Abstract
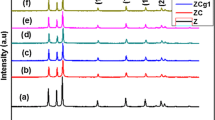
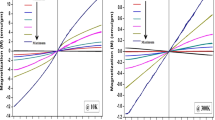
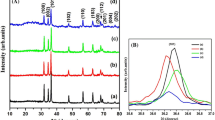
A chemical co-precipitation method is used to synthesize the Zn1–xCoxO nanoparticles and then examine its structural, morphological, chemical bond and magnetic properties. A single phase hexagonal wurtzite crystal structure is confirmed by X-ray diffraction for all the samples without any impurity phase. The substitution of Co-doping in ZnO lattice is confirmed by the peak shifting in XRD patterns, and reduction in crystallite size of Co-doped ZnO NPs. The enhanced optical absorption and red shift in band edge is observed in the Co-doped ZnO NPs. The reduced optical bandgap is found in Co dopant and which decreases further with increase in the Co content. M–H measurements show the ferromagnetic behavior of Co-doped ZnO NPs increases with increase in the Co content. This observed ferromagnetism is originated from increased oxygen vacancies which form bound magnetic polarons. These findings promote the usage of Co-doped ZnO materials for potential spintronics and magneto-optical applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
M.Y. Ali, M. Khan, A.T. Karim, M.M. Rahman, M. Kamruzzaman, Effect of Ni doping on structure, morphology and opto-transport properties of spray pyrolised ZnO nano-fiber. Heliyon 6, e03588 (2020)
A.B. Djurisic, X. Chen, Y.H. Leung, A.M.C. Ng, ZnO nanostructures: growth, properties and applications. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 6526–6535 (2012)
A.B. Djurisic, A.M.C. Ng, X.Y. Chen, ZnO nanostructures for optoelectronics: material properties and device applications. Prog. Quantum Electron. 34, 191–259 (2010)
T. Gao, T.H. Wang, Synthesis and properties of multipod-shaped ZnO nanorods for gas-sensor applications. Appl. Phys. A 80, 1451 (2005)
N. Lathiotakis, A.N. Andriotis, M. Menon, Co doping: a possible pathway for inducing ferromagnetism in ZnO. Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Mater. Phys. 78, 193311 (2008)
T.A. Abdel-Baset, Y.W. Fang, C.G. Duan, M. Abdel-Hafiez, Magnetic properties of chromium-doped ZnO. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 29, 1937–1942 (2016)
J.J. Beltrán, C.A. Barrero, A. Punnoose, Understanding the role of iron in the magnetism of Fe doped ZnO nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17, 15284–15296 (2015)
N. Sharma, R. Kant, V. Sharma, S. Kumar, Influence of silver dopant on morphological, dielectric and magnetic properties of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Electr. Mater. 47, 4098–4107 (2018)
S. Fabbiyola, V. Sailaja, L. John Kennedy, M. Bououdina, J. Judith Vijaya, Optical and magnetic properties of Ni-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 694, 522–531 (2017)
S.A. Ahmed, Structural, optical, and magnetic properties of Mn-doped ZnO samples. Results Phys. 7, 604–610 (2017)
S. Sinha, M. Singh, R. Singh, ZnO based diluted magnetic semiconductors for spintronic device applications: a review. Int. J. Emerg. Res. Manag. Technol 4, 16–20 (2015)
R. Khan, C.I.L. de Araujo, T. Khan, S.A. Khattak, E. Ahmed, A. Khan, B. Ullah, G. Khan, K. Safeen, A. Safeen, Effect of thermal calcination on the structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of (ZnO–Ni) semiconductor. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 3396–3404 (2019)
J.J. Chen, M.H. Yu, W.L. Zhou, Room-temperature ferromagnetic Co-doped ZnO nanoneedle array prepared by pulsed laser deposition. Appl. Phy. Lett. 87, 173119 (2005)
S.Y. Kuo, W.C. Chen, C.P. Cheng, Investigation of annealing-treatment on the optical and electrical properties of sol–gel-derived zinc oxide thin films. Superlattices Microstr. 39, 162–170 (2006)
S. Deka, R. Pasricha, P.A. Joy, Experimental comparison of the structural, magnetic, electronic, and optical properties of ferromagnetic and paramagnetic polycrystalline Zn1− xCoxO (x= 0, 0.05, 0.1). Phy. Rev. B 74, 033201 (2006)
I. Djerdj, Z. Jagličic, D. Arčon, M. Niederberger, Co-doped ZnO nanoparticles: Minireview. Nanoscale 2, 1096–1104 (2010)
W. Li, G. Wang, C. Chen, J. Liao, Z. Li, Enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanowires doped with Mn2+ and Co2+ ions. Nanomaterials 7, 20 (2017)
R. Kant, D. Sharma, A. Bansal, R. Singh, Structural, optical and dielectric properties of Al/Mn doped ZnO nanoparticles, a comparative study. Mater. Tech. 36, 513–520 (2021)
W.J. Qin, J. Sun, J. Yang, X.W. Du, Control of Cu-doping and optical properties of ZnO quantum dots by laser ablation of composite targets. Mater. Chem. Phys. 130, 425–430 (2011)
J. Li, L. Zhang, J. Zhu, Y. Liu, W. Hao, Aligned ZnO: Co nanorod arrays: Electrophoretic deposition fabrication and magnetic manipulation. Ceram. Int. 41, 3456–3460 (2015)
M. Shatnawi, A.M. Alsmadi, I. Bsoul, B. Salameh, G.A. Alnawashi, F. Al Dweri, F. El Akkad, Magnetic and optical properties of Co-doped ZnO nanocrystalline particles. J. Alloy. Compd. 655, 244–252 (2016)
C. Li, P. Che, C. Sun, W. Li, Effect of cobalt concentration and oxygen vacancy on magnetism of Co doped ZnO nanorods. J Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 16, 2719–2724 (2016)
D.A. Schwartz, D.R. Gamelin, Reversible 300 K ferromagnetic ordering in a diluted magnetic semiconductor. Adv. Mater. 16, 2115–2119 (2004)
M.H. Sluiter, Y. Kawazoe, P. Sharma, A. Inoue, A.R. Raju, C. Rout, U.V. Waghmare, First principles based design and experimental evidence for a ZnO-based ferromagnet at room temperature. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 187204 (2005)
J. Mohapatra, D.K. Mishra, D. Mishra, A. Perumal, V.R.R. Medicherla, D.M. Phase, S.K. Singh, Room temperature ferromagnetism in Co doped ZnO within an optimal doping level of 5%. Mater. Res. Bull. 47, 1417–1422 (2012)
K.R. Kittilstved, D.A. Schwartz, A.C. Tuan, S.M. Heald, S.A. Chambers, D.R. Gamelin, Direct kinetic correlation of carriers and ferromagnetism in Co2+: ZnO. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 037203 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. NS: writing of first draft of the manuscript. RK: writing-review, editing and Conceptualization (lead). VS: formal analysis (supporting).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that there are no conflicts of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, N., Kant, R. & Sharma, V. Band gap and magnetic properties modulation by substitution of cobalt in ZnO nanostructures. Appl. Phys. A 129, 223 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06517-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06517-0