Abstract
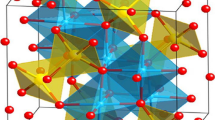
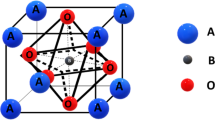
In this study, researchers investigated the potential of nanostructured gadolinium-doped bismuth ferrite (Bi0.9Gd0.1FeO3) thin film as an electrode material for supercapacitors. The thin film was synthesized using the sol–gel method and deposited onto a Si/SiO2/TiO2/Pt substrate using spin coating. X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements confirmed a rhombohedral distorted perovskite structure. Morphological analysis with SEM and AFM revealed the presence of nanorod-like structures, approximately 200 nm thick. FTIR spectroscopy confirmed the functional groups in the film. Through electrochemical measurements, including cyclic voltammetry (CV), galvanostatic charge and discharge (GCD), and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), a significant specific capacitance of 812 F/g was observed, indicating promising supercapacitor performance through superficial faradic reactions. The findings suggest that gadolinium-doped bismuth ferrite thin films hold potential as effective electrode materials for supercapacitors when operating in a liquid environment.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the document. Raw data that supoort the findings of this study are available from the correaponding author, upon responsable request.
References
F. Shi et al., Metal oxide/hydroxide-based materials for supercapacitors. RSC Adv. 4(79), 41910–41921 (2014)
I. Shaheen, I. Hussain, T. Zahra, M.S. Javed, S.S.A. Shah, K. Khan, K. Zhang, Recent advancements in metal oxides for energy storage materials: design, classification, and electrodes configuration of supercapacitor. J Energy Storage. 72, 108719 (2023)
M. Mustaqeem, G.A. Naikoo, M. Yarmohammadi, M.Z. Pedram, H. Pourfarzad, R.A. Dar, Y.F. Chen, Rational design of metal oxide-based electrode materials for high performance supercapacitors–a review. J Energy Storage 55, 105419 (2022)
A. Kumar, H.K. Rathore, D. Sarkar, A. Shukla, Nanoarchitectured transition metal oxides and their composites for supercapacitors. Electrochem Sci Adv 2(6), e2100187 (2022)
S. Wustoni, D. Ohayon, A. Hermawan, A. Nuruddin, S. Inal, Y.S. Indartono, B. Yuliarto, Material design and characterization of conducting polymer-based supercapacitors. Polym. Rev. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1080/15583724.2023.2220131
M.I. Ul Hoque, R. Holze, Intrinsically conducting polymer composites as active masses in supercapacitors. Polymers 15(3), 730 (2023)
R. Chandrashekhar, A.A. Yadav, Spray-deposited cobalt-doped RuO2 electrodes for high-performance supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 437, 141521 (2023)
Q. Wang, M. Wang, J. Sun, X. Zhang, W. Chen, X. Yu, W. Fan, Different assembled nano-MnO2 fiber supercapacitors applied for smart wearable clothing. Text. Res. J. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1177/00405175231181088
V.V. Jadhav, M.K. Zate, S. Liu, M. Naushad, R.S. Mane, K.N. Hui, S.H. Han, Mixed-phase bismuth ferrite nanoflake electrodes for supercapacitor application. Appl. Nanosci. 6(4), 511–519 (2016)
Dutta, N., Bandyopadhyay, S. K., Rana, S., Sen, P., & Himanshu, A. K. (2013). Remarkably high value of capacitance in BiFeO3 Nanorod. arXiv preprint arXiv:1309.5690. Accessed 23 Sep 2013.
P. Godara, A. Agarwal, N. Ahlawat, S. Sanghi, Crystal structure refinement, dielectric and magnetic properties of Sm modified BiFeO3 multiferroic. J. Mol. Struct. 1097, 207–213 (2015)
V.A. Khomchenko, J.A. Paixao, V.V. Shvartsman, P. Borisov, W. Kleemann, D.V. Karpinsky, A.L. Kholkin, Effect of Sm substitution on ferroelectric and magnetic properties of BiFeO3. Scripta Mater. 62(5), 238–241 (2010)
A. Mukherjee, S. Basu, P.K. Manna, S.M. Yusuf, M. Pal, Giant magnetodielectric and enhanced multiferroic properties of Sm doped bismuth ferrite nanoparticles. J Mater Chem C 2(29), 5885–5891 (2014)
T. Sindhu, A.T. Ravichandran, A.R. Xavier, M. Kumaresavanji, Structural, surface morphological and magnetic properties of Gd-doped BiFeO3 nanomaterials synthesised by EA chelated solution combustion method. Appl. Phys. A 129(10), 685 (2023)
P. Kumar, P. Chand, Structural, electric transport response and electro-strain-polarization effect in La and Ni modified bismuth ferrite nanostructures. J. Alloy. Compd. 748, 504–514 (2018)
P. Veluswamy, S. Sathiyamoorthy, P. Santhoshkumar, G. Karunakaran, C.W. Lee, D. Kuznetsov, H. Ikeda, Sono-synthesis approach of reduced graphene oxide for ammonia vapour detection at room temperature. Ultrasonicssonochemistry 48, 555–566 (2018)
C. Anthonyraj, M. Muneeswaran, S.G. Raj, N.V. Giridharan, V. Sivakumar, G. Senguttuvan, Effect of samarium doping on the structural, optical and magnetic properties of sol–gel processed BiFeO 3 thin films. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26(1), 49–58 (2015)
C.A. Kumar, G.G. Rao, K. Samatha, S. Bharadwaj, M.P. Dasari, Observation on magnetic variation for low concentration of bismuth and samarium doped Ni–Co ferrites. Karbala Int J Mod Sci 4(1), 143–150 (2018)
H. Wu, P. Xue, Y. Lu, X. Zhu, Microstructural, optical and magnetic characterizations of BiFeO3 multiferroic nanoparticles synthesized via a sol-gel process. J. Alloy. Compd. 731, 471–477 (2018)
R.A. Golda, A. Marikani, E.J. Alex, Enhancement of dielectric, ferromagnetic and electrochemical properties of BiFeO3 nanostructured films through rare earth metal doping. Ceram. Int. 46(2), 1962–1973 (2020)
Andrzejewski, B., Chybczynska, K., Hilczer, B., Blaszyk, M., Lucinski, T., Matczak, M., &Kepinski, L. (2014). Controlled growth of bismuth ferrite multiferroic flowers. arXiv preprint arXiv:1402.1336. Accessed 6 Feb 2014
A. Sarkar, A.K. Singh, D. Sarkar, G.G. Khan, K. Mandal, Three-dimensional nanoarchitecture of BiFeO3 anchored TiO2 nanotube arrays for electrochemical energy storage and solar energy conversion. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 3(9), 2254–2263 (2015)
Z. Yin, Q. Zheng, S.C. Chen, D. Cai, L. Zhou, J. Zhang, BandgapTunable Zn1-xMgxO thin films as highly transparent cathode buffer layers for high-performance inverted polymer solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 4(7), 1301404 (2014)
I.I. Suni, Impedance methods for electrochemical sensors using nanomaterials. TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem. 27(7), 604–611 (2008)
H. Haromae, P. Pattananuwat, Preparation of bismuth ferrite as photo-supercapacitive electrode. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng. 600(1), 012005 (2019)
S. Jo, S. Pak, Y.W. Lee, S. Cha, J. Hong, J.I. Sohn, Enhancing the electrochemical energy storage performance of bismuth ferrite supercapacitor electrodes via simply induced anion vacancies. Int. J. Energy Res. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/2496447
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EJA, BGM, and RAG: devised the project, the main conceptual ideas and proof outline. BGM and RAG carried out the experiments. BGM and RAG: wrote the manuscript with the support from EJA. EJA: contributed to the results interpretation and final version of the manuscript. All the authors provided official feedback and helped shape of the research, analysis and manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alex, E.J., Manju, B.G. & Golda, R.A. Improved electrochemical properties of nanostructured Bi0.9Gd0.1FeO3 thin film as electrode material for supercapacitors. Appl. Phys. A 130, 97 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-07226-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-07226-4