Abstract
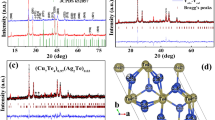
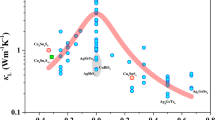
Copper and silver tetraiodomercurates (Cu2HgI4, Ag2HgI4) are thermochromic materials whose color changes result from a crystalline phase transition, affecting their electrical and thermal conductivities. Both materials, defined as superionic solids, are solid electrolytes where the metallic cations are the charge carriers in the higher temperature phase, which occurs at 50 °C for Ag2HgI4 and at 69 °C for Cu2HgI4. In this work, we present the thermal characterization of these materials by measuring the thermal diffusivity as a function of temperature, intending to elucidate the influence of randomly moving cations on thermal transport and their interactions with the phonons produced in the anion sublattice. The electrical conductivity characterization enabled us to contrast their different behavior as the phase transition occurs due to temperature changes. Thermal and electrical transport performance characterization of these materials opens the possibility of using them in different applications, such as solid-state batteries, optical devices for recording media, active materials for thermally controlled systems, temperature sensing devices, and fillers for manufacturing smart composites, among many others.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data are contained within the article.
References
S. Hull, D.A. Keen, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 12, 3751 (2000)
W.J. Pardee, G.D. Mahan, J. Solid State Chem. 15, 310 (1975)
A.B. Yaroslavtsev, Russ. Chem. Rev. 85, 1255 (2016)
S. Ohno, A. Banik, G.F. Dewald, M.A. Kraft, T. Krauskopf, N. Minafra, P. Till, M. Weiss, W.G. Zeier, Prog. Energy 2, 022001 (2020)
Z. Zou, Y. Li, Z. Lu, D. Wang, Y. Cui, B. Guo, Y. Li, X. Liang, J. Feng, H. Li, C.W. Nan, M. Armand, L. Chen, K. Xu, S. Shi, Chem. Rev. 120, 4169 (2020)
B. Hans, Chem. Rev. 5518, 37 (1978)
S.R. Yousefi, A. Sobhani, M. Salavati-Niasari, Adv. Powder Technol. 28, 1258 (2017)
R.C. Agrawal, R. Kumar, R.K. Gupta, M. Saleem, J. Non Cryst. Solids 181, 110 (1995)
H. Rickert, Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. English 17, 37 (1978)
A. Hakami, S.S. Srinivasan, P.K. Biswas, A. Krishnegowda, S.L. Wallen, E.K. Stefanakos, J. Coatings Technol. Res. 19, 377 (2022)
N. Mott, Metal-Insulator Transitions (CRC Press, 2004)
F. Grasselli, J. Chem. Phys. Chem. Phys. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0087382
I. Karbovnyk, S. Piskunov, I. Bolesta, S. Bellucci, M.C. Guidi, M. Piccinini, E. Spohr, A.I. Popov, Eur. Phys. J. B. 70, 443 (2009)
Y. Huang, B. Shao, F. Han, A.C.S. Symp, Ser. 1413, 1 (2022)
Q. Zhao, S. Stalin, C.Z. Zhao, L.A. Archer, Nat. Rev. Mater. 5, 229 (2020)
T. Famprikis, P. Canepa, J.A. Dawson, M.S. Islam, C. Masquelier, Nat. Mater. 18, 1278 (2019)
G. Yang, C. Abraham, Y. Ma, M. Lee, E. Helfrick, D. Oh, D. Lee, Appl. Sci. Sci. 10, 4727 (2020)
N. Preux, A. Rolle, R.N. Vannier, Electrolytes and Ion Conductors for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFCs) (Woodhead Publishing Limited, 2012)
H. Deng, W. Zhang, X. Wang, Y. Mi, W. Dong, W. Tan, B. Zhu, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 42, 22228 (2017)
L.E. Bell, Science 321(5895), 1457 (2008)
T. Ouyang, X. Zhang, M. Hu, Nanotechnology 26, 25702 (2015)
H. Liu, X. Shi, F. Xu, L. Zhang, W. Zhang, L. Chen, Q. Li, C. Uher, T. Day, G. Snyder Jeffrey, Nat. Mater. Mater. 11, 422 (2012)
D.A. Keen, J. Phys. Condens. Matter Phys. Condens. Matter 14, R819–R857 (2002)
J. He, K. Li, L. Jia, Y. Zhu, H. Zhang, J. Linghu, Appl. Therm. Eng. 236, 121813 (2024)
P.B. Allen, J.L. Feldman, Phys. Rev. B 48, 12581 (1993)
S. Hull, Reports Prog. Phys. 67, 1233 (2004)
Z. Wu, S. Zhang, Z. Liu, E. Mu, Z. Hu, Nano Energy 91, 106692 (2022)
M. Massetti, F. Jiao, A.J. Ferguson, D. Zhao, K. Wijeratne, A. Würger, J.L. Blackburn, X. Crispin, S. Fabiano, Chem. Rev. 121, 12465 (2021)
W. Yu, S.U.S. Choi, J. Nanopart. Res. 5, 167 (2003)
F. Deng, Q.-S. Zheng, L.-F. Wang, C.-W. Nan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 021914 (2007)
S. Yamada, H. Toshiyoshi, A.C.S. Appl, Mater. Interfaces 12, 36449 (2020)
Z. Liu, K. Shikinaka, Y. Otsuka, Y. Tominaga, Chem. Commun. 58, 4504 (2022)
J.ΑA. Ketelaar, Z. Phys, Chemistry 26, 327 (1934)
J.W. Brightwell, C.N. Buckley, R.C. Hollyoak, B. Ray, J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 3, 443 (1984)
T. Hibma, H.U. Beyeler, H.R. Zeller, Solid State Phys. 9, 1691 (1976)
A. Ahmad, J. Hazard. Mater. 179(1–3), 363 (2010)
C.S. Sunandana, P.S. Kumar, Bull. Mater. Sci. 27, 1 (2004)
A.M. Salem, Y.A. El-Gendy, G.B. Sakr, W.Z. Soliman, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 41, 025311 (2008)
F. Soofivand, M. Salavati-Niasari, J. Mol. Liq. 252, 112 (2018)
L. Suchow, G.R. Pond, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 75, 5242 (1953)
T.A. Hameed, I.M.E. Radaf, G.B. Sakr, Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 124, 1 (2018)
K.W. Browall, J.S. Kasper, J. Solid State Chem. 28, 20 (1973)
S.M. Girvin, G.D. Mahan, Solid State Commun. 23, 629 (1977)
K. Wakamura, Solid State Ionics 149, 73 (2002)
N. Mahato, A. Banerjee, A. Gupta, S. Omar, K. Balani, Prog. Mater. Sci. 72, 141 (2015)
K. Tuo, C. Sun, S. Liu, Electrochem. Energy Rev. 6, 17 (2023)
Z. Li, J. Fu, X. Zhou, S. Gui, L. Wei, H. Yang, H. Li, X. Guo, Adv. Sci. 10, 2201718 (2023)
J. Kumar, K. Akhila, P. Kumar, R.K. Deshmukh, K.K. Gaikwad, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 148, 6061 (2023)
M. Chocolatl-Torres, A.P. Franco-Bacca, J.A. Ramírez-Rincón, C.L. Gómez-Heredia, F. Cervantes-Alvarez, J.J. Alvarado-Gil, R. Silva-Gonzalez, M. Toledo, U. Salazar-Kuri, Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 126, 1 (2020)
F. Cervantes-Alvarez, J.D. Macias, J.J. Alvarado-Gil, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 51, 065302 (2018)
W. Hagenmuller, van Gool, Application Prospects of Solid Electrolytes (Elsevier, 1978)
I.M. Bolesta, O.V. Futey, O.G. Syrbu, Solid State Ionics 119, 103 (1999)
S.N. Girvin, Solid State Commun. 23, 629 (1977)
R. Sudharsanan, B.P. Clayman, Solid State Ionics 15, 287 (1985)
Acknowledgements
This work was partially funded by project CNR-CINVESTAV 2020: “Exploring the relation between near field and far field thermal emission tailored by coupling phase changing and plasmonic materials” and by CONAHCYT project A1-S-10011. F. C-A thanks to CONAHCYT by fellowship “Investigadores por México”. The authors are grateful to José Bante Guerra for their technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, FC-A, JAC-E, APF-B, and JJA-G; formal analysis, FC-A, JAC-E; funding acquisition JJA-G; investigation, FC-A, JAC-E, and APF-B; methodology, FC-A and JAC-E; resources, US-K, MC-T and JJA-G; supervision, RAM-E, and JJA-G; visualization, APF-B and FC-A; writing—original draft, FC-A and JAC-E; writing—review and editing, FC-A, RAM-E and JJA-G. All authors have read and agreed to publish this version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chan-Espinoza, J.A., Franco-Bacca, A.P., Cervantes-Alvarez, F. et al. Exploring the temperature-dependent phase transitions of the solid electrolytes copper and silver tetraiodomercurates (Cu2, Ag2) HgI4: a study of thermal and electrical conductivities. Appl. Phys. A 130, 169 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-024-07342-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-024-07342-9