Abstract
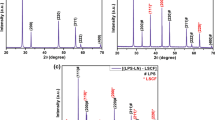
This paper, it is aimed that nanometer-sized powders can be successfully prepared by using the sol–gel process so that sintering temperatures can be reduced and they can be used as suitable electrolyte candidate materials for medium-temperature SOFC applications. Fort his, bare CeO2 (cerium dioxide), which has not yet been encountered in the literature, and La,Cu co-doped CeO2 nanoparticles with different molar ratios (1%, 5%, and 10%) were synthesized as electrolyte material using the sol–gel method for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells (IT-SOFCs) applications. The synthesized samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), UV–Vis spectroscopy, and particle size analysis techniques. In order to examine the effect of doping, the structural, morphological, and optical properties of bare cerium oxide and doped cerium oxide powders were compared. With the doping process, reductions in average particle sizes were observed, and it was determined that the sample with the lowest average particle size was 5% (La, Cu) co-doped CeO2. It has been confirmed by XRD and SEM/EDX that bare CeO2 and co-doped CeO2 powder synthesized have been successfully achieved by the sol–gel technique. The results show that the La,Cu co-doped CeO2 sample is promising as an electrolyte material in SOFC applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
S. Biswas, S.S. Rathore, A.P. Kulkarni, S. Giddey, S. Bhattacharya, Energies (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/en14154517
J.W. Fergus, J. Power. Sources (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.06.062
D.A. Katrana, G.R. Kumar, C. Prerna, B.K. Amarsinht, V. Sabarinathan, T.R. Rajesekaran, J. Mater. Sci. Electro. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03612-3
Y. Zheng, H. Gu, H. Chen, L. Gao, X. Zhu, L. Guo, Mater. Res. Bull. (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2008.09.021
F. Aydin, I. Demir, M.D. Mat, Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2014.02.003
B. Xu, H. Yang, Q. Zhang, S. Yuan, A. Xie, M. Zhang, T. Ohno, ChemCatChem (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201902309
S. Chahal, S. Singh, A. Kumar, P. Kumar, Vacuum (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2020.109395
E. Kumar, P. Selvarajan, D. Muthuraj, Mater. Res. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-14392013005000021
X. Hou, Q. Lu, X. Wang, J. Sci, Adv. Mater. Devices. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsamd.2017.02.006
M. Mousavi-Kamazani, F. Azizi, Ultrason. Sonochem.. Sonochem. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.104695
P. Ebrahimi, A. Kumar, M. Khraisheh, Catalysts (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12101101
M. Michalska, K. Lemański, A. Sikora, Heliyon. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06958
B. Wang, B. Zhu, S. Yun, W. Zhang, C. Xia, M. Afzal, H. Wang, NPG Asia Mater. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41427-019-0152-8
Y. Liu, H. Qin, M. Li, J. Cheng, C. Tang, J. Xiao, Y. Xie, Ionics (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-022-04677-2
C. Dejoie, Y. Yu, F. Bernardi, N. Tamura, M. Kunz, M.A. Marcus, Z. Liu, Z. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c08284
A. Solovyev, A. Shipilova, E. Smolyanskiy, S. Rabotkin, V. Semenov, Membranes (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12090896
F. Hossam, A.M. Elseman, M. Rasly, R.M. Mahani, S.A. Sayed, M.M. Rashad, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10901-0
Y. Zheng, M. Zhou, L. Ge, S. Li, H. Chen, L. Guo, J. Alloys Compd. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.09.203
D. Chen, G. Yang, Z. Shao, F. Ciucci, Electrochem. Commun.. Commun. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2013.08.017
D.E. Puente-Martínez, J.A. Díaz-Guillén, S.M. Montemayor, J.C. Díaz-Guillén, O. Burciaga-Díaz, M.E. Bazaldúa-Medellín, A.F. Fuentes, Int. J. Hydrog. EnergyHydrog. Energy (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.11.032
F. Zhang, W. Chan, J.E. Spanier, E. Apak, Q. Jin, R.D. Robinson, I.P. Herman, Appl. Phys. Lett. (2002). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1430502
S. Liang, E. Broitman, Y. Wang, A. Cao, G. Veser, J. Mater. Sci. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-5168-y
G. Killivalavan, B. Sathyaseelan, G. Kavitha, I. Baskarann, K. Senthilnathan, D. Sivakumar, M. Maaza, MRS Adv. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1557/adv
G. Killivalavan, A.C. Prabakar, K.C.B. Naidu, B. Sathyaseelan, G. Rameshkumar, D. Sivakumar, B.R. Rao, Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. (2020). https://doi.org/10.33263/BRIAC102.306311
P.P. Tumkur, N.K. Gunasekaran, B.R. Lamani, N. Nazario-Bayon, K. Prabhakaran, J.C. Hall, G.T. Ramesh, Nanomanufacturing (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing1030013
Q. Sun, Z. Fu, Z. Yang, Ceram. Int. Int. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.11.149
P. Makuła, M. Pacia, W. Macyk, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.8b02892
P.U. Aparna, N.K. Divya, P.P. Pradyumnan, J Mater Sci Chem Eng. (2016). https://doi.org/10.4236/msce.2016.42009
E. Jothinathan, K. Vanmeensel, J. Vleugels, O.V. Biest, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. Eur Ceram Soc. (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.01.003
F.A. Unal, S. Ok, M. Unal, S. Topal, K. Cellat, F. Şen, J. Mol. Liq. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.112177
E. Moghaddam, A.A. Youzbashi, A. Kazemzadeh, M.J. Eshraghi, Appl. Surf. Sci. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.03.207
S. Samiee, E.K. Goharshadi, Mater. Res. Bull. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2011.12.058
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Alanya Alaaddin Keykubat University, Scientific Research Projects Coordinatorship under Project Number 2022-02-03-LAP05. The author would like to thank undergraduate student Kübra Nur Küçük for her help during the experimental phase.
Funding
The author did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work. No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript. No funding was received for conducting this study. No funds, grants, or other support was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The author contributed to all stages of the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No financial interest or any conflict of interest exists.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Aydın Ünal, F. Synthesis and characterization of (La, Cu) co-doped CeO2 nanomaterials used as electrolyte material in SOFC applications. Appl. Phys. A 129, 817 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-07114-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-07114-x