Abstract
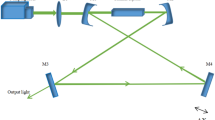
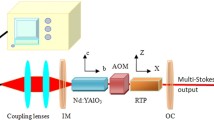
In order to enhance the efficiency and the output average power of the synchronously pumped stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) system, we studied a picosecond pulse-train synchronously pumped SRS system experimentally. A compact KGd(WO4)2 (KGW) Raman cavity was synchronously pumped by high average power picosecond pulse-train laser. 1.22 W including eight-order Stokes Raman components were obtained and the maximum Raman conversion efficiency was 35.4% which was the highest efficiency for all-solid-state picosecond synchronously pumped SRS system to our best knowledge. And the “parasitical SRS process” under SRS process in synchronously pumping condition was observed for the first time.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.G. Zverev, J.T. Murray, R.C. Powell, R.J. Reeves, T.T. Basiev, Stimulated Raman scattering of picosecond pulses in barium nitrate crystals. Opt. Commun. 97, 59 (1993)
P.G. Zverev, T.T. Basiev, A.M. Prokhorov, Stimulated Raman scattering of laser radiation in Raman crystals. Opt. Mater. 11, 335–352 (1999)
W. Wei, X.Y. Zhang, Q.P. Wang, Theoretical and experimental study on intracavity pumped SrWO4 anti-Stokes Raman laser. Appl. Phys. B Lasers Opt. 116(3), 561–568 (2014)
X. Li, Multiwavelength visible laser based on the stimulated Raman scattering effect and beta barium borate angle tuning. Chin. Opt. Lett. 14(2), 021404 (2016)
J. Jakutis-Neto, J. Lin, N.U. Wetter, H. Pask, Continuous-wave watt-level Nd:YLF/KGW Raman laser operating at near-ir, yellow and lime-green wavelengths. Opt. Express 20(9), 9841–9850 (2012)
J.T. Murray, W.L. Austin, R.C. Powell, Intracavity Raman conversion and Raman beam cleanup. Opt. Mater. 11, 353–371 (1999)
J.D. Miller, M.N. Slipchenko, J.G. Mance, S. Roy, J.R. Gord, H.U. Stauffer, Burst-mode two-dimensional coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering (2D-cars) at 1 khz, in Imaging and Applied Optics 2016, LW5G.5. (Optical Society of America, 2016)
A. McKay, O. Kitzler, R.P. Mildren, Thermal lens evolution and compensation in a high power KGW Raman laser. Opt. Express 22(6), 6707–6718 (2014)
D.K. Mohanty, V.K. Rai, Y. Dwivedi, S.B. Rai, Enhancement of up conversion intensity in Er3+ doped tellurite glass in presence of Yb3+. Appl. Phys. B 104(1), 233–236 (2011)
K. Mishra, Y. Dwivedi, S.B. Rai, Observation of avalanche up conversion emission in Pr:Y2O3 nanocrystals on excitation with 532 nm radiation. Appl. Phys. B 106(1), 101–105 (2012)
X.Q. Gao, M.L. Long, M. Chen, Compact KGd(WO4)2 picosecond pulse-train synchronously pumped broad-band Raman laser. Appl. Opt. 55, 6554–6558 (2016)
D.J. Spence, E. Granados, H.M. Pask, R.P. Mildren. KGW and diamond picosecond visible Raman lasers, in Lasers, Sources and Related Photonic Devices (Optical Society of America, 2010), p. ATuA20
I.V. Mochalov, Laser and nonlinear properties of the potassium gadolinium tungstate laser crystal KGd(WO4)2:Nd3+-(KGW:Nd). Opt. Eng. 36(6), 1660–1669 (1997)
T. Graf, J.E. Balmer, Lasing properties of diode-laser-pumped Nd:KGW. Opt. Eng. 34(8), 2349–2352 (1995)
A.A. Kaminskii, P.V. Klevtsov, L. Li, A.A. Pavlyuk, Stimulated emission from KY(WO4)2: Nd3+ crystal laser. Phys. Status Solidi (a) 5(2), K79–K81 (1971)
R.T. Mildren, M. Convery, H.M. Pask, J.A. Piper, Efficient, all-solid-state, Raman laser in yellow, orange and red. Opt. Express 12(5), 785–790 (2004)
M.C. Pujol, M. Rico, C. Zaldo, R. Sole, V. Nikolov, X. Solans, M. Aguilo, F. Diaz, Crystalline structure and optical spectroscopy of Era+-doped KGd(WO4)2 single crystals. Appl. Phys. B 68(2), 187–197 (1999)
W.A. Pisarski, J. Pisarska, R. Lisiecki, Ł. Grobelny, G. Dominiak-Dzik, W. Ryba-Romanowski, Luminescence spectroscopy of rare earth-doped oxychloride lead borate glasses. J. Lumin. 131(4), 649–652 (2011)
Xu Wei, Zhiguo Zhang, Wenwu Cao, Excellent optical thermometry based on short-wavelength upconversion emissions in Era+/Yb3+ codoped CAWO4. Opt. Lett. 37(23), 4865–4867 (2012)
B.I. Denker, B.I. Galagan, S.E. Sverchkov, Up conversion losses in different erbium-doped laser glasses. Appl. Phys. B 120(2), 367–372 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, X., Chen, M. Study on stimulated Raman scattering and up-conversion phenomenon in impure KGd(WO4)2 crystal. Appl. Phys. B 123, 133 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-017-6710-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-017-6710-2