Abstract
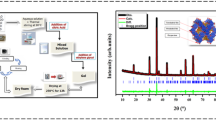
In this study, cobalt ferrite and magnesium oxide nanoparticles were synthesized by co-precipitation and sol–gel methods, respectively. Magnesium oxide doped cobalt ferrite nanocomposites were prepared by mixing powder forms of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles with 10% and 25% in weight MgO powders. The SEM and XRD analyses revealed that pure spinel ferrite structure and single phase magnesium oxide nanoparticles without impurities are obtained. The structural analyses also approved the formation of both phases coexisting in the nanocomposite with homogenous distribution in nanometer particle sizes. In vitro cytotoxic effects of the samples with several concentrations on L929 mouse fibroblast cells were investigated. It is seen that cobalt ferrite nanoparticles increased cell viability in all concentrations and the cell viability of nanocomposites also has been observed as over 95%. Additionally, the energy storage ability of the nanocomposites is performed by frequency-dependent admittance measurements in 5 Hz–13 MHz frequency ranges. It is seen that the addition of magnesium oxide content reduced the complex dielectric constant and dielectric loss of the cobalt ferrite-based nanocomposites effectively. The results showed that magnesium oxide-doped cobalt ferrite nanocomposites sustain nontoxic behavior for biomedical applications in addition to their adjustable dielectric parameters.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author.
References
M. Hasanzadeh, N. Shadjou, M. de la Guardia, Iron, and iron-oxide magnetic nanoparticles as signal-amplification elements in electrochemical biosensing. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. (Ref. Ed.) 72, 1–9 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2015.03.016
I. Ibrahim, I.O. Ali, T.M. Salama, A.A. Bahgat, M.M. Mohamed, Synthesis of magnetically recyclable spinel ferrite (MFe2O4, M = Zn Co, Mn) nanocrystals engineered by sol gel-hydrothermal technology: high catalytic performances for nitroarenes reduction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 181, 389–402 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.08.005
X. Zhao, W. Wang, Y. Zhang, S. Wu, F. Li, J.P. Liu, Synthesis and characterization of gadolinium doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles with enhanced adsorption capability for Congo Red. Chem. Eng. J. 250, 164–174 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.03.113
K.K. Kefeni, T.A. Msagati, T.T. Nkambule, B.B. Mamba, Spinel ferrite nanoparticles and nanocomposites for biomedical applications and their toxicity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 107, 110314 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.110314
S.D. Bhame, P.A. Joy, Enhanced strain sensitivity in magnetostrictive spinel ferrite Co1−xZnxFe2O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 447, 150–154 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.09.075
K.D. Sattler, Handbook of Nanophysics: Nanoparticles and Quantum Dots, 1st edn. (CRC Press, Florida; United States, 2010). https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420075519
K. Ali, A. Bahadur, A. Jabbar, S. Iqbal, I. Ahmad, M.I. Bashir, Synthesis, structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of CuFe2O4/MnO2 nanocomposites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 434, 30–36 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.12.009
R.K. Panda, R. Muduli, D. Behera, Electric and magnetic properties of Bi substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: evolution of grain effect. J. Alloy. Compd. 634, 239–245 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.02.087
K.K. Kefeni, T.A. Msagati, B.B. Mamba, Ferrite nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and applications in electronic device. Mater. Sci. Eng., B 215, 37–55 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2016.11.002
M. Kamran, M. Anis-ur-Rehman, Enhanced transport properties in Ce doped cobalt ferrites nanoparticles for resistive RAM applications. J. Alloys Compd. 822, 153583 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.153583
M. Atif, W. Asghar, M. Nadeem, W. Khalid, Z. Ali, S. Badshah, Synthesis and investigation of structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of zinc substituted cobalt ferrites. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 123, 36–42 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2018.07.010
A. Sathiya Priya, D. Geetha, N. Kavitha, Evaluation of structural and dielectric properties of Al, Ce co-doped cobalt ferrites. Mater. Res. Express 5(6), 066109 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aacd1e
S. Iqbal, M. Fakhar-e-Alam, M. Atif, N. Âmin, K. Alimgeer, A. Ali, A. Ahmad, A. Hanif, A. Farooq, Structural, morphological, antimicrobial, and ın vitro photodynamic therapeutic assessments of novel Zn+2-substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Results Phys 15, 102529 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2019.102529
V.S. Kirankumar, S. Sumathi, Photocatalytic and antibacterial activity of bismuth and copper co-doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29, 8738–8746 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8890-x
M. Madhukara Naika, H.S. Bhojya Naika, G. Nagarajub, M. Vinuthc, K. Vinud, R. Viswanath, Green synthesis of zinc doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles Structural, optical, photocatalytic and antibacterial studies. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 19, 100322 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoso.2019.100322
S.M. Peymani-Motlagh, N. Moeinian, M. Rostami, M. Fasihi-Ramandi, S.A. Obhani-Nasab, M. Rahimi-Nasrabadi, N. Ajami, Effect of Gd3+-, Pr3+-or Sm3+-substituted cobalt–zinc ferrite on photodegradation of methyl orange and cytotoxicity tests. J. Rare Earths 37(12), 1288–1295 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2019.04.010
M.A. Almessiere, Y. Slimani, M. Sertkol, F.A. Khan, M. Nawaz, H. Tombuloglu, A. Baykal, Ce–Nd Co-substituted nanospinel cobalt ferrites: An investigation of their structural, magnetic, optical, and apoptotic properties. Ceram. Int. 45, 16147–16156 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.05.133
S.J. Mercy, D. Parajuli, N. Murali, A. Ramakrishna, Y. Ramakrishna, V. Veeraiah, K. Samatha, Microstructural, thermal, electrical and magnetic analysis of Mg2+ substituted Cobalt ferrite. Appl. Phys. A 126, 873 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-04048-6
V. Vithal, P.K. Pankaj, D.B. Shankar, P.K. Gaikwad, N.D. Shinde, K.M. Jadhav, Low temperature synthesis of magnesium doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles and their structural properties. Int. Adv. Res. J. Sci. Eng. Technol. (2015). https://doi.org/10.17148/IARJSET.2015.2313
H.S. Mund, B.L. Ahuja, Structural and magnetic properties of Mg doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles prepared by sol-gel Method. Mater. Res. Bull. 85, 228–233 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2016.09.027
I.C. Nlebedim, R.L. Hadimani, R. Prozorov, D.C. Jiles, Structural, magnetic, and magnetoelastic properties of magnesium substituted cobalt ferrite. J. Appl. Phys. 113, 17A928 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4798822
V. Pillai, D.O. Shah, Synthesis of high-coercivity cobalt ferrite particles using water-in-oil microemulsions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 163(1–2), 243–248 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(96)00280-6
K. Maaz, A. Mumtaz, S.K. Hasanain, A. Ceylan, Synthesis, and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) nanoparticles prepared by wet chemical route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 308(2), 289–295 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2006.06.003
R. Wahab, S.G. Ansari, M.A. Dar, Y.S. Kim, H.S. Shin, Synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles by sol-gel process. Mater. Sci. Forum 558, 983–986 (2007). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.558-559.983
Z. Güven Özdemir, M. Kılıç, Y. Karabul, B. Süngü Mısırlıoğlu, Ö. Çakır, N.D. Kahya, A transition in the electrical conduction mechanism of CuO/CuFe2O4 nanocomposites. J. Electroceram. 44(12), 1–15 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-019-00194-3
O.M. Lemine, A. Alanazi, E.L. Albert et al., γ-Fe2O3/Gd2O3-chitosan magnetic nanocomposite for hyperthermia application: structural, magnetic, heating efficiency and cytotoxicity studies. Appl. Phys. A 126, 471 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03649-5
E. Yavuz, S. Dinc, M. Kara, Effects of endogenous molasses carbon dots on macrophages and their potential utilization as anti-inflammatory agents. Appl. Phys. A 126, 22 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3189-1
J. Panda, S. Das, S. Kumar et al., Investigation of antibacterial, antioxidant, and anticancer properties of hydrothermally synthesized cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 128, 562 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05700-z
B. Pashaei, A. Aghaei, M. Shaterian, Cobalt ferrite magnetic nanoceramics as an efficient nanocatalyst for the oxidation of olefins in the presence of molecular O2 as an environmentally safe oxidant. Appl. Organomet. Chem. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.7126
L. Ai, J. Jiang, Influence of annealing temperature on the formation, microstructure and magnetic properties of spinel nanocrystalline cobalt ferrites. Curr. Appl. Phys. 10(1), 284–288 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2009.06.007
D. Karakaş, F. Ari, E. Ulukaya, The MTT viability assay yields strikingly false-positive viabilities although the cells are killed by some plant extracts. Turk. J. Biol. 41(6), 919–925 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3906/biy-1703-104
M. Abudayyak, T. Altınçekiç Gürkaynak, G. Özhan, In vitro evaluation of the toxicity of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles in kidney cell. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 14(2), 169–173 (2017). https://doi.org/10.4274/tjps.99609
M. Lickmichand, C.S. Shaji, N. Valarmathi, A.S. Benjamin, R.K.A. Kumar, S. Nayak, In vitro biocompatibility and hyperthermia studies on synthesized cobalt ferrite nanoparticles encapsulated with polyethylene glycol for biomedical applications. Mater. Today: Proc. 15, 252–261 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.05.002
S.M. Ansari, R.D. Bhor, K.R. Pai, S. Mazumder, D. Sen, Y.D. Kolekar, Size and chemistry controlled cobalt-ferrite nanoparticles and their anti-proliferative effect against the MCF-7 breast cancer cells. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2(12), 2139–2152 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.6b00333
A. Sunny, K.S. Ak, V. Karunakaran, M. Aathira, G.R. Mutta, K.K. Maiti, Magnetic properties of biocompatible CoFe2O4 nanoparticles using a facile synthesis. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 16, 69–76 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoso.2018.04.003
B. Süngü Mısırlıoğlu, Ö. Çakır, H. Çalık, R. Çakır-Koç, Assessment of structural and cytotoxic properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Inorg. Nano-Metal Chem. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/24701556.2020.1862216
M.K. Patel, M. Zafaryab, M.M.A. Rizvi, V.V. Agrawal, Z.A. Ansari, B.D. Malhotra, Antibacterial and cytotoxic effect of magnesium oxide nanoparticles on bacterial and human cells. J. Nanoeng. Nanomanuf. 3(2), 162–166 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1166/jnan.2013.1122
A. Mittag, T. Schneider, M. Westermann, M. Glei, Toxicological assessment of magnesium oxide nanoparticles in HT29 intestinal cells. Arch. Toxicol. 93(6), 1491–1500 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02451-4
S. Ge, G. Wang, Y. Shen, Q. Zhang, D. Jia, H. Wang, Cytotoxic effects of MgO nanoparticles on human umbilical vein endothelial cells in vitro. IET Nanobiotechnol. 5(2), 36 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-nbt.2010.0022
S.I. Ahmad, A. Rauf, T. Mohammed, A. Bahafi, D.R. Kumar, M.B. Suresh, Dielectric, impedance, AC conductivity and low-temperature magnetic studies of Ce and Sm co-substituted nanocrystalline cobalt ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 492, 165666 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.165666
M. Kılıç, N.D. Kahya, B. Süngü Mısırlıoğlu, Ö. Çakır, Z. Güven Özdemir, Dielectric and magnetic properties of CuFe2O4/CuO nanocomposites. Ferroelectrics 571(1), 183–199 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/00150193.2020.1853752
R.K. Selvan, C.O. Augustin, V. Šepelák, L.J. Berchmans, C. Sanjeeviraja, A. Gedanken, Synthesis and characterization of CuFe2O4/CeO2 nanocomposites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 112(2), 373–380 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2008.05.094
A.N. Yusoff, M.H. Abdullah, Microwave electromagnetic and absorption properties of some LiZn ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 269(2), 271–280 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(03)00617-6
A.P. Singh, O.P. Pandey, P. Sharma, Effect of sintering additives on structural, magnetic, and dielectric properties of Ba3Co2Fe24O41 ferrite. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 33, 519–526 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-019-05202-9
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by TUBITAK 2209-A National Research Projects Support Programme for Undergraduate Students under Project Number: 1919B011801056 (2018/1). The authors also would like to thank Prof.Dr. Naime Didem Kahya for her support in terms of the synthesis of the particles.
Funding
TUBİTAK 2209-A National Research Projects Support Programme for Undergraduate Students, 1919B011801056 (2018/1), Volkan Kurt.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The synthesis stage of the cobalt ferrite and magnesium oxide particles was performed by VK. BSM and VK performed the experimental processes of the preparation of the nanocomposites. The structural measurements were analyzed by BSM, VK, and ÖÇ. The dielectric measurements of the samples were performed and analyzed by BSM and VK. The In Vitro Experiments were performed and analyzed by HC and RC-K. All authors contributed to the writing stages of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mısırlıoğlu, B.S., Kurt, V., Calik, H. et al. Toxicity and energy storage properties of magnesium oxide doped cobalt ferrite nanocomposites for biomedical applications. Appl. Phys. A 129, 506 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06792-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06792-x