20
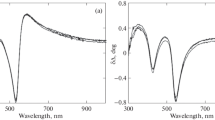
cm-3 and above) induce oscillations in the reflected intensity.
The evolution of the layers morphology is shown to depend on two effects: (i)the locally high surface concentration of carbon which blocks locally the growth and hence induces holes at the surface, (ii)the occurrence of dislocations at thicknesses larger than the critical thickness which are revealed chlorides produced by the decomposition of CCl4 (the carbon precursor) and form deep etch pits.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 13 February 1998 / Accepted: 26 October 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rebey, A., El Jani, B., Leycuras, A. et al. In situ optical monitoring of metalorganic vapor phase epitaxy growth of C-doped GaAs . Appl Phys A 68, 349–352 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003390050901
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003390050901