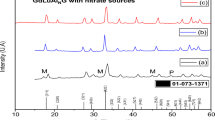
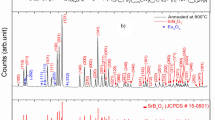
Abstract
Trivalent erbium ions doped (48 – x) AlPO4 + 15K2O + 12MgF + 20Na2O + 5NaF + xEr2O3 glass samples have been prepared utilizing the melt-quench process and studied to understand the efficacy of Er3+ ions content on physical, structural and luminescence attributes of host glass. The functional groups of the glass structure such as metaphosphate, orthophosphate and pyrophosphate have been elucidated through Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopic investigation. The least-square approach was used to calculate the Judd–Ofelt parameter from the oscillator strength of the Er3+ ion transitions. The luminescence emission data captured in the visible and near-infrared (NIR) province using 380 and 980 nm excitation wavelengths. The up-conversion (recorded at the excitation at 980 nm) of 0.5 Er glass exhibited emission at 664, 550 and 488 nm wavelengths. The decay plots of the studied glass specimens were measured at 980 nm excitation. The McCumber (MC) theory has been implemented to calculate the gain coefficient of the 0.5 Er glass and flat gain curve was drawn for S-band, C-band and L-band. The attributes for optical amplification were ascertained, including the quality factor (0.85), branching ratio (1), stimulated emission cross-section (1.3 × 10–20 cm2), gain bandwidth (1.26 × 10–25 cm3) and optical gain (0.394 × 10–23 cm2 s) for 0.5 Er glass. The yellowish green light emission ability of the 0.5 Er glass after 980 nm excitation evident through CIE co-ordinates position (x 0.36, y 0.58) at 1931 CIE chromaticity diagram. The spectroscopic and luminescence results endorse that the alumino–phosphate glass specimens loaded with 0.5 mol% of Er2O3 are beneficial for NIR and green light emission applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw data that support the findings are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
P. Babu, H.J. Seo, C.R. Kesavulu, K.H. Jang, C.K. Jayasankar, Thermal and optical properties of Er3+-doped oxyfluorotellurite glasses. J. Lumin. 129, 444–448 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2008.11.014
A. Jha, B. Richards, G. Jose, T. Teddy-Fernandez, P. Joshi, X. Jiang, J. Lousteau, Rare-earth ion doped TeO2 and GeO2 glasses as laser materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 57, 1426–1491 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2012.04.003
C. Madhukar Reddy, B. Deva Prasad Raju, N. John Sushma, N.S. Dhoble, S.J. Dhoble, A review on optical and photoluminescence studies of RE3+ (RE=Sm, Dy, Eu, Tb and Nd) ions doped LCZSFB glasses. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 51, 566–584 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.06.025
C. Wang, M. Zhang, Y. Chen, Y. Wang, J. Lu, X. Huang, Y. Wei, L. Wan, S. Huang, Z. Li, Z. Chen, Z. Li, Synthesis and study of novel erbium-doped La2O3-Al2O3 glasses for on-chip waveguide amplifier. J. Alloys Compd. 899, 162915 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162915
F. Lahoz, C. Pérez-Rodríguez, S.E. Hernández, I.R. Martín, V. Lavín, U.R. Rodríguez-Mendoza, Upconversion mechanisms in rare-earth doped glasses to improve the efficiency of silicon solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 95, 1671–1677 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2011.01.027
A. Lemiere, B. Bondzior, I. Aromäki, L. Petit, Study of visible, NIR, and MIR spectroscopic properties of Er3+-doped tellurite glasses and glass–ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 105, 7186–7195 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.18649
C.R. Kesavulu, H.J. Kim, S.W. Lee, J. Kaewkhao, N. Wantana, S. Kothan, S. Kaewjaeng, Influence of Er3+ ion concentration on optical and photoluminescence properties of Er3+-doped gadolinium–calcium silica borate glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 683, 590–598 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.04.314
X. Huang, H. Cheng, W. Luo, W. Zhang, M. Jiang, C. Yang, T. Yu, Z. Cai, Z. Xu, X. Shu, Z. Yang, J. Qiu, S. Zhou, Er-activated hybridized glass fiber for laser and sensor in the extended wavebands. Adv. Opt. Mater. 9, 2101394 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.202101394
X. Feng, S. Tanabe, T. Hanada, Spectroscopic properties and thermal stability of Er3+-doped germanotellurite glasses for broadband fiber amplifiers. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 84, 165–171 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.2001.tb00625.x
X. Shen, S. Chen, Y. Sun, X. Wang, W. Wei, L. Hu, Investigation of Er3+-doped phosphate glass for L+ band optical amplification. IEEE Photonics J. 13, 2200506 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/JPHOT.2021.3124132
H.C. Çamiçi, T. Guérineau, V.A.G. Rivera, R.F. Falci, S. LaRochelle, Y. Messaddeq, The role of tungsten oxide in Er3+-doped bismuth-germanate glasses for optical amplification in L-band. Sci. Rep. 13, 8835 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-35995-8
P. Joshi, S. Shen, A. Jha, Er3+-doped boro-tellurite glass for optical amplification in the 1530–1580nm. J. Appl. Phys. (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2908873
D. Pugliese, A. Veber, A. Lemière, N.G. Boetti, L. Petit, Effect of post-heat-treatment on the structural, spectroscopic and dissolution properties of a highly stable Er3+-doped multi-component phosphate glass. J. Alloys Compd. 883, 160878 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.160878
F. Zaman, G. Rooh, N. Chanthima, S.U. Khan, H.J. Kim, S. Kothan, N. Chanlek, M. Arshad, J. Kaewkhao, Investigation of spectroscopic and photoluminescence properties of Erbium doped phosphate (P2O5–K2O3–Al2O3) glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 893, 162215 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162215
L.R. Moorthy, M. Jayasimhadri, S.A. Saleem, D.V.R. Murthy, Optical properties of Er3+-doped alkali fluorophosphate glasses. J. Non Cryst. Solids 353, 1392–1396 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2006.10.062
B. Afef, M.M. Alqahtani, H.H. Hegazy, E. Yousef, K. Damak, R. Maâlej, Green and near infrared emission of Er3+ doped PZS and PZC glasses. J. Lumin. 194, 706–712 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2017.09.040
N. Deopa, M.K. Sahu, S. Kaur, A. Prasad, K. Swapna, V. Kumar, R. Punia, A.S. Rao, Enhanced visible green and 1.5 μm radiative emission of Er3+ ions in Li2O–PbO–Al2O3–B2O3 glasses for photonic applications. J. Rare Earths 39, 520–525 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2020.05.002
V. Hegde, C.S.D. Viswanath, V. Upadhyaya, K.K. Mahato, S.D. Kamath, Red light emission from europium doped zinc sodium bismuth borate glasses. Physica B Condens. Matter 527, 35–43 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2017.09.113
P. Ramprasad, Ch. Basavapoornima, C.R. Kesavulu, V. Venkatramu, J. Kaewkhao, C.K. Jayasankar, Spectroscopic properties of Er3+-doped barium phosphate glasses for optical gain media. Results Opt. 12, 100489 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rio.2023.100489
M. Lu, F. Wang, Q. Liao, K. Chen, J. Qin, S. Pan, FTIR spectra and thermal properties of TiO2-doped iron phosphate glasses. J. Mol. Struct. 1081, 187–192 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2014.10.029
A.H. Almuqrin, M. Rashad, C.V. More, M.I. Sayyed, M. Elsafi, An experimental and theoretical study to evaluate Al2O3–PbO–B2O3–SiO2–BaO radiation shielding properties. Rad. Phys. Chem. 222, 111824 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2024.111824
Y.B. Saddeek, M.A. Kaid, M.R. Ebeid, FTIR and physical features of Al2O3–La2O3–P2O5–PbO glasses. J. Non Cryst. Solids 387, 30–35 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2013.12.029
Z.A.S. Mahraz, E.S. Sazali, M.R. Sahar, N.U. Amran, S.N.S. Yaacob, S.M. Aziz, S.Q. Mawlud, F.M. Noor, A.N. Harun, Spectroscopic investigations of near-infrared emission from Nd3+-doped zinc–phosphate glasses: Judd–Ofelt evaluation. J. Non Cryst. Solids 509, 106–114 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2018.05.013
H.J. Alasali, U. Rilwan, K.A. Mahmoud, T.A. Hanafy, M.I. Sayyed, Comparative analysis of TiO2, Fe2O3, CaO and CuO in borate based glasses for gamma ray shielding. Nucl. Engg. Technol. 56, 1845 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.net.2023.12.042
P.K. Jha, O.P. Pandey, K. Singh, Structure and crystallization kinetics of Li2O modified sodium-phosphate glasses. J. Mol. Struct. 1094, 174–182 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2015.03.066
A. Kaur, A. Khanna, L.I. Aleksandrov, Structural, thermal, optical and photo-luminescent properties of barium tellurite glasses doped with rare-earth ions. J. Non Cryst. Solids 476, 67–74 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2017.09.025
S. Tanabe, T. Ohyagi, N. Soga, T. Hanada, Compositional dependence of Judd–Ofelt parameters of Er ions in alkali-metal borate glasses. Phys. Rev. B 46, 3305–3310 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.46.3305
Sk.N. Rasool, B.C. Jamalaiah, K. Suresh, L.R. Moorthy, C.K. Jayasankar, Spectroscopic properties of Er3+-doped phosphate based glasses for broadband 1.54 μm emission. J. Mol. Struct. 1130, 837–843 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2016.10.090
W.T. Carnall, P.R. Fields, K. Rajnak, Electronic energy levels in the trivalent lanthanide aquo ions. I. Pr3+, Nd3+, Pm3+, Sm3+, Dy3+, Ho3+, Er3+, and Tm3+. J. Chem. Phys. 49, 4424–4442 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1669893
A. Amarnath Reddy, S. Surendra Babu, G. Vijaya Prakash, Er3+-doped phosphate glasses with improved gain characteristics for broadband optical amplifiers. Opt. Commun. 285, 5364–5367 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2012.08.031
K. Selvaraju, K. Marimuthu, Structural and spectroscopic studies on concentration dependent Er3+ doped boro-tellurite glasses. J. Lumin. 132, 1171–1178 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2011.12.056
G. Devarajulu, G. Lakshminarayana, P. Venkateswara-Rao, D.-E. Lee, J. Yoon, T. Park, Er3+-doped SiO2-based glasses: an exploration of structural, visible, chromatic, and NIR fluorescence characteristics. Mater. Res. Bull. 147, 111634 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2021.111634
C. Basavapoornima, K. Linganna, C.R. Kesavulu, S. Ju, B.H. Kim, W.T. Han, C.K. Jayasankar, Spectroscopic and pump power dependent upconversion studies of Er3+-doped lead phosphate glasses for photonic applications. J. Alloys Compd. 699, 959–968 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.12.199
M.E. Alvarez-Ramos, F. Félix-Domínguez, G. Saavedra-Rodríguez, R.C. Carrillo-Torres, Structural, luminescent and upconversion characteristics of Er3+ doped titanium zinc tellurite glass. Opt. Mater. 120, 111413 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2021.111413
B.N. Swetha, G. Devarajulu, K. Keshavamurthy, G. Jagannath, H.R. Deepa, Enhanced 1.53 µm emission of Er3+ in nano-Ag embedded sodium–boro-lanthanate glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 856, 158212 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.158212
G. Lakshminarayana, A.N. Meza-Rocha, O. Soriano-Romero, U. Caldiño, A. Lira, D.E. Lee, J. Yoon, T. Park, Assessment of optical and fluorescence aspects of Er3+-doped multicomponent B2O3 glasses as active media for 1.532 μm near-infrared optical amplifiers. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 18, 3457–3477 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.04.012
F. Aouaini, A. Maaoui, N.B.H. Mohamed, M.M. Alanazi, L.A. El Maati, Visible to infrared down conversion of Er3+ doped tellurite glass for luminescent solar converters. J. Alloys Compd. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162506
M. Shoaib, I. Khan, N. Chanthima, A. Alhuthali, N. Intachai, S. Kothan, A. Ahad, I. Ullah, S. Khattak, G. Rooh, J. Kaewkhao, T. Ahmad, Photoluminescence analysis of Er3+-ions doped P2O5–Gd2O3/GdF3–BaO–ZnO glass systems. J. Alloys Compd. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.163766
M. Kumar, M.K. Sahu, S. Kaur, A. Prasad, R. Bajaj, R.A. Talewar, Y. Tayal, K. Swapna, A.S. Rao, Visible and NIR spectral analysis of Er3+ doped LiBiAlBSi glasses for laser applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12281-5
A. Jose, S. Gopi, T. Krishnapriya, T.A. Jose, C. Joseph, N.V. Unnikrishnan, P.R. Biju, Spectroscopic investigations on 1.53 μm NIR emission of Er3+ doped multicomponent borosilicate glasses for telecommunication and lasing applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 261, 124223 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.124223
N.S. Prabhu, A.N. Meza-Rocha, O. Soriano-Romero, U. Caldiño, E.F. Huerta, C. Falcony, M.I. Sayyed, H. Al-Ghamdi, A.H. Almuqrin, S.D. Kamath, Spectroscopic study of Er3+ doped borate glass system for green emission device NIR laser, and optical amplifier applications. J. Lumin. 238, 118216 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2021.118216
Acknowledgements
The authors express their gratitude to Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Researchers Supporting Project number (PNURSP2024R2), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. R. Rajaramakrishna would like to thank for the kind support for the research through the Strategic Academic Leadership Program “Priority-2030”, Siberian Federal University, Krasnoyarsk, Russia.
Funding
The authors express their gratitude to Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Researchers Supporting Project number (PNURSP2024R2), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
VH: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data Curation, Writing–Original Draft and Editing, Writing–Review, KRV: Data Curation, SDK: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing–Review and Editing, Project administration, CSDV: Data curation, Software, AHA: Data curation, Writing–Review and Editing, MIS: Methodology, Data Curation, Writing–Review and Editing, GJ: Methodology, Data Curation, Formal analysis, Writing–Original Draft and Editing, Writing–Review and Editing, RR: Formal analysis, Software, Writing–Review, KK: Methodology, Data Curation, Formal analysis, Writing–Review.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hegde, V., Vighnesh, K.R., Kamath, S.D. et al. Near-infrared and green light emission spectroscopic characteristics of Er3+ doped alumina–phosphate glasses. Appl. Phys. A 130, 411 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-024-07531-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-024-07531-6