Abstract
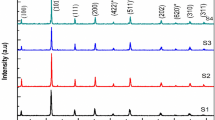
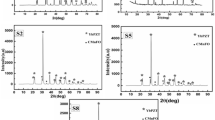
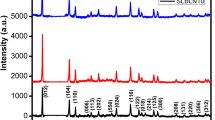
Multiferroic composites offer promising prospects for low-power multifunctional devices. Here, we report the structural, electrical, dielectric, magnetic, and magnetodielectric properties of the multiferroic composite material (1 − x)LiNbO3–xLa0.9Na0.1MnO3 (where x = 0.1, 0.2, and 0.3). Ferroelectric and magnetic phases were synthesized using citrate gel method and the conventional solid-state reaction method was used for the preparation of multiferroic composite material with different mixing percentage values of x. X-ray diffraction was used to confirm the crystalline purity and the crystal structure of the material. The microstructural and elemental composition analyses were done by FE-SEM, X-ray photon spectroscopic (XPS), and EDAX techniques. Dielectric studies and impedance analysis imply the dynamic behavior of charge carriers inside the composites. The maximum value of dielectric constant (5000) was obtained at x = 0.3 for xLa0.9Na0.1MnO3 phase. From impedance analysis method, the equivalent circuit of (1 − x)LiNbO3–xLa0.9Na0.1MnO3 (where x = 0.1, 0.2, and 0.3) composite was found out. The P–E hysteresis loop reveals the ferroelectric nature of the composite. Sample with x = 0.1 of xLa0.9Na0.1MnO3 phase gives the highest values for maximum polarization and remnant polarization. The enhanced magnetic properties of the composite material were substantiated with M–H hysteresis loop measurements. The magnetodielectric and magnetoelectric coupling measurements revealed the presence of ferroelectric and ferromagnetic coupling nature of the composite material. From all these analyses, the multiferroic composites with the composition x = 0.3(La0.9Na0.1MnO3) yields the maximum ferroelectric and magnetic coupling behavior. So, this composite material has wide applications in multifunctional nano devices.





















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data available on request from the authors.
References
M. Fiebig, Revival of the magnetoelectric effect. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 38, R123 (2005)
H. Schmid, Multi-ferroicmagnetoelectrics. Ferroelectrics 162, 317–338 (1994)
Biao Wang, Multiferroic materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 8,377–441 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33596-9_8
J. Van Suchtelen, Product Properties: A New Application Of Composite Materials. Phillips Research Reports 27, 28–37 (1972)
V.J. Folen, G.T. Rado, E.W. Stalder, Anistropy of the magnetodielectric effect in Cr2O3. Phys. Rev. Lett. 6, 607–608 (1961)
K. Bhoi, H.S. Mohanty, Ravikant, M.F. Abdullah, D.K. Pradhan, Unravelling the nature of magneto-electric coupling in room temperature multiferroic particulate (PbFe0.5Nb0.5O3)–(Co0.6Zn0.4Fe1.7Mn0.3O4) composites. Sci. Rep. 11, 3149 (2021)
Y. Cheng, B. Peng, Z. Hu, Z. Zhou, M. Liu, Recent development and status magnetoelectric materials and devices. Phys. Lett. A 382, 3018–3025 (2018)
C.W. Nan, N. Cai, L. Liu, J. Zhai, Y. Ye, Y. Lin, Coupled magnetic–electric properties and critical behaviour in multiferroic particulate composites. J. Appl. Phys. 94, 5930–5936 (2003)
C.S. Werner, S.J. Herr, K. Buse, B. Sturman, E. Soergel, C. Razzaghi, I. Breunig, Large and accessible conductivity of charged domain walls in lithium niobate. Sci. Rep. 7, 1–8 (2017)
M.A. Fakhri, Y. Al-Douri, U. Hasim, Optical investigations of photonics lithium niobate. Sol. Energy 120, 381–388 (2015)
C. Diaz-Moreno, R. Farois, A. Hurtado-Macias, J. Elizalde-Galindo, J. Hernandez-Paz, Multiferroic response of nanocrystalline lithium niobate. J. Appl. Phys. 111, 07D907 (2012)
M.C. Mozzati, L. Malavasi, C.B. Azzoni, Magnetic properties of nanostructured sodium-doped lanthanum manganites. J. Magn. Magn. Matter 1579, 272–276 (2004)
S. Roy, Y.Q. Guo, S. Venkatesh, N. Ali, Interplay structure and transport properties of sodium-doped lanthanum manganite. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 13, 9547–9559 (2001)
A.I. Tovstolytkin, V.M. Tsmots, L.I. Pankiv, P.G. Litovchenko, Magnetic and magnetoresistive properties of sodium substituted lanthanum manganites. J. Low Temp. Phys. 36, 220–225 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3331493
G.H. Rao, J.R. Sun, K. Barner, N. Hamad, Crystal structure and magnetoresistance of Na-doped LaMnO3. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 11, 1523–1528 (1999)
D. Dhruv, B. Kataria, B. Kataria, C.M. Thaker, S. Rayaprol, C.L. Prajapat, M.R. Singh, P.S. Solanki, D.G. Kuberkar, N.A. Shah, Ceram. Int. 41, 7162–7173 (2015)
A. El Bacheri, M. El Hasnaoui, A. Louardi, A. Narjis, Structural and dielectric studied for the conduction mechanism analyses of Lithium niobate oxide ferroelectric ceramics. Phys. B Condens. Matter 57, 181–187 (2019)
E.A. Skryleva, B.R. Senatulin, D.A. Kiselev, T.S. Ilina, D.A. Podgorny, Y.N. Parkhomenko, Ar gas cluster ion beam assisted XPS study of LiNbO3 Zcut surface. Surf. Interfaces 26, 101428 (2021)
A. Machocki, T. Ioannides, Manganese–lanthanum oxides modified with silver for the catalytic combustion of methane. J. Catal. 227, 282–296 (2004)
N. Adhlakha, K.L. Yadav, Structural, dielectric, magnetic, and optical properties of Ni0.75Zn0.25FeO4-BiFeO3. J. Mater. Sci. 49, 4423–4438 (2014)
S. Kumar, Ravikant, R. Kurchania, A. Kumar, Dielectric and Impedance spectroscopic study of lithium doped potassium tantalum niobium. Ceram. Int. 45, 17137–17143 (2019)
A. Srivastava, A.K. Singh, O.N. Srivastava, Magnetic and dielectric properties of La and Ni Co-substituted BiFeO3 nanoceramics. Front. Phys. 282, 8 (2020)
F.S. Shanta, A.K. Matique Ullah, M.F. Kabir, A.N. Tamanna, structural, electrical and magnetic properties of Ba1−xAlxTi0.5Mn0.5O3 (x = 0.0–0.3) Perovskites, J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 28, 2447–2454 (2018)
A.M. Abdeen, Dielectric behaviour in Ni–Zn ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 192, 121–129 (1999)
P.P. Mohapatraa, S. Pittala, P. Dobbidi, Temperature dependent broadband dielectric, magnetic and electrical studies on Li1−xMg2xFe5−xO8 for microwave devices. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 2992–3004 (2020)
R.M. Henson, R.R. Zeyfang, K.V. Kiehl, Dielectric and electromechanical properties of (Li, Na)NbO3 ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 60, 15–17 (1977)
H. Du, W. Zhou, D. Zhu et al., Sintering, characteristic, microstructure, and dielectric relaxor behavior of (K0.5Na0.5)NbO3–(Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3 lead-free ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 91, 2903–2909 (2018)
M. Rawat, K.L. Yadav, Study of structural, electrical, magnetic and optical properties of 0.65BaTiO3–0.35Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3-BiFeO3 multiferroic composite. J. Alloys Compd. 597, 188–199 (2014)
A. Kumar, B.P. Singh, R.N.P. Choudhary, A.K. Thakur, Impedance analysis of the effect of dopant concentration on electrical properties of calcium modified BaSnO3. J. Alloys Compd. 394, 292–302 (2005)
S.T. Assar, E.H. El-Ghazzawy, H.F. Abosheiasha, Study on dielectric properties, electric modulus, and impedance spectroscopy of Ni–Ca ferrite nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 287, 126336 (2022)
L. Singh, U.S. Rai, K.D. Mandal, Dielectric, modulus and impedance spectroscopic studies of nanostructured CaCu0.70Mg0.30Ti4O12 electro-ceramic synthesized by modified sol–gel route. J. Alloys Compd. 555, 176–183 (2012)
R. Padhy, S.K.S. Parashar, N. Rao, A.P. Chaudhuri, Negative temperature coefficient of resistance (NTCR) effect of nano Li2TiO3. IJPRET 8, 210–219 (2013). (ISSN: 2319-507X)
L. H. Omari, S. Sayouri, T. Lamcharfi, L. Hajji, H. Lemziouka, Impedance spectroscopy characterization of Pb0.96La0.04Fe0.03Ti0.97O3 nano-ceramics for negative coefficient thermistor (NCT). J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 7(3), 871–877 (2016) (ISSN: 2028–2508)
K. Funke, Jump relaxation in solid electrolytes. Prog. Solid. State Chem. 22, 111–195 (1993)
A.K. Jonscher, Jonscher, Dielectric relaxation in solids. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 32, R57–R70 (1999)
M. Stewart, M. G. Cain, Ferroelectric hysteresis measurement and analysis, NPL report CMMT(A) 152 (1999) (ISSN:1368-6550)
A.A. Bokov, Z.G. Ye, Recent progress in relaxor ferroelectric with perovskite structure. J. Mater. Sci. 41, 31–52 (2006)
M. M. Devi, A. Anand, R.K. Veena, V.S. Veena, S. Bharadwaj, S. Sagar, Investigations on structural, ferroic and magnetodielectric properties of multiferroic Bi0.9Sm0.1FeO3 and its composite (0.9)Bi0.9Sm0.1FeO3/(0.1)La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 at room temperature. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 11640–11648 (2021)
I. Yeung, R.M. Roshko, G. Williams, Arrott-plot criterion for ferromagnetism in disordered systems. Phys. Rev. B. 34, 3456–3457 (1986)
A. Mukherjee, M. Banerjee, S. Basu, M.D. Mukadam, S.M. Yusuf, M. Pal, Enhanced magnetodielectric and multiferroic properties of Er-doped bismuth ferrite nanoparticle. Mater. Chem. Phys 162, 140–148 (2015)
A.G. Koops, On the dispersion of resistivity and dielectric constant of some semiconductors at audio frequencies. Phys. Rev. 83, 121–124 (1951)
G. Lawes, T. Kimura, C.M. Varma, M.A. Subramanian, N. Rogado, R.J. Cava, A.P. Ramirez, Magnetodielectric effects at magnetic ordering transitions. Prog. Solid State Chem. 37, 40–54 (2009)
S.N. Tripathy, D.K. Pradhan, Phase transition and enhanced magneto-dielectric response in BiFeO3–DyMnO3 multiferroics. J. Appl. Phys. 117, 144103 (2015)
R. Samad, M.U.D. Rather, K. Ashokan, D. Want, Magnetodielectric effect in rare earth doped BaTiO3–CoFe2O4 multiferroic composites. J. Alloys Compd. 794, 402–416 (2019)
D.K. Pradhan, V.S. Puli, S. Kumari, S. Sahoo, P.T. Das, K. Pradhan, D.K. Pradhan, J.F. Scott, R.S. Katiyar, Studies of phase transitions and magnetoelectric coupling in PFN-CZFO multiferroic composites. J. Phys. Chem. C 120, 1936–1944 (2016)
R. Samad, M.U.D. Rather, K. Asokan, D. Want, Magneto-dielectric studies on multiferroic composites of Pr doped CoFe2O4 and Yb doped PbZrTiO3. J. Alloys Compd. 744, 453–462 (2018)
H. Shen, Li. Shen, Z. Lin, M. Li, Y. Liu, Enhanced magnetic properties and magnetodielectric effects inBi2Fe4O9/BaTiO3 composite. J. Alloys Compd. 924, 166535 (2022)
M.M. Devi, A. Anand, R.K. Veena, V.S. Veena, S. Sagar, Dielectric and magneto electric coupling properties of lead free (1 − x)Bi0.9Sm0.1FeO3/(x)La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 (x=0, 0.5, 0.1) composites at room temperature. Mater. Today Proc. 47, 1755–1759 (2021)
R.T. Thomson, P. Jain, A.K. Cheetham, M.A. Carpenter, Elastic relaxation behaviour, Magnetoelastic coupling and order disorder process in multiferroic metal organic frame works. Phys. Rev. B 86, 214304 (2012)
F.U. Wang, Field-induced inter-ferroelectric phase transformations and domain mechanisms in high-strain piezoelectric materials: insights from phase field modelling and simulation. J. Mater. Sci. 44, 5525–5534 (2009)
S.N. Babu, K. Srinivas, T.B. Sankaram, Studies on lead-free multiferroic magnetoelectric composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 3764–3770 (2009)
C.W. Nan, Magnetoelectric effect in composites of piezoelectric and piezomagnetic phases. Phys. Rev. B 50, 6082–6088 (1994)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the University of Kerala for providing financial assistance through University Junior Research Fellowship. Authors fully acknowledge CLIF Karyavattam, UGC-DAE Consortium for Scientific Research Indore, School of Pure and Applied Physics and IIUCNN, MG University, Kottayam, Institute of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, University of Kashan Iran for providing various instrumentation facilities and we would also like to thank Sashank. S and Jisty Ann Jiji, Marian College Kuttikanam for their valuable help for some characterization part of the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RKV: conceptualization, methodology, writing part of original manuscript. AA: joint experimental execution, methodology. MM: joint experimental execution, methodology. VSV: joint experimental execution, methodology. NK: resources. JC: methodology, writing part of original manuscript, support. SS: supervision, support, reviewing and editing. The final manuscript was read and approved by all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state that they have no financial conflicts of interest or close personal ties that would have affected the research presented in this publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Veena, R.K., Anand, A., Manjula devi, M. et al. Unraveling the structural, dielectric, magnetodielectric, multiferroic, and magnetic properties of (1 − x)LiNbO3–xLa0.9Na0.1MnO3 (x = 0.1, 0.2, and 0.3) nanocomposite materials. Appl. Phys. A 129, 598 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06864-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06864-y