Abstract
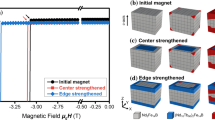
Grain boundary diffusion (GBD) process is an effective method to fabricate high-coercive Nd-Fe-B magnets with less consumption of heavy rare earth (HRE). By this approach, HRE-rich shell forms around the Nd2Fe14B grain, which can hinder the magnetic reversal starting at the edge of the grains and enhance the coercivity of whole magnet. Recently, an anti-core–shell structure was observed in the HRE diffused magnets after over-saturated diffusion, where the HRE concentration in the core is even higher than that in the shell. In this work, the effects of the anti-core–shell structure on the magnetization reversal and magnetic properties of diffused magnet have been clarified by micromagnetic simulations. Three-dimension models were established to analyze the demagnetization process. The results indicate that the anti-core–shell structure leads to a large stray field, which will accelerate the magnetization reversal of the whole magnet. As a result, the beneficial effect of HRE GBD on the coercivity has been reduced. Combined with the existing experimental results, the formation of anti-core–shell structure should be avoided during diffusion. Hence, appropriate diffusion time and diffusion source dosage should be selected for GBD process in order to obtain high-performance products and efficiently use the HRE resources.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
O. Gutfleisch, M.A. Willard, E. Bruck, C.H. Chen, S.G. Sankar, J.P. Liu, Magnetic materials and devices for the 21st century: stronger, lighter, and more energy efficient. Adv. Mater. 23, 821–842 (2011)
J. He, Z. Yu, J. Cao, W. Song, K. Xu, W. Fan, H. Yu, X. Zhong, H. Mao, C. Mao, Z. Liu, Rationally selecting the chemical composition of the Nd–Fe–B magnet for high-efficiency grain boundary diffusion of heavy rare earths. J. Mater. Chem. C 10, 2080–2088 (2022)
N. Oono, M. Sagawa, R. Kasada, H. Matsui, A. Kimura, Production of thick high-performance sintered neodymium magnets by grain boundary diffusion treatment with dysprosium–nickel–aluminum alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 297–300 (2011)
R. Grossinger, X.K. Sun, R. Eibler, K.H.J. Buschow, H.R. Kirchmayr, Temperature dependence of anisotropy fields and initial susceptibilities in R2Fe14B compounds. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 58, 55–60 (1986)
J.F. Herbst, R2Fe14B materials: intrinsic properties and technological aspects. Rev. Mod. Phys. 63, 819–898 (1991)
S. Hirosawa, Y. Matsuura, H. Yamamoto, S. Fujimura, M. Sagawa, H. Yamauchi, Magnetization and magnetic anisotropy of R2Fe14B measured on single crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 59, 873–879 (1986)
Z. Liu, J. He, R.V. Ramanujan, Significant progress of grain boundary diffusion process for cost-effective rare earth permanent magnets: a review. Mater. Des. 209, 110004 (2021)
J. He, J. Cao, Z. Yu, W. Song, H. Yu, M. Hussain, Z. Liu, Grain boundary diffusion sources and their coating methods for Nd-Fe-B permanent magnets. Metals 11, 1434 (2021)
Z. Liu, J. He, Q. Zhou, Y. Huang, Q. Jiang, Development of non-rare earth grain boundary modification techniques for Nd-Fe-B permanent magnets. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 98, 51–61 (2022)
S. Sugimoto, Current status and recent topics of rare-earth permanent magnets. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 44, 064001 (2011)
H. Nakamura, K. Hirota, M. Shimao, T. Minowa, M. Honshima, Magnetic properties of extremely small Nd-Fe-B sintered magnets. IEEE Trans. Magn. 41, 3844–3846 (2005)
T.-H. Kim, S.-R. Lee, H.-J. Kim, M.-W. Lee, T.-S. Jang, Simultaneous application of Dy–X (X = F or H) powder doping and dip-coating processes to Nd-Fe-B sintered magnets. Acta Mater. 93, 95–104 (2015)
K. Loewe, D. Benke, C. Kübel, T. Lienig, K.P. Skokov, O. Gutfleisch, Grain boundary diffusion of different rare earth elements in Nd-Fe-B sintered magnets by experiment and FEM simulation. Acta Mater. 124, 421–429 (2017)
K. Lu, X. Bao, M. Tang, G. Chen, X. Mu, J. Li, X. Gao, Boundary optimization and coercivity enhancement of high (BH)max Nd-Fe-B magnet by diffusing Pr-Tb-Cu-Al alloys. Scr. Mater. 138, 83–87 (2017)
K. Lu, X. Bao, M. Tang, L. Sun, J. Li, X. Gao, Influence of annealing on microstructural and magnetic properties of Nd-Fe-B magnets by grain boundary diffusion with Pr-Cu and Dy-Cu alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 441, 517–522 (2017)
Y. Liu, J. He, H. Yu, Z. Liu, G. Zhang, Restoring and enhancing the coercivity of waste sintered (Nd, Ce, Gd)FeB magnets by direct Pr-Tb-Cu grain boundary diffusion. Appl. Phys. A 126, 657 (2020)
L. Zhao, J. He, W. Li, X. Liu, J. Zhang, L. Wen, Z. Zhang, J. Hu, J. Zhang, X. Liao, K. Xu, W. Fan, W. Song, H. Yu, X. Zhong, Z. Liu, X. Zhang, Understanding the role of element grain boundary diffusion mechanism in Nd–Fe–B magnets. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 2109529 (2022)
H. Sepehri-Amin, J. Liu, T. Ohkubo, K. Hioki, A. Hattori, K. Hono, Enhancement of coercivity of hot-deformed Nd-Fe-B anisotropic magnet by low-temperature grain boundary diffusion of Nd60Dy20Cu20 eutectic alloy. Scr. Mater. 69, 647–650 (2013)
K. Löewe, C. Brombacher, M. Katter, O. Gutfleisch, Temperature-dependent Dy diffusion processes in Nd-Fe-B permanent magnets. Acta Mater. 83, 248–255 (2015)
T.-H. Kim, T.T. Sasaki, T. Koyama, Y. Fujikawa, M. Miwa, Y. Enokido, T. Ohkubo, K. Hono, Formation mechanism of Tb-rich shell in grain boundary diffusion processed Nd-Fe-B sintered magnets. Scr. Mater. 178, 433–437 (2020)
K.Ž Soderžnik, K.Ž Rožman, M. Komelj, A. Kovács, P. Diehle, T. Denneulin, A. Savenko, M. Soderžnik, S. Kobe, R.E. Dunin-Borkowski, J. Mayer, B. Markoli, S. Šturm, Microstructural insights into the coercivity enhancement of grain-boundary-diffusion-processed Tb-treated Nd-Fe-B sintered magnets beyond the core-shell formation mechanism. J. Alloys Compd. 864, 158915 (2021)
W. Li, Q. Zhang, Q. Zhu, S. Xiao, C. Xu, L. Yang, B. Zheng, S. Mao, Z. Song, Formation of anti-shell/core structure of heavy rare earth elements (Tb, Dy) in sintered Nd-Fe-B magnet after grain boundary diffusion process. Scr. Mater. 163, 40–43 (2019)
S. SDVSS Varma, K.R. Mangipudi, P.R. Budarapu, A coupled quantum-molecular mechanics approach for performance analysis of defective Silicon based photovoltaic solar cells. Phys. Scripta 98, 35007 (2023)
S.M. Dsouza, T.M. Varghese, P.R. Budarapu, S. Natarajan, A Non-intrusive stochastic isogeometric analysis of functionally graded plates with material uncertainty. Axioms 9(3), 92 (2020)
W. Li, Q. Zhou, L.Z. Zhao, Q.X. Wang, X.C. Zhong, Z.W. Liu, Micromagnetic simulation of anisotropic grain boundary diffusion for sintered Nd-Fe-B magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 451, 704–709 (2018)
A. Vansteenkiste, J. Leliaert, M. Dvornik, M. Helsen, F. Garcia-Sanchez, B. Van Waeyenberge, The design and verification of MuMax3. AIP Adv. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4899186
T. Schrefl, J. Fidler, Finite element modeling of nanocomposite magnets. IEEE Trans. Magn. 35, 3223–3228 (1999)
K. Hono, H. Sepehri-Amin, Strategy for high-coercivity Nd-Fe-B magnets. Scr. Mater. 67, 530–535 (2012)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U21A2052), Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Fund Project (No. 2022A1515240060) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2023M733642).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., He, J., Yuan, B. et al. The role of anti-core–shell structure caused by over-saturation diffusion of heavy rare earths in Nd-Fe-B magnets: a micromagnetic simulation study. Appl. Phys. A 129, 619 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06905-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06905-6