Abstract
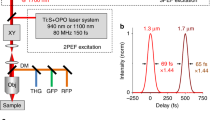
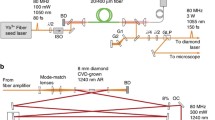
We report on design of a multi-color laser set up that allows for high spectral, time and spatial resolution imaging based on second- and third-order optical nonlinearities in soft condensed matter. Two femtosecond optical parametric oscillators (OPOs) are pumped simultaneously to provide intrinsically synchronized pulses at more than a dozen tunable colors across visible and infrared wavelengths. We demonstrate the use of independently tunable OPOs in a variety of imaging modalities. In one useful application, we explore brain tissue in a two-photon absorption fluorescence imaging experiment with near infrared optical pulses (λ ~ 1,070 nm). We also demonstrate second and sum-frequency generation microscopies in different tissues. Results from application of time-resolved, three-color coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering in tissue are presented to demonstrate feasibility of quantitative spectroscopic imaging.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Denk, J.H. Strickler, W.W. Webb, Two-photon laser scanning fluorescence microscopy. Science 248(4951), 73–76 (1990)
P.J. Campagnola, A.C. Millard, M. Terasaki, P.E. Hoppe, C.J. Malone, W.A. Mohler, Three-dimensional high-resolution second-harmonic generation imaging of endogenous structural proteins in biological tissues. Biophys. J. 81, 493–508 (2002)
D. Yelin, Y. Silberberg, Laser scanning third-harmonic generation microscopy in biology. Opt. Express 5(8), 169 (1999)
D. Débarre, W. Supatto, E. Beaurepaire, Structure sensitivity in third-harmonic generation microscopy. Opt. Lett. 30(16), 2134–2136 (2005)
A. Zumbusch, G.R. Holtom, X.S. Xie, Three-dimensional vibrational imaging by coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82(20), 4142–4145 (1999)
F.W. Christian, W. Min, B.G. Saar, S. Lu, G.R. Holtom, C. He, J.C. Tsai, J.X. Kang, X.S. Xie, Label-free biomedical imaging with high sensitivity by stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. Science 322, 1857–1861 (2008)
C.P. Pfeffer, B.R. Olsen, F. Ganikhanov, F. Légaré, Multimodal nonlinear optical imaging of collagen arrays. J. Struct. Biol. 164(1), 140–145 (2008)
R. Araya, J. Jiang, K.B. Eisenthal, R. Yuste, The spine neck filters membrane potentials. PNAS 103(47), 17961–17966 (2006)
R.M. Williams, W.R. Zipfel, W.W. Webb, Interpreting second-harmonic generation images of collagen I fibrils. Biophys. J. 88, 1377–1386 (2005)
D.A. Dombeck, K.A. Kasischke, H.D. Vishwasrao, M. Ingelsson, B.T. Hyman, W.W. Webb, Uniform polarity microtubule assemblies imaged in native brain tissue by second-harmonic generation microscopy. PNAS 100(12), 7081–7086 (2003)
S.V. Plotnikov, A.C. Millard, P.J. Campagnola, W.A. Mohler, Characterization of the myosin-based source for second-harmonic generation from muscle sarcomeres. Biophys. J. 90(2), 693–703 (2006)
C.P. Pfeffer, B.R. Olsen, F. Ganikhanov, F. Légaré, Imaging skeletal muscle using second harmonic generation and coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering microscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2(5), 1366–1376 (2011)
C.L. Evans, E.O. Potma, M. Puoris’haag, D. Cote, C.P. Lin, X.S. Xie, Chemical imaging of tissue in vivo with video-rate coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering microscopy. PNAS 102(46), 16807–16812 (2005)
X. Nan, E.O. Potma, X.S. Xie, Nonperturbative chemical imaging of organelle transport in living cells with coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering microscopy. Biophys. J. 91, 728–735 (2006)
D. Débarre, W. Supatto, A.-M. Pena, A. Fabre, T. Tordjmann, L. Combettes, M.-C. Schanne-Klein, E. Beaurepaire, Imaging lipid bodies in cells and tissues using third-harmonic generation microscopy. Nat. Methods 3(1), 47–53 (2006)
T. Hellerer, C. Axa¨ng, C. Brackmann, P. Hillertz, M. Pilon, A. Enejder, Monitoring of lipid storage in Caenorhabditis elegans using coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering (CARS) microscopy. PNAS 104(37), 14658–14663 (2007)
V. Raghunathan, Y. Han, O. Korth, N. Ge, E.O. Potma, Rapid vibrational imaging with sum frequency generation microscopy. Opt. Lett. 36(19), 3891–3893 (2011)
M.D. Duncan, J. Reintjes, T.J. Manuccia, Scanning coherent anti-stokes Raman microscope. Opt. Lett. 7(8), 350–352 (1982)
M. Hashimoto, T. Araki, S. Kawata, Molecular vibration imaging in the fingerprint region by use of coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering microscopy with a collinear configuration. Opt. Lett. 25(24), 1768–1770 (2000)
E.O. Potma, D.J. Jones, J.-X. Cheng, X.S. Xie, J. Ye, High-sensitivity coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering microscopy with two tightly synchronized picosecond lasers. Opt. Lett. 27(13), 1168–1170 (2002)
T.W. Kee, M.T. Cicerone, Simple approach to one-laser, broadband coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering microscopy. Opt. Lett. 29(23), 2701–2703 (2004)
E.R. Andresen, C.K. Nielsen, J. Thøgersen, S.R. Keiding, Fiber laser-based light source for coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering microspectroscopy. Opt. Express 15, 4848–4856 (2007)
A.A. Ivanov, A.A. Podshivalov, A.M. Zheltikov, Frequency-shifted megawatt soliton output of a hollow photonic-crystal fiber for time-resolved coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering microspectroscopy. Opt. Lett. 31, 3318 (2006)
A.F. Pegoraro, A. Ridsdale, D.J. Moffatt, Y. Jia, J.P. Pezacki, A. Stolow, Optimally chirped multimodal CARS microscopy based on a single Ti:sapphire oscillator. Opt. Express 17, 2984 (2009)
G.I. Petrov, V.V. Yakovlev, Enhancing red-shifted white-light continuum generation in optical fibers for applications in nonlinear Raman microscopy. Opt. Express 13, 1299 (2005)
F. Ganikhanov, S. Carrasco, X.S. Xie, M. Katz, W. Seitz, D. Kopf, Broadly tunable dual-wavelength light source for coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering microscopy. Opt. Lett. 31, 1292 (2006)
M. Jurna, J.P. Korterik, H.L. Offerhaus, C. Otto, Noncritical phase-matched lithium triborate optical parametric oscillator for high resolution coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering spectroscopy and microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 251116 (2006)
K.V. Bhupathiraju, A.D. Seymour, F. Ganikhanov, Femtosecond optical parametric oscillator based on periodically poled stoichiometric LiTaO3 crystal. Opt. Lett. 34, 2093 (2009)
J. Rowley, S. Yang, F. Ganikhanov, Power and tuning characteristics of a broadly tunable femtosecond optical parametric oscillator based on periodically poled stoichiometric lithium tantalate. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 28, 1036 (2011)
W.S. Pelouch, P.E. Powers, C.L. Tang, Ti:sapphire-pumped, high-repetition-rate femtosecond optical parametric oscillator. Opt. Lett. 17, 1070–1072 (1992)
S. Akhmanov, A. Chirkin, K. Drabovich, A. Kovrigin, R. Khokhlov, A. Sukhorukov, Nonstationary nonlinear optical effects and ultrashort light pulse formation. IEEE J. Quantum Electron 4, 598–605 (1968)
E.C. Cheung, J.M. Liu, Theory of a synchronously pumped optical parametric oscillator in steady-state operation. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 7, 1385–1401 (1990)
J.C. Bjorkholm, Some effects of spatially nonuniform pumping in pulsed optical parametric oscillators. IEEE J. Quant. Electron. QE-7, 109 (1971)
S.V. Plotnikov, A.C. Millard, P.J. Campagnola, W.A. Mohler, Characterization of the myosin-based source for second-harmonic generation from muscle sarcomeres. Biophys. J. 90, 693 (2006)
C.P. Pfeffer, B.R. Olsen, F. Ganikhanov, F. Legare, Imaging skeletal muscle using second harmonic generation and coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering microscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2, 1366 (2011)
A. Laubereau, W. Kaiser, Vibrational dynamics of liquids and solids investigated by picosecond light pulses. Rev. Mod. Phys. 50, 607 (1978)
S. Yang, F. Ganikhanov. Dispersion of nonlinear optical susceptibility obtained with femtosecond time-domain coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering. Phys. Rev. Lett. (in review)
L.B. Lyndgaard, K.M. Sørensen, F. van den Berga, S.B. Engelsena, Depth profiling of porcine adipose tissue by Raman spectroscopy. J. Raman Spectrosc. 43, 482 (2012)
O. Abbas, J.A. Fernández Pierna, R. Codony, C. von Holst, V. Baeten, Assessment of the discrimination of animal fat by FT-Raman spectroscopy. J. Mol. Struct. 924–926, 294 (2009)
A. Hopt, E. Neher, Highly nonlinear photodamage in two-photon fluorescence microscopy. Biophys. J. 80, 2029 (2001)
Acknowledgments
Authors thank professor A. Agmon of Sensory Neuroscience Research Center for providing cortical tissue. FG acknowledges financial support from NSF CAREER award (No0952532), NSF ECCS (award No0925437) grants, and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) NIH/NIGMS CoBRE grant P30 GM103503 and ARRA Supplement S1 to the WVU Center for Neuroscience. Shan Yang’s current address is Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Case Western Reserve University, 10900 Euclid Avenue, Cleveland, OH, 44106.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, S., Adhikari, S., Dobbala, M. et al. Multi-color ultrafast laser platform for nonlinear optical imaging based on independently tunable optical parametric oscillators. Appl. Phys. B 111, 617–625 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-013-5381-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-013-5381-x