than λ/40 peak–valley value. The final results may promote the application of this method in other fields of optical measurement.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.W. Ng, Optical inspection of ball bearing defects. Meas. Sci. Technol. 18, N73–N76 (2007)
J. Schmit, S. Han, E. Novak, Ball bearing measurement with white light interferometry. Proc. SPIE 7389, 73890P–73890P–73812 (2009)
J.A. Lipa, G.J. Siddall, High precision measurement of gyro rotor sphericity. Precis. Eng. 2, 123–128 (1980)
B. Kimbrough, J. Millerd, J. Wyant, J. Hayes, Low-coherence vibration insensitive Fizeau interferometer. Proc. SPIE 6292, 62920F (2006)
M.V. Mantravadi, D. Malacara. In: D. Malacara Optical Shop Testing (eds) Newton, Fizeau, and Haidinger Interferometers, 3rd edn. (Wiley, Hoboken, 2007)
J. Peng, Y. Shen, K. Wang, D. Wang, Error impact analysis and experimental research for absolute testing of spherical surfaces. Infrar. Laser. Eng. 41, 1345–1350 (2012)
Y.-Y. Cheng, J.C. Wyant, Two-wavelength phase shifting interferometry. Appl. Opt. 23(24), 4539 (1984)
D. Mo, R. Wang, G. Li, N. Wang, K. Zhang, Y. Wu, Double-sideband frequency scanning interferometry for long-distance dynamic absolute measurement. Appl. Phys. B-Lasers O 11, 123 (2017)
H. Wu, F. Zhang, T. Liu, P. Balling, X. Qu, Absolute distance measurement by multi-heterodyne interferometry using a frequency comb and a cavity-stabilized tunable laser. Appl. Opt. 55, 4210–4218 (2016)
G. Baer, Automated surface positioning for a non-null test interferometer. Opt. Eng. 49, 095602 (2010)
B. Li, B. Li, B. Liu, T. Jiang, An improved calibration method for structured light projection measurement system. Proc. SPIE 8791, 879116 (2013)
E.D. Kim, M.S. Kang, S.C. Choi, Y.W. Choi, Reverse-optimization alignment algorithm using Zernike sensitivity. J. Opt. Soc. Korea 9, 68–73 (2005)
L. Zhang, D. Liu, T. Shi, Y. Yang, Y. Shen, Practical and accurate method for aspheric misalignment aberrations calibration in non-null interferometric testing. Appl. Opt. 52, 8501–8511 (2013)
X. Hou, F. Wu, L. Yang, Q. Chen, Experimental study on measurement of aspheric surface shape with complementary annular subaperture interferometric method. Opt. Exp. 15, 12890–12899 (2007)
R. Kulkarni, P. Rastogi, Direct unwrapped phase estimation in phase shifting interferometry using Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm. J. Opt. 19, 015608 (2017)
S.S. Lee, J.H. Kim, E.S. Choi, Phase shifting interferometry based on a vibration sensor—feasibility study on elimination of the depth degeneracy. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 70, 687–692 (2017)
Y. Zhang, Z. Pang, X. Fan, Z. Ma, Q. Chen, L. Xiang, S. To, The computer-aided alignment study of three-mirror off-axis field bias optical system. Proc. SPIE 8417, 84170L (2012)
J. Li, H. Shen, R. Zhu, Method of alignment error control in free-form surface metrology with the tilted-wave-interferometer. Opt. Eng. 55, 044101 (2016)
W.A. Ramadan, H.H. Wahba, Simulated Fizeau ring fringes in transmission through spherical and plane reflected surfaces. Appl. Phys. B-Lasers O 1, 124 (2017)
Q. Hao, S. Wang, Y. Hu, H. Cheng, M. Chen, T. Li, Virtual interferometer calibration method of a non-null interferometer for freeform surface measurements. Appl. Opt. 55, 9992–10001 (2016)
G. Baer, J. Schindler, C. Pruss, J. Siepmann, W. Osten, Calibration of a non-null test interferometer for the measurement of aspheres and free-form surfaces. Opt. Exp. 22, 31200 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Grant numbers 51635010, 51875447).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, W., Liu, Z., Gu, S. et al. Virtual wavefront calibration method based on ray tracing for alignment error compensation in the interferometric bearing ball measurement system. Appl. Phys. B 125, 45 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-019-7156-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-019-7156-5