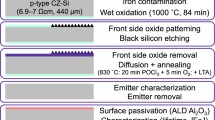
Abstract.
Acceptor deactivation in the near-surface region of as-grown, boron-doped Si wafers was detected by in-depth profiles of the free-carrier density obtained by capacitance–voltage measurements. As this deactivation was only observed in wafers subjected to the standard cleaning procedures used in Si manufacturing, we ascribed it to boron passivation by an impurity introduced during the cleaning process. From the study of the free-carrier reactivation kinetics and of the diffusion behaviour of boron–impurity complexes, we have concluded that the impurity is possibly related to hydrogen introduced during the cleaning treatments. The characteristics of the deep level associated with this impurity have been analysed by deep-level transient spectroscopy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 22 August 2001 / Accepted: 27 October 2001 / Published online: 29 May 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castaldini, A., Cavalcoli, D., Cavallini, A. et al. Hydrogen-induced boron passivation in Cz Si . Appl Phys A 75, 601–605 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003390101067
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003390101067