Abstract
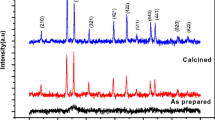
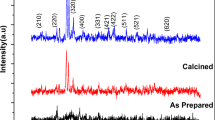
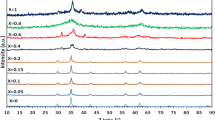
For enhancing the charge storage of nanoparticles by modifying the grains, a novel lithium-doped iron-based nanoparticle (Li2xMn1–xFe2O4) was designed and synthesized. Lithium-doped manganese ferrite (Li2xMn1–xFe2O4) nanoparticles were prepared using sol–gel route with different doping concentrations of lithium, i.e., x = 0, 0.25, 0.50, 0.75, and 1.0 when annealed at 500 °C temperature. The structure (crystal structure and crystallite size), vibrational modes (functional groups of molecules), morphology, and composition were investigated and confirmed by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transformed infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX). The vibrational bands shifted towards high wavenumbers due to small ionic radii of Li+1 to Mn+2 which indicated the successful replacement of lithium with manganese in Li2xMn1–xFe2O4 nanoparticles and redistribution of cations between octahedral and tetrahedral sites. Moreover, the dielectric parameters of Li2xMn1–xFe2O4 nanoparticles were investigated using LCR at room temperature. The dielectric parameters revealed improved dielectric properties (\(\varepsilon_{r}^{^{\prime}}\) 168, \(\varepsilon_{r}^{^{\prime\prime}}\) 332, tanδ 2.63, and σac 3.78 × 10–4 Ω−1 m−1) with increasing concentrations of lithium in Li2xMn1–xFe2O4 nanoparticles owed to increasing Fe2+ ions at the octahedral sites. Furthermore, these Li2xMn1–xFe2O4 nanoparticles offered large places and provoke more active sites for storage due to their high ac-conductivity. Henceforth, it can be suggested that lithium-doped manganese ferrite nanoparticles can be the best candidate for energy storage devices.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Y. Lu et al., Effect of Gd and Co contents on the microstructural, magneto-optical and electrical characteristics of cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 48(2), 2782–2792 (2022)
Z. Heydariyan et al., Insights into impacts of Co3O4-CeO2 nanocomposites on the electrochemical hydrogen storage performance of g-C3N4: Pechini preparation, structural design and comparative study. J. Alloys Compound. 924, 166564 (2022)
M. Amiri et al., Magnetically retrievable ferrite nanoparticles in the catalysis application. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 271, 101982 (2019)
N. Mir et al., Preparation of TiO2 nanoparticles by using tripodal tetraamine ligands as complexing agent via two-step sol–gel method and their application in dye-sensitized solar cells. Mater. Res. Bull. 48(4), 1660–1667 (2013)
S. Zinatloo-Ajabshir et al., Enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic performance for degradation of organic contaminants using PbWO4 nanostructure fabricated by a new, simple and green sonochemical approach. Ultrason. Sonochem. 72, 105420 (2021)
M. Amiri et al., Removal of malachite green (a toxic dye) from water by cobalt ferrite silica magnetic nanocomposite: herbal and green sol-gel autocombustion synthesis. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 42(39), 24846–24860 (2017)
Z. Heydariyan et al., EuMnO3/EuMn2O5/MWCNT nanocomposites: insights into synthesis and application as potential materials for development of hydrogen storage capacity. Fuel 351, 128885 (2023)
M. Salavati-Niasari et al., Pure cubic ZrO2 nanoparticles by thermolysis of a new precursor. Polyhedron 28(14), 3005–3009 (2009)
H. Teymourinia et al., Synthesis of graphene quantum dots from corn powder and their application in reduce charge recombination and increase free charge carriers. J. Mol. Liq. 242, 447–455 (2017)
M. Panahi-Kalamuei et al., Facile microwave synthesis, characterization, and solar cell application of selenium nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compound. 617, 627–632 (2014)
H. Khojasteh et al., Facile reduction of graphene using urea in solid phase and surface modification by N-doped graphene quantum dots for adsorption of organic dyes. Diamond Related Mater. 79, 133–144 (2017)
A.F. Gochuyeva et al., Thermophysical and structural properties of manganese ferrite nanoparticles. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 36(2), 2150542 (2022)
S. Balamurugan et al., Ion and electron-conducting additive effect on Li-ion charge storage performance of CuFe2O4/SiO2 composite aerogel anode. Ceram. Int. 46(16), 25330–25340 (2020)
S. Khan et al., Spinel M0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 (M = Ni Co, and Cu) ferrites for energy storage applications: dielectric, magnetic and electrochemical properties. Ceram. Int. 48(19), 29291–29297 (2022)
H. Mahajan et al., Effect of sintering temperature on structural, morphological, magnetic, and electrochemical properties of Mn0.3Co0.2Zn0.5Fe2O4 Ferrite. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 105(2), 388–404 (2022)
T. Dippong et al., Effect of silica embedding on the structure, morphology and magnetic behavior of (Zn0.6Mn0.4Fe2O4)δ/(SiO2)(100−δ) nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 11(9), 2232 (2021)
T. Dippong et al., Investigation on the formation, structural and photocatalytic properties of mixed Mn-Zn ferrites nanoparticles embedded in SiO2 matrix. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 158, 105281 (2021)
T. Dippong et al., Impact of annealing temperature and ferrite content embedded in SiO2 matrix on the structure, morphology and magnetic characteristics of (Co0.4Mn0.6Fe2O4)δ/(SiO2)(100−δ) nanocomposites. J. Alloys Compound. 868, 159203 (2021)
R. Topkaya et al., Effect of bimetallic (Ni and Co) substitution on magnetic properties of MnFe2O4 nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 42, 13773–13782 (2016)
S. Malathi et al., A study of lithium ferrite and vanadium-doped lithium ferrite nanoparticles based on the structural, optical, and magnetic properties. J. Nanomater. 2, 1–7 (2023)
D. Andhare et al., Effect of Zn doping on structural, magnetic and optical properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles synthesized via Co-precipitation method. Phys. B Condensed Matter. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2020.412051
S. Debnath et al., Effect of cobalt doping on structural parameters, cation distribution and magnetic properties of nickel ferrite nanocrystals. Ceram. Int. 47(12), 16467–16482 (2021)
B. Mali et al., Tuning of magnetic properties in Cr-doped lithium ferrite. J. Alloys Compound. 911, 165036–165077 (2022)
M. Junaid et al., Evaluations of structural, thermal, spectral, and magnetic properties of Li0.5Fe2.5O4 multi magnetic oxide fabricated via sol-gel auto-ignition technique. Ceram. Int. 48(15), 21610–21615 (2022)
T. Dippong et al., Dependence of structural, morphological and magnetic properties of manganese ferrite on Ni-Mn substitution. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23(6), 3097 (2022)
T. Dippong et al., Investigation of structural, morphological and magnetic properties of MFe2O4 (M= Co, Ni, Zn, Cu, Mn) obtained by thermal decomposition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23(15), 8483 (2022)
T. Dippong et al., Influence of Mn2+ substitution with Co2+ on structural, morphological and coloristic properties of MnFe2O4/SiO2 nanocomposites. Mater Charact 172, 110835 (2021)
B. Aslibeiki et al., Nanostructural, magnetic and electrical properties of Ag doped Mn-ferrite nanoparticles. Curr. Appl. Phys. 14(12), 1659–1664 (2014)
R. Jabbar et al., Structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of Mn+2 doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 494, 165726 (2020)
M.A. Yousuf et al., Magnetic and electrical properties of yttrium substituted manganese ferrite nanoparticles prepared via micro-emulsion route. Results Phys. 16, 102973 (2020)
G.R. Gajula et al., Structural, ferroelectric, dielectric, impedance and magnetic properties of Gd and Nb doped barium titanate-lithium ferrite solid solutions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 494, 165822 (2020)
G. Aravind et al., Electrical transport properties of nano crystalline Li–Ni ferrites. J. Mater. 1(4), 348–356 (2015)
Mubasher et al., Comparative study of frequency-dependent dielectric properties of ferrites MFe2O4 (M = Co, Mg, Cr and Mn) nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 126, 334 (2020)
Mubasher et al., Enhancement of lithium ions storage capacity of manganese ferrites through hybridization with multi-walled carbon nanotube. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 34, 147 (2023)
M. Junaid et al., The influence of Zr and Ni co-substitution on structural, dielectric and magnetic traits of lithium spinel ferrites. Ceram. Int. 48(10), 14307–14314 (2022)
K. Mujasam et al., Study of dielectric and impedance properties of Mn ferrites. Phys. B Condensed Matter. 406(3), 382–387 (2011)
R. Jain et al., Influence of Fe2+ substitution on FTIR and Raman spectra of Mn ferrite nanoparticles. Vib. Spectrosc. 126, 103540 (2023)
I. Sadiq et al., Structural and dielectric properties of doped ferrite nanomaterials suitable for microwave and biomedical applications. Progress Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 25(5), 419–424 (2015)
P. Donta et al., Structural, morphological, dielectric behavior and AC conductivity of GaxFe(3–x)O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 562, 169809 (2022)
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M: conceptualization, methodology, supervision, formal analysis, writing—original draft preparation. MM: methodology, supervision, formal analysis. HA, HUT, MA: reviewing and editing experimental design. AI, MI-u-H, MFS: formal analysis, software, data curation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Not applicable. Also declare that authors have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
Not applicable. Also declare that this paper is original and has not been submitted or is not being considered for publication elsewhere. Furthermore, all authors have seen and approved the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mubasher, Mumtaz, M., Ali, H. et al. Effect of lithium doping on frequency-dependent dielectric properties of manganese ferrite nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 130, 99 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-07251-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-07251-3