Abstract.
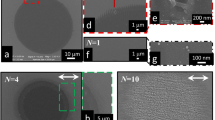
The formation and development of the large-scale periodic structures on a single crystal Si surface are studied upon its evaporation by pulsed radiation of a copper vapor laser (wavelength of 510.6 nm, pulse duration of 20 ns). The development of structures occurs at a high number of laser shots (∼104) at laser fluence of 1–2 J/cm2 below optical breakdown in a wide pressure range of surrounding atmosphere from 1 to 105 Pa. The structures are cones with angles of 25, which grow towards the laser beam and protrude above the initial surface for 20–30 μm. It is suggested that the spatial period of the structures (10–20 μm) is determined by the capillary waves period on the molten surface. The X-ray diffractometry reveals that the modified area of the Si substrate has a polycrystalline structure and consists of Si nanoparticles with a size of 40–70 nm, depending on the pressure of surrounding gas. Similar structures are also observed on Ge and Ti.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 12 February 2000 / Accepted: 28 March 2000 / Published online: 20 June 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dolgaev, S., Lavrishev, S., Lyalin, A. et al. Formation of conical microstructures upon laser evaporation of solids . Appl Phys A 73, 177–181 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003390100530
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003390100530