Abstract
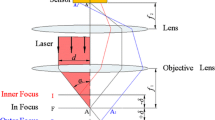
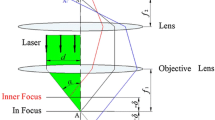
This study designs and characterizes a novel precise optics-based autofocusing microscope with both the large linear autofocusing range and the rapid response. In contrast to conventional optics-based autofocusing microscopes with centroid method, the proposed microscope comprises two optical paths, namely one optical path which provides a short linear autofocusing range but an extremely high focusing accuracy and a second optical path which achieves a long linear autofocusing range but a reduced focusing accuracy. The two optical paths are combined using a self-written autofocus-processing algorithm to realize an autofocusing microscope with a large linear autofocusing range, a rapid response, and a high focusing accuracy. The microscope is characterized numerically using commercial software ZEMAX and is then verified experimentally using a laboratory-built prototype. The experimental results show that compared to conventional optics-based autofocusing microscopes with centroid method and a single optical path, the proposed microscope achieves both a longer autofocusing range and a more rapid response with no reduction in the focusing accuracy. Overall, the results presented in this study show that the proposed microscope provides an ideal solution for automatic optical inspection and industrial applications.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.H. Kang, C.B. Lee, J.Y. Joo, S.K. Lee, Phase-locked loop based on machine surface topography measurement using lensed fibers. Appl. Opt. 50, 460–467 (2011)
P. Petruck, R. Riesenberg, R. Kowarschik, Optimized coherence parameters for high resolution holographic microscopy. Appl. Phys. B 106, 339–348 (2012)
Z. Zhang, Q. Feng, Z. Gao, C. Kuang, C. Fei, Z. Li, J. Ding, A new laser displacement sensor based on triangulation for gauge real-time measurement. Opt. Laser Technol. 40, 252–255 (2008)
W.Y. Hsu, C.S. Lee, P.J. Chen, N.T. Chen, F.Z. Chen, Z.R. Yu, C.H. Kuo, C.H. Hwang, Development of the fast astigmatic auto-focus microscope system. Meas. Sci. Technol. 20, 045902-1–045902-9 (2009)
S.B. Andersson, A nonlinear controller for three-dimensional tracking of a fluorescent particle in a confocal microscope. Appl. Phys. B 104, 161–173 (2011)
J.G. Ritter, R. Veith, J.P. Siebrasse, U. Kubitscheck, High-contrast single-particle tracking by selective focal plane illumination microscopy. Opt. Express 16, 7142–7152 (2008)
P. Calzavara-Pinton, C. Longo, M. Venturini, R. Sala, G. Pellacani, Reflectance confocal microscopy for in vivo skin imaging. Photochem. Photobiol. 84, 1421–1430 (2008)
M. Zeder, J. Pernthaler, Multispot live-image autofocusing for high-throughput microscopy of fluorescently stained bacteria. Cytom. Part A 75A, 781–788 (2009)
T. Pengo, A. Munoz-Barrutia, C. Ortiz-De-Solorzano, Halton sampling for autofocus. J. Microsc. 235, 50–58 (2009)
H.C. Chang, T.M. Shih, N.Z. Chen, N.W. Pu, A microscope system based on bevelaxial method auto-focus. Opt. Lasers Eng. 47, 547–551 (2009)
C.Y. Chen, R.C. Hwang, Y.J. Chen, A passive auto-focus camera control system. Appl. Soft Comput. 10, 296–303 (2010)
M.A. Bueno-Ibarra, J. Alvarez-Borrego, L. Acho, M.C. Chavez-Sanchez, Fast autofocus algorithm for automated microscopes. Opt. Eng. 44, 063601-1–063601-8 (2005)
V.V. Bezzubik, S.N. Ustinov, N.R. Belashenkov, Optimization of algorithms for autofocusing a digital microscope. J. Opt. Technol. 76(10), 603–608 (2009)
Y. Liron, Y. Paran, N.G. Zatorsky, B. Geiger, Z. Kam, Laser autofocusing system for high-resolution cell biological imaging. J. Microsc. 221, 145–151 (2006)
J.H. Lee, Y.S. Kim, S.R. Kim, I.H. Lee, H.J. Pahk, Real-time application of critical dimension measurement of TFT-LCD pattern using a newly proposed 2D image-processing algorithm. Opt. Lasers Eng. 46, 558–569 (2008)
S.L. Brazdilova, M. Kozubek, Information content analysis in automated microscopy imaging using an adaptive autofocus algorithm for multimodal functions. J. Microsc. 236, 194–202 (2009)
S. Yazdanfar, K.B. Kenny, K. Tasimi, A.D. Corwin, E.L. Dixon, R.J. Filkins, Simple and robust image-based autofocusing for digital microscopy. Opt. Express 16, 8670–8677 (2008)
C.H. Chen, T.L. Feng, Fast 3D shape recovery of a rough mechanical component from real time passive autofocus system. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 34, 944–957 (2007)
E.F. Wright, D.M. Wells, A.P. French, C. Howells, N.M. Everitt, A low-cost automated focusing system for time-lapse microscopy. Meas. Sci. Technol. 20, 027003-1–027003-4 (2009)
H. Oku, M. Ishikawa, High-speed autofocusing of a cell using diffraction patterns. Opt. Express 14, 3952–3960 (2006)
P. Langehanenberg, B. Kemper, D. Dirksen, G. von Bally, Autofocusing in digital holographic phase contrast microscopy on pure phase objects for live cell imaging. Appl. Opt. 47, D176–D182 (2008)
T. Kim, T.C. Poon, Autofocusing in optical scanning holography. Appl. Opt. 48, H153–H159 (2009)
S. Lee, J.Y. Lee, W. Yang, D.Y. Kim, Autofocusing and edge detection schemes in cell volume measurements with quantitative phase microscopy. Opt. Express 17, 6476–6486 (2009)
M. Moscaritolo, H. Jampel, F. Knezevich, R. Zeimer, An image based auto-focusing algorithm for digital fundus photography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 28, 1703–1707 (2009)
Y. Shao, J. Qu, H. Li, Y. Wang, J. Qi, G. Xu, H. Niu, High-speed spectrally resolved multifocal multiphoton microscopy. Appl. Phys. B 99, 633–637 (2010)
S.J. Abdullah, M.M. Ratnam, Z. Samad, Error-based autofocus system using image feedback in a liquid-filled diaphragm lens. Opt. Eng. 48, 123602-1–123602-9 (2009)
R.M. Wasserman, P.G. Gladnick, K.W. Atherton, Systems and methods for rapidly automatically focusing a machine vision inspection system, U.S. Patent 7030351B2 (2006)
J.Y. Lee, Y.H. Wang, L.J. Lai, Y.J. Lin, Y.H. Chang, Development of an auto-focus system based on the Moiré method. Measurement 44, 1793–1800 (2011)
I. Chremmos, N.K. Efremidis, D.N. Christodoulides, Pre-engineered abruptly autofocusing beams. Opt. Lett. 36, 1890–1892 (2011)
B.J. Jung, H.J. Kong, B.G. Jeon, D.Y. Yang, Y. Son, K.S. Lee, Autofocusing method using fluorescence detection for precise two-photon nanofabrication. Opt. Express 19, 22659–22668 (2011)
P. Zhang, J. Prakash, Z. Zhang, M.S. Mills, N.K. Efremidis, D.N. Christodoulides, Z. Chen, Trapping and guiding microparticles with morphing autofocusing Airy beams. Opt. Lett. 36, 2883–2885 (2011)
D.K. Cohen, W.H. Gee, M. Ludeke, J. Lewkowicz, Automatic focus control: the astigmatic lens approach. Appl. Opt. 23, 565–570 (1984)
K.C. Fan, C.L. Chu, J.I. Mou, Development of a low-cost autofocusing probe for profile measurement. Meas. Sci. Technol. 12, 2137–2146 (2001)
Q.P. Li, F. Ding, P. Fang, Flash CCD laser displacement sensor. Electron. Lett. 42, 910–912 (2006)
Y. Tanaka, T. Watanabe, K. Hamamoto, H. Kinoshita, Development of nanometer resolution focus detector in vacuum for extreme ultraviolet microscope. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 45, 7163–7166 (2006)
S.J. Lee, D.Y. Chang, A laser sensor with multiple detectors for freeform surface digitization. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 31, 1181–1190 (2007)
Z. Li, K. Wu, Autofocus system for space cameras. Opt. Eng. 44, 053001-1–053001-5 (2005)
H.G. Rhee, D.I. Kim, Y.W. Lee, Realization and performance evaluation of high speed autofocusing for direct laser lithography. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 80, 073103-1–073103-5 (2009)
Y. Nishio, Optical displacement meter, optical displacement measuring method, optical displacement measuring program, computer-readable recording medium, and device that records the program, U.S. Patent 7489410B2 (2009)
M. Kataoka, K. Nemoto, Focusing servo device and focusing servo method, U.S. Patent 7187630B2 (2007)
M. He, W. Zhang, X. Zhang, A displacement sensor of dual-light based on FPGA. Optoelectron. Lett. 3, 294–298 (2007)
K.H. Kim, S.Y. Lee, S. Kim, S.G. Jeong, DNA microarray scanner with a DVD pick-up head. Curr. Appl. Phys. 8, 687–691 (2008)
S.H. Wang, C.J. Tay, C. Quan, H.M. Shang, Z.F. Zhou, Laser integrated measurement of surface roughness and micro-displacement. Meas. Sci. Technol. 11, 454–458 (2000)
A. Weiss, A. Obotnine, A. Lasinski, Method and apparatus for the auto-focussing infinity corrected microscopes, U.S. Patent 7700903 (2010)
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided to this study by the National Science Council of Taiwan under Grant No. NSC 100-2218-E-194-008. The authors would like to express their thanks to Mr. Yu-Hsiu Chang of the Laser Application Technology Center, Industrial Technology Research Institute, Taiwan, for his technological assistance throughout the course of the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, CS., Hu, PH. & Lin, YC. Design and experimental validation of novel optics-based autofocusing microscope. Appl. Phys. B 109, 259–268 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-012-5171-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-012-5171-x