Abstract
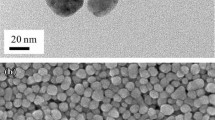
Pulsed laser ablation can be used to repair misprinted patterns in printed electronics. The properties of the conductive ink varied with sintering temperature. This property variation significantly affected the ablation process. Thus, we compared the pulsed laser scanning ablation of dried Ag nanoparticle (NP) layers, which were sintered at 150 ℃, and sintered at 200 ℃ with quantitative evaluations. With higher thermal diffusion, the AgNP layer sintered at higher temperatures had more protruding Ag parts at the ablated line boundary. Ablation threshold fluence values of 264, 547, and 1370 mJ/cm2 were obtained for the Ag NP layers that were dried, sintered at 150 ℃, and sintered at 200 ℃ using D2-law fittings, respectively. For the ablation process, the increase in the protruding Ag parts and the increase in the ablation threshold fluence would be problematic. For the sintered AgNP layers, D2-law predicted the ablation threshold fluence quite well. The sintering temperature of the Ag NPs affects the ablation phenomenon by changing the surface morphology and physical properties of the pre-sintered layer.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request from the authors.
References
A. Hussain, H. Lee, Y. Moon, H. Kang, S. Moon, J. Hwang, Temperature estimation during pulsed laser sintering of silver nanoparticles. Appl. Sci. 12, 3467 (2022)
Y.H. Wang, D.X. Du, H. Xie, X.B. Zhang, K.W. Lin, K. Wang, E. Fu, Printability and electrical conductivity of silver nanoparticle-based conductive inks for inkjet printing. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 496–508 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04828-z
A. Alam, G. Saeed, S.M. Hong, S. Lim, Development of 3d-printed MWCNTs/AC/BNNTs ternary composite electrode material with high-capacitance performance. Appl. Sci. 11, 2636 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062636
I. Lee, A. Hussain, H.L. Lee, Y.J. Moon, J.Y. Hwang, S.J. Moon, The effect of current supply duration during stepwise electrical sintering of silver nanoparticles. Metals (Basel). 11, 1878 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/met11111878
D. Kim, A. Hussain, H.L. Lee, Y.J. Moon, J. Hwang, S.J. Moon, Stepwise current increment sintering of silver nanoparticle structures. Crystals 11, 1264 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11101264
S. Lai, G. Casula, P.C. Ricci, P. Cosseddu, A. Bonfiglio, All-organic, low voltage, transparent and compliant organic field-effect transistor fabricated by means of large-area, cost-effective techniques. Appl. Sci. 10, 6656 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/APP10196656
H.H. Lee, K. Sen Chou, K.C. Huang, Inkjet printing of nanosized silver colloids. Nanotechnology. 16, 2436–2441 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/16/10/074
S.H. Ko, H. Pan, C.P. Grigoropoulos, C.K. Luscombe, J.M.J. Fréchet, D. Poulikakos, All-inkjet-printed flexible electronics fabrication on a polymer substrate by low-temperature high-resolution selective laser sintering of metal nanoparticles. Nanotechnology (2007). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/18/34/345202
J. Perelaer, A.W.M. De Laat, C.E. Hendriks, U.S. Schubert, Inkjet-printed silver tracks: low temperature curing and thermal stability investigation. J. Mater. Chem. 18, 3209–3215 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1039/b720032c
D. Kim, J. Moon, Highly conductive ink jet printed films of nanosilver particles for printable electronics. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 8, J30–J33 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2073670
M. Moras, C. Martínez-Domingo, R. Escudé, C. Herrojo, F. Paredes, L. Terés, F. Martín, E. Ramon, Programmable organic chipless rfid tags inkjet printed on paper substrates. Appl. Sci. 11, 7832 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/app11177832
S.H. Ko, Y. Choi, D.J. Hwang, C.P. Grigoropoulos, J. Chung, D. Poulikakos, Nanosecond laser ablation of gold nanoparticle films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 141126 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2360241
S.H. Ko, H. Pan, D.J. Hwang, J. Chung, S. Ryu, C.P. Grigoropoulos, D. Poulikakos, High resolution selective multilayer laser processing by nanosecond laser ablation of metal nanoparticle films. J. Appl. Phys. (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2802302
J. Chung, S. Han, D. Lee, S. Ahn, C.P. Grigoropoulos, J. Moon, S.H. Ko, Nanosecond laser ablation of silver nanoparticle film. Opt. Eng. 52, 024302 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.oe.52.2.024302
A. Miotello, R. Kelly, Laser-induced phase explosion: new physical problems when a condensed phase approaches the thermodynamic critical temperature. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 69(Suppl), S67–S73 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003399900296
L.V. Zhigilei, B.J. Garrison, Microscopic mechanisms of laser ablation of organic solids in the thermal and stress confinement irradiation regimes. J. Appl. Phys. 88, 1281–1298 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.373816
Y.J. Moon, H. Kang, K. Kang, S.J. Moon, J. Young hwang, Effect of thickness on surface morphology of silver nanoparticle layer during furnace sintering. J. Electron. Mater. 44, 1192–1199 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-015-3639-2
I.S. Lee, K. Ryu, K.H. Park, Y.J. Moon, J.Y. Hwang, S.J. Moon, Temperature effect on physical properties and surface morphology of printed silver ink during continuous laser scanning sintering. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 108, 1960–1968 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2016.11.095
J.H. Choi, K. Ryu, K. Park, S.J. Moon, Thermal conductivity estimation of inkjet-printed silver nanoparticle ink during continuous wave laser sintering. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 85, 904–909 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2015.01.056
J.M. Liu, Simple technique for measurements of pulsed Gaussian-beam spot sizes. Opt. Lett. 7, 196–198 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1364/ol.7.000196
A. Bogaerts, Z. Chen, Effect of laser parameters on laser ablation and laser-induced plasma formation: a numerical modeling investigation. Spectrochim Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 60, 1280–1307 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sab.2005.06.009
Y. Zhang, D. Zhang, J. Wu, Z. He, X. Deng, A thermal model for nanosecond pulsed laser ablation of aluminum. AIP Adv. 7, 075010 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4995972
A. Hussain, H.-L. Lee, Y.-J. Moon, J.Y. Hwang, S.-J. Moon, Effect of pulse overlapping on temperature field and physical characteristics in pulsed laser sintering of inkjet-printed silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 202, 123678 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2022.123678
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), titled “Development of Coal Analyzing System Using Laser-induced Breakdown Spectroscopy for Clean Coal Power Plant” (No. NRF-2016R1D1A1B03935556).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: SJM, JYH, and H-LL. Methodology: Y-JM, and H-LL; Formal analysis and investigation: SJM, JYH, and H-LL; Writing—original draft preparation: H-LL; Writing—review and editing: SJM; Funding acquisition: JYH and SJM; Resources: JYH; Supervision: SJM and JYH.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests or personal relationships that may have influenced the work reported in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, HL., Hussain, A., Moon, YJ. et al. Influence of pre-sintering on the nanosecond pulsed laser ablation patterns of spin-coated silver nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 129, 705 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06964-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06964-9