x
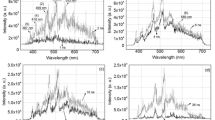
) films in a nitrogen atmosphere within the range 5×10-4–4×10-1 Torr. In the presence of a magnetic field, the emission intensities of N2 (second positive system) and CN species in the graphite ablation plumes were altered significantly, depending on the pressure of the N2 environment. Corresponding to an intense CN emission, a magnetic field-induced enhancement of N incorporation – for example, up to 37% at an N2 pressure of 300 mTorr – and the formation of sp3 tetrahedral CN bonding were both observed in the films. This suggests that the arrival of CN species at the substrate surface with kinetic energies is important for film deposition.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 27 August 1997/Accepted: 8 September 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kokai, F., Yamamoto, K., Koga, Y. et al. Characterization of ablation plumes and carbon nitride films produced by reactive pulsed laser deposition in the presence of a magnetic field . Appl Phys A 66, 403–406 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003390050685
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003390050685