Abstract
Superhydrophobicity has been a crucial research topic due to its ability to make surfaces stay dry and self-clean. Low-surface-energy organic coatings are widely used to fabricate superhydrophobic surfaces by modifying surface groups and minimizing surface energy. Considering defects would seriously undermine these coatings, which would further lead to hydrophobicity dwindling and lifetime decreasing, researchers have begun to investigate the development of superhydrophobic surfaces without organic coatings. However, it is still controversial whether these superhydrophobic surfaces are really free of organic substances with low surface energy. In this work, O3 bombardment was utilized to construct micro–nanostructures on aluminum foil. The aluminum foil surface turns to superhydrophobic after ozone bombardment with the contact angle (CAs) increasing from 20° to 161°. Results showed the presence of silicon contaminations on alumina surfaces despite the fact that no organic coatings are utilized in the fabrication process. The transition of hydrophilic-to-superhydrophobic was attributed to both surface morphology and silicon contamination from pump oil. Our work reveals that trace organic contamination from pump oil is a key factor that cannot be ignored in scenarios with vacuum pump use, which could provide some favorable evidence to figure out the controversial issue mentioned above.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
C. Neinhuis, W. Barthlott, Characterization and distribution of water-repellent, self-cleaning plant surfaces. Ann. Bot. 79(6), 667–677 (1997)
I.P. Parkin, R.G. Palgrave, Self-cleaning coatings. J. Mater. Chem. 15(17), 1689–1695 (2005)
S. Farhadi, M. Farzaneh, S.A. Kulinich, Anti-icing performance of superhydrophobic surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257(14), 6264–6269 (2011)
S.A. Kulinich, S. Farhadi, K. Nose, X.W. Du, Superhydrophobic surfaces: are they really ice-repellent? Langmuir 27(1), 25–29 (2011)
O. Parent, A. Ilinca, Anti-icing and de-icing techniques for wind turbines: critical review. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 65(1), 88–96 (2011)
Q.L. Zhang, M. He, J. Chen, J.J. Wang, Y.L. Song, L. Jiang, Anti-icing surfaces based on enhanced self-propelled jumping of condensed water microdroplets. Chem. Commun. 49(40), 4516–4518 (2013)
S.L. Zheng, C. Li, Q.T. Fu, W. Hu, T.F. Xiang, Q. Wang, M.P. Du, X.C. Liu, Z. Chen, Development of stable superhydrophobic coatings on aluminum surface for corrosion-resistant, self-cleaning, and anti-icing applications. Mater. Des. 93, 261–270 (2016)
E. Vazirinasab, R. Jafari, G. Momen, Application of superhydrophobic coatings as a corrosion barrier: a review. Surf. Coat. Technol. 341, 40–56 (2018)
F.Z. Zhang, L.L. Zhao, H.Y. Chen, S.L. Xu, D.G. Evans, X. Duan, Corrosion resistance of superhydrophobic layered double hydroxide films on aluminum. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 47(13), 2466–2469 (2008)
G.Y. Wang, Y.Z. Shen, J. Tao, X.Y. Luo, L.Q. Zhang, Y.P. Xia, Fabrication of a superhydrophobic surface with a hierarchical nanoflake–micropit structure and its anti-icing properties. RSC Adv. 7(16), 9981–9988 (2017)
R.Y. Sun, J. Zhao, Z. Li, N. Qin, J.L. Mo, Y.J. Pan, D.B. Luo, Robust superhydrophobic aluminum alloy surfaces with anti-icing ability, thermostability, and mechanical durability. Prog. Org. Coat. 147, 105745 (2020)
C.H. Xue, S.T. Jia, J. Zhang, J.Z. Ma, Large-area fabrication of superhydrophobic surfaces for practical applications: an overview. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 11(3), 033002 (2010)
E.K. Sam, D.K. Sam, X.M. Lv, B.T. Liu, X.X. Xiao, S.H. Gong, W.T. Yu, J. Chen, J. Liu, Recent development in the fabrication of self-healing superhydrophobic surfaces. Chem. Eng. J. 373, 531–546 (2019)
N.F. Himma, N. Prasetya, S. Anisah, I.G. Wenten, Superhydrophobic membrane: progress in preparation and its separation properties. Rev. Chem. Eng. 35(2), 211–238 (2019)
Y.X. Bai, H.P. Zhang, Y.Y. Shao, H. Zhang, J. Zhu, Recent progresses of superhydrophobic coatings in different application fields: an overview. Coatings 11(2), 116–146 (2021)
S.W. Lv, X.M. Zhang, X.D. Yang, X.L. Liu, Z.J. Yang, Y. Zhai, Fabrication of superhydrophobic surface with corrosion resistance via cyclic chemical etching process on aluminum substrate. Mater. Res. Express 9(2), 026520 (2022)
Q. Yin, Q. Guo, Z.L. Wang, Y.Q. Chen, H.G. Duan, P. Cheng, 3D-printed bioinspired Cassie-Baxter wettability for controllable microdroplet manipulation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13(1), 1979–1987 (2021)
L. Savio, K.B. Bhavitha, G. Bracco, G. Luciano, D. Cavallo, G. Paolini, S. Passaglia, G. Carraro, L. Vattuone, R. Masini, M. Smerieri, Correlating hydrophobicity to surface chemistry of microstructured aluminium surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 542, 148574 (2021)
H.Y. Tao, X.W. Song, Z.Q. Hao, J.Q. Lin, One-step formation of multifunctional nano- and microscale structures on metal surface by femtosecond laser. Chin. Opt. Lett. 13(6), 061402–061405 (2015)
M.J. Eskandari, A. Shafyei, F. Karimzadeh, Investigation of wetting properties of gold nanolayer coated aluminum surfaces textured with continuous-wave fiber laser ablation. Thin Solid Films 711, 138278 (2020)
X.L. Wang, H.Y. Hu, Q. Ye, T.T. Gao, F. Zhou, Q.J. Xue, Superamphiphobic coatings with coralline-like structure enabled by one-step spray of polyurethane/carbon nanotube composites. J. Mater. Chem. 22(19), 9624–9631 (2012)
A. Hooda, M.S. Goyat, J.K. Pandey, A. Kumar, R. Gupta, A review on fundamentals, constraints and fabrication techniques of superhydrophobic coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 142, 105557 (2020)
S.J. Choi, K.Y. Suh, H.H. Lee, A geometry controllable approach for the fabrication of biomimetic hierarchical structure and its superhydrophobicity with near-zero sliding angle. Nanotechnology 19(27), 275305 (2008)
S.Y. Li, X.G. Xiang, B.H. Ma, X.D. Meng, Facile preparation of diverse alumina surface structures by anodization and superhydrophobic surfaces with tunable water droplet adhesion. J. Alloys Compd. 779, 219–228 (2019)
S. Peng, D. Tian, X.J. Yang, W.L. Deng, Highly efficient and large-scale fabrication of superhydrophobic alumina surface with strong stability based on self-congregated alumina nanowires. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6(7), 4831–4841 (2014)
T. Fujii, Y. Aoki, H. Habazaki, Fabrication of super-oil-repellent dual pillar surfaces with optimized pillar intervals. Langmuir 27(19), 11752–11756 (2011)
X.T. Zhu, Z.Z. Zhang, X.H. Xu, X.H. Men, J. Yang, X.Y. Zhou, Q.J. Xue, Facile fabrication of a superamphiphobic surface on the copper substrate. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 367(1), 443–449 (2012)
X. Deng, L. Mammen, H.J. Butt, D. Vollmer, Candle soot as a template for a transparent robust superamphiphobic coating. Science 335(6064), 67–70 (2012)
D. Nakajima, T. Kikuchi, S. Natsui, R.O. Suzuki, Highly ordered anodic alumina nanofibers fabricated via two distinct anodizing processes. ECS Electrochem. Lett. 4(5), H14–H17 (2015)
T. Kikuchi, F. Onoda, M. Iwai, R.O. Suzuki, Influence of sub-10 nm anodic alumina nanowire morphology formed by two-step anodizing aluminum on water wettability and slipping behavior. Appl. Surf. Sci. 546, 149090 (2021)
D. Nakajima, T. Kikuchi, S. Natsui, R.O. Suzuki, Mirror-finished superhydrophobic aluminum surfaces modified by anodic alumina nanofibers and self-assembled monolayers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 440, 506–513 (2018)
D. Nakajima, T. Kikuchi, T. Yoshioka, H. Matsushima, M. Ueda, R.O. Suzuki, S. Natsui, A superhydrophilic aluminum surface with fast water evaporation based on anodic alumina bundle structures via anodizing in pyrophosphoric acid. Materials (Basel) 12(21), 3497–3509 (2019)
R. Kondo, D. Nakajima, T. Kikuchi, S. Natsui, R.O. Suzuki, Superhydrophilic and superhydrophobic aluminum alloys fabricated via pyrophosphoric acid anodizing and fluorinated SAM modification. J. Alloys Compd. 725, 379–387 (2017)
D. Nakajima, T. Kikuchi, S. Natsui, R.O. Suzuki, Advancing and receding contact angle investigations for highly sticky and slippery aluminum surfaces fabricated from nanostructured anodic oxide. RSC Adv. 8(65), 37315–37323 (2018)
P. Hale, S. Turgeon, P. Horny, F. Lewis, N. Brack, G.V. Riessen, P. Pigram, D. Mantovani, X-ray photoelectron emission microscopy and time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry analysis of ultrathin fluoropolymer coatings for stent applications. Langmuir 24(15), 7897–7905 (2008)
H.C. Hu, Y. Li, N. Zhang, Y.S. Ding, Synthesis and characterization of a poly(o-anisidine)–SiC composite and its application for corrosion protection of steel. RSC Adv. 7(19), 11732–11742 (2017)
J.C. Ma, H. Cha, M.K. Kim, D.G. Cahill, N. Miljkovic, Condensation induced delamination of nanoscale hydrophobic films. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29(43), 4516–4518 (2019)
D.H. Wang, Q.Q. Sun, M.J. Hokkanen, C.L. Zhang, F.Y. Lin, Q. Liu, S.P. Zhu, T.F. Zhou, Q. Chang, B. He, Q. Zhou, L.Q. Chen, Z.K. Wang, R. Ras, X. Deng, Design of robust superhydrophobic surfaces. Nature 582(7810), 55–59 (2020)
Z.J. Chen, Y.B. Guo, S.M. Fang, A facial approach to fabricate superhydrophobic aluminum surface. Surf. Interface Anal. 42(1), 1–6 (2009)
B. Yan, J. Tao, C. Pang, Z. Zheng, Z. Shen, C.H. Huan, T. Yu, Reversible UV-light-induced ultrahydrophobic-to-ultrahydrophilic transition in an alpha-Fe2O3 nanoflakes film. Langmuir 24(19), 10569–10571 (2008)
C. Yang, S.H. Cui, Y.C. Weng, Z.C. Wu, L.L. Liu, Z.Y. Ma, X.B. Tian, R.K.Y. Fu, P.K. Chu, Z.Z. Wu, Scalable superhydrophobic T-shape micro/nano structured inorganic alumina coatings. Chem. Eng. J. 409, 128142 (2021)
S. Parvate, P. Dixit, S. Chattopadhyay, Superhydrophobic surfaces: insights from theory and experiment. J. Phys. Chem. B 124(8), 1323–1360 (2020)
A. Chaudhary, H.C. Barshilia, Nanometric multiscale rough CuO/Cu(OH)2 superhydrophobic surfaces prepared by a facile one-step solution-immersion process: transition to superhydrophilicity with oxygen plasma treatment. J. Phys. Chem. C 115(37), 18213–18220 (2011)
K.S. Liu, M.Y. Cao, A. Fujishima, L. Jiang, Bio-inspired titanium dioxide materials with special wettability and their applications. Chem. Rev. 114(19), 10044–10094 (2014)
D.V. Ta, A. Dunn, T.J. Wasley, R.W. Kay, J. Stringer, P.J. Smith, C. Connaughton, J.D. Shephard, Nanosecond laser textured superhydrophobic metallic surfaces and their chemical sensing applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 357, 248–254 (2015)
L.B. Boinovich, A.M. Emelyanenko, K.A. Emelyanenko, A.G. Domantovsky, A.A. Shiryaev, Comment on “Nanosecond laser textured superhydrophobic metallic surfaces and their chemical sensing applications” by Duong V. Ta, Andrew Dunn, Thomas J. Wasley, Robert W. Kay, Jonathan Stringer, Patrick J. Smith, Colm Connaughton, Jonathan D. Shephard (Appl. Surf. Sci. 357 (2015) 248–254). Appl. Surf. Sci. 379, 111–113 (2016)
Z.X. Lian, J.K. Xu, Z.J. Yu, P. Yu, W.F. Ren, Z.B. Wang, H.D. Yu, Bioinspired reversible switch between underwater superoleophobicity/superaerophobicity and oleophilicity/aerophilicity and improved antireflective property on the nanosecond laser-ablated superhydrophobic titanium surfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12(5), 6573–6580 (2020)
P. Gregorčič, Comment on “Bioinspired reversible switch between underwater superoleophobicity/superaerophobicity and oleophilicity/aerophilicity and improved antireflective property on the nanosecond laser-ablated superhydrophobic titanium surfaces.” ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13(2), 2117–2127 (2021)
T.L. Liu, C.J. Kim, Repellent surfaces. Turning a surface superrepellent even to completely wetting liquids. Science 346(6213), 1096–1100 (2014)
Q.S. Zheng, Y. Yu, Z.H. Zhao, Effects of hydraulic pressure on the stability and transition of wetting modes of superhydrophobic surfaces. Langmuir 21(26), 12207–12212 (2005)
L.B. Boinovich, A.M. Emelyanenko, A.S. Pashinin, C.H. Lee, J. Drelich, Y.K. Yap, Origins of thermodynamically stable superhydrophobicity of boron nitride nanotubes coatings. Langmuir 28(2), 1206–1216 (2012)
V.S. Yalishev, M. Iqbal, V.V. Kim, S.A. Khan, R.A. Ganeev, A.S. Alnaser, Reversible wettability transition of laser-textured metals after vacuum storing and low-temperature annealing. Appl. Phys. A 127(5), 393 (2021)
J.M. Bailey, I.M. Ritchie, Metal oxidation: an electrochemical perspective. Oxid. Met. 30(5–6), 405–418 (1988)
C. Ocal, S. Ferrer, N. García, Diffusion of metallic atoms through thin oxides in metallic substrates. Surf. Sci. 162(1–3), 558–562 (1985)
M.C. Muñoz, J.L. Sacedón, Electron stimulated oxidation of silicon surfaces. J. Chem. Phys. 74(8), 4693–4700 (1981)
L.P. Ramírez, F. Bournel, J.J. Gallet, L. Dudy, F. Rochet, Testing the Cabrera-Mott oxidation model for aluminum under realistic conditions with near-ambient pressure photoemission. J. Phys. Chem. C 126(5), 2517–2530 (2022)
Z.Q. Yang, L.L. He, J. Chen, H.T. Cong, H.Q. Ye, Microstructure and thermal stability of an ultrafine Al/Al2O3 composite. J. Mater. Res. 18(2), 272–278 (2011)
S. Fukuzaki, H. Urano, T. Yamaguchi, Effect of modification of alumina surfaces by ozone on adsorption behavior of bovine serum albumin at alumina-water interfaces. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 84(5), 407–413 (1997)
F. Qi, Z.L. Chen, B.B. Xu, J.M. Shen, J. Ma, C. Joll, A. Heitz, Influence of surface texture and acid–base properties on ozone decomposition catalyzed by aluminum (hydroxyl) oxides. Appl. Catal. B 84(3–4), 684–690 (2008)
K. Thomas, P.E. Hoggan, L. Mariey, J. Lamotte, J.C. Lavalley, Experimental and theoretical study of ozone adsorption on alumina. Catal. Lett. 46(1/2), 77–82 (1997)
I. Popova, V. Zhukov, J.T. Yates, Comparative study of Al(111) oxidation with O3 and O2. Surf. Sci. 518(1–2), 39–48 (2002)
A. Marmur, Wetting on hydrophobic rough surfaces: to be heterogeneous or not to be? Langmuir 19(20), 8343–8348 (2003)
J.W. Drelich, L. Boinovich, E. Chibowski, C.D. Volpe, L. Hołysz, A. Marmur, S. Siboni, Contact angles: history of over 200 years of open questions. Surf. Innov. 8(1–2), 3–27 (2020)
L.D. Lai, J.F. Yan, J. Li, B. Lai, Co/Al2O3-EPM as peroxymonosulfate activator for sulfamethoxazole removal: performance, biotoxicity, degradation pathways and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 343, 676–688 (2018)
P. Marcus, C. Hinnen, I. Olefjord, Determination of attenuation lengths of photoelectrons in aluminium and aluminium oxide by angle-dependent X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Surf. Interface Anal. 20(11), 923–929 (1993)
Y. Ai, N. Yin, Y.Q. Ouyang, Y.X. Xu, P.F. Yang, Waste non-burn-free brick derived sulfhydryl functioned magnetic zeolites and their efficient removal of uranium (VI) ions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 571, 151241 (2022)
M.B. Kant, S.D. Shinde, D. Bodas, K.R. Patil, V.G. Sathe, K.P. Adhi, S.W. Gosavi, Surface studies on benzophenone doped PDMS microstructures fabricated using KrF excimer laser direct write lithography. Appl. Surf. Sci. 314, 292–300 (2014)
I. Milošev, Ž Jovanović, J.B. Bajat, R. Jančić-Heinemann, V.B. Mišković-Stanković, Surface analysis and electrochemical behavior of aluminum pretreated by vinyltriethoxysilane films in mild NaCl solution. J. Electrochem. Soc. 159(7), C303–C311 (2012)
T.P. Galhenage, D.C. Webster, A.M.S. Moreira, R.J. Burgett, S.J. Stafslien, L. Vanderwal, J.A. Finlay, S.C. Franco, A.S. Clare, Poly(ethylene) glycol-modified, amphiphilic, siloxane–polyurethane coatings and their performance as fouling-release surfaces. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 14(2), 307–322 (2016)
S. Aerts, A. Vanhulsel, A. Buekenhoudt, H. Weyten, S. Kuypers, H. Chen, M. Bryjak, L.E.M. Gevers, I.F.J. Vankelecom, P.A. Jacobs, Plasma-treated PDMS-membranes in solvent resistant nanofiltration: characterization and study of transport mechanism. J. Membr. Sci. 275(1–2), 212–219 (2006)
S.H. Tan, N.T. Nguyen, Y.C. Chua, T.G. Kang, Oxygen plasma treatment for reducing hydrophobicity of a sealed polydimethylsiloxane microchannel. Biomicrofluidics 4(3), 32204 (2010)
A. Öztürk, A.B. Yurtcan, Effect of calcination temperature on hydrophobicity of microporous layers prepared with two different molecular weights of PDMS polymer on PEM fuel cell performance with low Pt loading. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 42(9), 6250–6261 (2017)
K.Q. Li, X.R. Zeng, H.Q. Li, X.J. Lai, H. Xie, Effects of calcination temperature on the microstructure and wetting behavior of superhydrophobic polydimethylsiloxane/silica coating. Colloids Surf. A 445, 111–118 (2014)
Y.G. Kim, N. Lim, J. Kim, C. Kim, J. Lee, K.H. Kwon, Study on the surface energy characteristics of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) films modified by C4F8/O2/Ar plasma treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 477, 198–203 (2019)
Acknowledgements
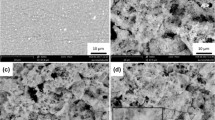
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Granted no. 51777152), the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (Granted no. 2021JZ-01), and the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (Granted no. 2020M683465). The authors thank Mr. Ren at the Instrument Analysis Center of Xi’an Jiaotong University for his assistance with SEM measurement. The authors thank Ms. Liang of Xi’an Jiaotong University for her assistance with the mechanism study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, ZL, XD, LX; methodology, ZL, ZL; investigation, ZL, ZZ; writing—original draft, ZL; writing—review and editing, ZL, XD, LX; funding acquisition, XD, ZL. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Liang, Z., Du, X. et al. Effects of trace organic contamination on micro–nanostructure-induced superhydrophobic properties. Appl. Phys. A 129, 432 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06712-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06712-z