2
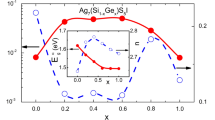
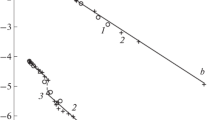
SO4. The solid solubility limits up to x≤3 mole% for monovalent, x≤5.27 mole% for divalent and x≤3.63 mole% for trivalent cation doped Ag2SO4 are set with XRD, SEM, IR and DSC techniques. A predominant dependence of conductivity on the ionic size of iso- and alio-valent cations is observed. In particular, the conductivity enhances in both α and β phases, despite having a lower ionic-size dopant cation (relative to that of Ag+) in the transition element cation doped Ag2SO4. Ca2+, Ba2+, Y3+ and Dy3+ doped samples show depature from the regular behaviour in the β-phase. The conductivity behaviour is discussed considering ionic size, valence and electronic structure of the guest cations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 3 February 1997/Accepted: 27 May 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, K., Pande, S., Anwane, S. et al. A study of iso- and alio-valent cation doped Ag2SO4 solid electrolyte . Appl Phys A 66, 205–215 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003390050657
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003390050657