Abstract
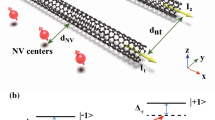
We propose an experimentally viable setup for the realization of one-dimensional ultracold atom gases in a nanoscale magnetic waveguide formed by single doubly-clamped suspended carbon nanotubes. We show that all common decoherence and atom loss mechanisms are small, guaranteeing a stable operation of the trap. Since the extremely large current densities in carbon nanotubes are spatially homogeneous, our proposed architecture allows for creation of a very regular trapping potential for the atom cloud. Adding a second nanowire allows creation of a double-well potential with a moderate tunneling barrier which is desired for tunneling and interference experiments with the advantage of tunneling distances being in the nanometer regime.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Folman R, Krüger P, Schmiedmayer J, Denschlag J, Henkel C (2002) Adv. At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 48:263
Reichel J (2002) Appl. Phys. B 75:469
Ott H, Fortagh J, Schlotterbeck G, Grossmann A, Zimmermann C (2001) Phys. Rev. Lett. 87:230401
Hänsel W, Hommelhoff P, Hänsch TW, Reichel J (2001) Nature 413:498
Leanhardt A, Shin Y, Chikkatur AP, Kielpinski D, Ketterle W, Pritchard DE (2003) Phys. Rev. Lett. 90:100404
Schneider S, Kasper A, vom Hagen C, Bartenstein M, Engeser B, Schumm T, Bar-Joseph I, Folman R, Feenstra L, Schmiedmayer J (2003) Phys. Rev. A 67:023612
Henkel C, Pötting S, Wilkens M (1999) Appl. Phys. B 69:379
Lin Y-J, Teper I, Chin C, Vuletić V (2004) Phys. Rev. Lett. 92:050404
Schroll C, Belzig W, Bruder C (2003) Phys. Rev. A 68:043618
Kasevich MA (2002) Science 298:136
Dresselhaus MS, Dresselhaus G, Avouris P (eds) (2001) Carbon Nanotubes. Springer, Berlin
Petrov DS, Gangardt DM, Shlyapnikov GV (2004) J. Phys. IV 116:5
Chen S, Egger R (2003) Phys. Rev. A 68:063605
Tokatly IV (2004) Phys. Rev. Lett. 93:090405
Fuchs JN, Recati A, Zwerger W (2004) Phys. Rev. Lett. 93:090408
Mora C, Egger R, Gogolin AO, Komnik A (2004) Phys. Rev. Lett. 93:170403
Olshanii M (1998) Phys. Rev. Lett. 81:938
Bergeman T, Moore MG, Olshanii M (2003) Phys. Rev. Lett. 91:163201
Stöferle T, Moritz H, Schori C, Köhl M, Esslinger T (2004) Phys. Rev. Lett. 92:130403
Paredes B, Widera A, Murg V, Mandel O, Fölling S, Cirac I, Shlyapnikov GV, Hänsch TW, Bloch I (2004) Nature 429:277
Kinoshita T, Wenger T, Weiss DS (2004) Science 305:112
Görlitz A, Vogels JM, Leanhardt AE, Raman C, Gustavson TL, Abo-Shaeer JR, Chikkatur AP, Gupta S, Inouye S, Rosenband T, Ketterle W (2001) Phys. Rev. Lett. 87:130402
Sukumar CV, Brink DM (1997) Phys. Rev. A 56:2451
Jones MPA, Vale CJ, Sahagun D, Hall BV, Hinds EA (2003) Phys. Rev. Lett. 91:080401
Sapmaz S, Blanter YM, Gurevich L, van der Zant HSJ (2003) Phys. Rev. B 67:235414
Casimir HBG, Polder D (1948) Phys. Rev. 73:360
V. Peano, M. Thorwart, C. Mora, R. Egger, unpublished results, see also cond-mat/0411517
Lieb EH, Liniger W (1963) Phys. Rev. 130:1616
Dunjko V, Lorent V, Olshanii M (2001) Phys. Rev. Lett. 86:5413
Weiss U (1999) Quantum Dissipative Systems. World Scientific, Singapore
Postma HWC, Sellmeijer A, Dekker C (2000) Adv. Mater. 17:1299
Kim GT, Gu G, Waizman U, Roth S (2002) Appl. Phys. Lett. 80:1815
Reichel J, Thywissen JH (2004) J. Phys. IV 116:265
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
PACS
03.75.Gg; 03.75.Dg; 73.63.Fg
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peano, V., Thorwart, M., Kasper, A. et al. Nanoscale atomic waveguides with suspended carbon nanotubes. Appl. Phys. B 81, 1075–1080 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-005-1971-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-005-1971-6