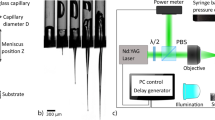
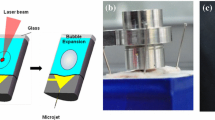
Abstract
The expansion of the laser-induced bubble is the main mechanism in the developed microjet injector. In this study, Nd:YAG and Er:YAG lasers are used as triggers of the bubble formation. The impact of the laser parameters on the bubble dynamics is studied and the performance of the injector is evaluated. We found that the main cause of the differences in the bubble behavior comes from the pulse duration and wavelength. For Nd:YAG laser, the pulse duration is very short relative to the bubble lifetime making the behavior of the bubble close to that of the cavitation bubble, while in Er:YAG case, the high absorption in the water and long pulse duration change the initial behavior of the bubble making it close to a vapor bubble. The contraction and subsequent rebound are typical for cavitation bubbles in both cases. The results show that the laser-induced microjet injector generates velocity which is sufficient for the drug delivery for both laser beams of different pulse duration. We estimate the typical velocity within 30–80 m/s range and the breakup length to be larger than 1 mm suitable for trans-dermal drug injection.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.A.F. Kendall, Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology, vol. 197, (2010), pp. 193–219
M.R. Prausnitz, R. Langer, Nat. Biotechnol. (2008). doi:10.1038/nbt.1504
S. Mitragotri, Nat. Rev. 5, 543–548 (2006)
D.A. Fletcher, D.V. Palanker, Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 1933–1935 (2001)
M. Park, H. Jang, F.V. Sirotkin, J.J. Yoh, Opt. Lett. 37, 3894–3896 (2012)
T. Han, J.J. Yoh, J. Appl. Phys. 107, 103110 (2010)
I. Akhatov, O. Lindau, A. Topolnikov, R. Mettin, N. Vakhitova, W. Lauterborn, Phys. Fluids 10, 2805–2819 (2001)
A. Vogel, S. Busch, J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 100, 148–165 (1996)
J. Noack, D.X. Hammer, G.D. Noojin, B.A. Rockwell, A. Vogel, J. Appl. Phys. 83, 7488 (1998)
G.M. Hale, M.R. Querry, Appl. Opt. 12, 555–563 (1973)
P.A. Barnes, Studies of laser induced breakdown phenomena in liquid water, Ph.D. Dissertation, 1969
M.S. Plesset, A. Prosperetti, Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 9, 145–185 (1977)
Acknowledgments
We thank the National Research Foundation of Korea (DOYAK-2010) for financial support through IAAT at Seoul National University. H. Jang and M. Park are also supported by the Korea Ministry of Land, Transport and Maritime Affairs (Haneul Project).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, Hj., Park, Ma., Sirotkin, F.V. et al. Laser-induced microjet: wavelength and pulse duration effects on bubble and jet generation for drug injection. Appl. Phys. B 113, 417–421 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-013-5479-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-013-5479-1