Abstract
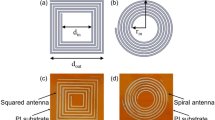
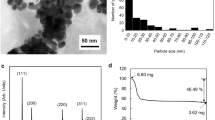
Copper (Cu) nanoparticle (NP) ink was employed to fabricate conductive Cu NP patterns on flexible polyimide (PI) substrates using thermal sintering under various atmospheres, such as air, nitrogen (N2), and five carboxylic acid vapors. Carboxylic acids included three monocarboxylic acids (acetic acid, formic acid, and propionic acid), one dicarboxylic acid (oxalic acid), and one tricarboxylic acid (citric acid). The sintering temperature was chosen among 140, 200, and 260 ℃. The sintering time varied in the range of 15–60 min. It was demonstrated that formic acid vapors played a role in effective removal of organic compounds, leading to particles connect for necking and coalescence and a further dense microstructure. Although cuprous oxides were observed, the Cu NP patterns sintered under formic acid vapor atmosphere achieved low sheet resistance values in the range of 0.0006–0.4032 Ω/sq for all temperatures and times. Vickers hardness for the Cu patterns sintered in formic acid vapor atmosphere showed in the range of 17.24–29.85 N/mm2 for all temperatures. Cu NP patterns sintered under formic acid vapors at 260 ℃ for 15 min were chosen for the flexible radio-frequency identification (RFID) antenna fabrication with two different shapes of spiral and squared antennas. From the return loss graphs, the quality factors were obtained in the range of 6.80–20.53 and 13.66–32.91 for spiral and squared antennas, respectively.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
T. Eiselt, J.B. Preinfalk, K. Bittkau, G. Gomard, T. Hanemann, U. Lemmer, Inkjet-printed internal light extraction layers for organic light emitting diodes. Flex. Print. Electron. 3, 015007 (2018)
J.S. Kang, H.S. Kim, J. Ryu, H.T. Hahn, S. Jang, J.W. Joung, Inkjet printed electronics using copper nanoparticle ink. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 21, 1213–1220 (2010)
B.K. Park, D. Kim, S. Jeong, J. Moon, J.S. Kim, Direct writing of copper conductive patterns by ink-jet printing. Thin Solid Films 515, 7706–7711 (2007)
K. Woo, Y. Kim, B. Lee, J. Kim, J. Moon, Effect of carboxylic acid on sintering of inkjet-printed copper nanoparticulate films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 3, 2377–2382 (2011)
S.-M. Yi, J.-K. Jung, S.-H. Choi, I. Kim, H. C. Jung, J. Joung, Y.-C. Joo, Effect of microstructure on electrical and mechanical properties: Impurities of inkjet-printed Ag and Cu interconnects. In: 58th Electronic Components and Technology Conference, pp. 1277–1281, (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/ECTC.2008.4550139
S. Jang, Y. Seo, J. Choi, T. Kim, J. Cho, S. Kim, D. Kim, Sintering of inkjet printed copper nanoparticles for flexible electronics. Scr. Mater. 62, 258–261 (2010)
H.Y. Jun, E.J. Lee, S.O. Ryu, Synthesis and characterization of copper ink and direct printing of copper patterns by inkjet printing for electronic devices. Curr. Appl. Phys. 20, 853–861 (2020)
I. Kim, J. Kim, The effect of reduction atmospheres on the sintering behaviors of inkjet-printed Cu interconnectors. J. Appl. Phys. 108, 102807 (2010)
A. Rida, L. Yang, R. Vyas, M.M. Tentzeris, Conductive inkjet-printed antennas on flexible low-cost paper-based substrates for RFID and WSN applications. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 51, 13–23 (2009)
J.D. Park, S. Lim, H. Kim, Patterned silver nanowires using the gravure printing process for flexible applications. Thin Solid Films 586, 70–75 (2015)
Q. Huang, Y. Zhu, Gravure printing of water-based silver nanowire ink on plastic substrate for flexible electronics. Sci. Rep. 8, 15167 (2018)
J. Seong, S. Kim, J. Park, D. Lee, K.-H. Shin, Online noncontact thickness measurement of printed conductive silver patterns in Roll-to-Roll gravure printing. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 16, 2265–2270 (2015)
K.-S. Kim, W.-R. Myung, S.-B. Jung, Effects of sintering conditions on microstructure and characteristics of screen-printed Ag thin film. Electron. Mater. Lett. 8, 309–314 (2012)
K.-S. Kim, Y. Kim, S.-B. Jung, Microstructure and adhesion characteristics of a silver nanopaste screen-printed on Si substrate. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 7, 49 (2012)
M.L. Allen, K. Jaakkola, K. Nummila, H. Seppa, Applicability of metallic nanoparticle inks in RFID applications. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Technol. 32, 325–332 (2009)
B. Cruz1, A. Albrecht, P. Eschlwech, and E. Biebl, Inkjet printing of metal nanoparticles for green UHF RFID tags, Adv. Radio Sci. 17, 119–127 (2019).
T. Zhong, N. Jin, W. Yuan, C. Zhou, W. Gu, Z. Cui, Printable stretchable silver ink and application to printed RFID tags for wearable electronics. Materials 12, 3036 (2019)
S.E. Habas, H.A.S. Platt, M.F.A.M. van Hest, D.S. Ginley, Low-cost inorganic solar cells: from ink to printed device. Chem. Rev. 110, 6571–6594 (2010)
R. Søndergaard, M. Hösel, D. Angmo, T.T. Larsen-Olsen, F.C. Krebs, Roll-to-roll fabrication of polymer solar cells. Mater. Today 15, 36–49 (2012)
B.H. Teo, A. Khanna, V. Shanmugam, M.L.O. Aguilar, M.E.D. Santos, D.J.W. Chua, W.-C. Chang, T. Mueller, Development of nanoparticle copper screen printing pastes for silicon heterojunction solar cells. Sol. Energy 189, 179–185 (2019)
J.-B. Nam, Y.-R. Jang, Y.-T. Hwang, H.-H. Kim, I.-H. Jung, H.-S. Kim, Intense pulsed light sintering of screen-printed paste electrode on silicon solar cell for high throughput and cost-effective low temperature metallization. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Green. Tech. 9, 523–535 (2022)
D. Zhang, K. Ryu, X. Liu, E. Polikarpov, J. Ly, M.E. Tompson, C. Zhou, Transparent, conductive, and flexible carbon nanotube films and their application in organic light-emitting diodes. Nano Lett. 6, 1880–1886 (2006)
M. Kim, H. Jee, J. Lee, Photo-sintered silver thin films by a high-power UV-LED module for flexible electronic applications. Nanomaterials 11, 2840 (2021)
R. Su, S.H. Park, X. Ouyang, S.I. Ahn, M.C. McAlpine, 3D-printed flexible organic light-emitting diode displays. Sci. Adv. 8, eabl8798 (2022)
M. Segev-Bar, H. Haick, Flexible sensors based on nanoparticles. ACS Nano 7, 8366–8378 (2013)
Y.S. Rim, S. Bae, H. Chen, N. De Marco, Y. Yang, Recent progress in materials and devices toward printable and flexible sensors. Adv. Mater. 28, 4415–4440 (2016)
Z. Li, R. Zhang, X. Lu, L. Hu, X. Wang, W. Liu, C. Cui, X. Liu, Multiplexed analysis of photochemical oxidants using a nanoparticle-based optoelectronic nose. Anal. Chem. 93, 13990–13997 (2021)
S. Jang, H. Cho, Y. Lee, D. Kim, Atmospheric effects on the thermally induced sintering of nanoparticulate gold films. J. Mater. Sci. 47, 5134–5140 (2012)
S. Jang, J. Joung, Y. Oh, Microstructure changes in nanoparticulate gold films under different thermal atmospheres and the effects on bondability. Acta Mater. 57, 5613–5620 (2009)
S. Mekhmouken, N. Battaglini, G. Mattana, A. Maurin, S. Zrig, B. Piro, D. Capitao, V. Noel, Gold nanoparticle-based eco-friendly ink for electrode patterning on flexible substrates. Electrochem. Commun. 123, 106918 (2021)
J. Im, G.F. Trindade, T.T. Quach, A. Sohaib, F. Wang, J. Austin, L. Turyanska, C.J. Roberts, R. Wildman, R. Hague, C. Tuck, Functionalized gold nanoparticles with a cohesion enhancer for robust flexible electrodes. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 5, 6708–6716 (2022)
V.I. Borisov, A.A. Lizunova, D. Malo, E.I. Kameneva, A.A. Ramanenka, V.V. Ivanov, Synthesis of gold nanoparticles by the spark discharge method for visible plasmonics. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2086, 012002 (2021)
W. Liu, C. Wang, C. Wang, X. Jiang, X. Huang, Laser sintering of nano-Ag particle paste for high-temperature electronics assembly. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 7, 1050–1057 (2017)
K.S. Bhat, R. Ahmad, Y. Wang, Y.-B. Hahn, Low-temperature sintering of highly conductive silver ink for flexible electronics. J. Mater. Chem. C 4, 8522–8527 (2016)
S. Jang, M. Rahman, Effect of sintering atmospheres on printed silver nanoparticle patterns for flexible electronics application. Appl. Phys. A 127, 769 (2021)
N. Turan, M. Saeidi-Javash, J. Chen, M. Zeng, Y. Zhang, D.B. Go, Atmospheric pressure and ambient temperature plasma jet sintering of aerosol jet printed silver nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13, 47244–47251 (2021)
J. Noh, Q. Bai, R. Shen, D. Kim, Laser-induced shock wave sintering of silver nanoparticles on flexible substrates. Appl. Surf. Sci. 546, 149097 (2021)
M. Joo, B. Lee, S. Jeong, M. Lee, Comparative studies on thermal and laser sintering for highly conductive Cu films printable on plastic substrate. Thin Solid Films 520, 2878–2883 (2012)
B. Abbas, Y. Mohammad, E. Jewell, J. Searle, Thermal sintering of printable copper for enhanced conductivity of FTO coated glass substrates. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 19917–19927 (2019)
A. Soltani, B. Khorramdel Vahed, A. Mardoukhi, M. Mäntysalo, Laser sintering of copper nanoparticles on top of silicon substrates. Nanotechnology 27, 035203 (2016)
W.-Y. Chung, Y.-C. Lai, T. Yonezawa, Y.-C. Liao, Sintering copper nanoparticles with photonic additive for printed conductive patterns by intense pulsed light. Nanomaterials (Basel). 9, 1071 (2019)
J.C. Hernandez-Castaneda, B.K. Lok, H. Zheng, Laser sintering of Cu nanoparticles on PET polymer substrate for printed electronics at different wavelengths and process conditions. Front. Mech. Eng. 15, 303–318 (2020)
H. Imamura, Y. Kamikoriyama, A. Muramatsu, K. Kanie, A mild aqueous synthesis of ligand-free copper nanoparticles for low temperature sintering nanopastes with nickel salt assistance. Sci. Rep. 11, 24268 (2021)
C.M. Tan, A. Roy, Electromigration in ULSI interconnects. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Reports 58, 1–75 (2007)
R. Ma, C. Guo, Y. Zhou, J. Liu, Electromigration induced break-up phenomena in liquid metal printed thin films. J. Electron. Mater. 43, 4255–4261 (2014)
K. Andritsos, I. Theodorakos, F. Zacharatos, I. Zergioti, The effect of electromigration on the lifetime and performance of flexible interconnections fabricated by laser printing and sintering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 506, 144968 (2020)
D. Li, Y. Mei, Y. Xin, Z. Li, P.K. Chu, C. Ma, G.-Q. Lu, Reducing migration of sintered Ag for power devices operating at high temperature. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 35, 12646–12650 (2020)
P.J. Soininen, K.-E. Elers, V. Saanila, S. Kaipio, T. Sajavaara, S. Haukka, Reduction of copper oxide film to elemental copper. J. Electrochem. Soc. 152, G122 (2005)
F. Hermerschmidt, D. Burmeister, G. Ligorio, S.M. Pozov, R. Ward, S.A. Choulis, E.J.W. List-Kratochvil, Truly low temperature sintering of printed copper ink using formic acid. Adv. Mater. Technol. 3, 1800146 (2018)
ASTM-D-3359 Standard Test Methods for Measuring Adhesion by Tape Test. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA (2010)
V. Mancier, A.-L. Daltin, D. Leclercq, Synthesis and characterization of copper oxide (I) nanoparticles produced by pulsed sonoelectrochemistry. Ultrason. Sonochem. 15, 157–163 (2008)
M. Rabiei, A. Palevicius, A. Monshi, S. Nasiri, A. Vilkauskas, G. Janusas, Comparing methods for calculating nano crystal size of natural hydroxyapatite using X-ray diffraction. Nanomaterials 10, 1627 (2020)
E. Biro, D.C. Weckman, Y. Zhou, Pulsed Nd:YAG laser welding of copper using oxygenated assist gases. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 33, 2019–2030 (2002)
S. Jeong, K. Woo, D. Kim, S. Lim, J.S. Kim, H. Shin, Y. Xia, J. Moon, Controlling the thickness of the surface oxide layer on Cu nanoparticles for the fabrication of conductive structures by ink-jet printing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 18, 679–686 (2008)
X. Niu, H. Zhang, Design and simulation of 13.56MHz RFID reader antenna. In: Proceedings of ICCT2015, pp. 400–402. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCT.2015.7399867
AN2972 Application note: How to design an antenna for dynamic NFC tags, STMicroelectronics, pp. 1–26, March 2019
AN2866 Application note: how to design a 13.56 MHz customized antenna for ST25 NFC/RFID tags, pp. 1–20, August 2021
A. H. Sarhadi, A. Hashemi, H. Emami, Optimization of Q factor in complementary spiral resonator for RFID application. In: 2013 21st Telecommunications Forum Telfor (TELFOR), pp. 693–696 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/TELFOR.2013.6716323
X. Niu, H. Zhang, Design and simulation of 13.56MHz RFID reader antenna. In: IEEE 16th International Conference on Communication Technology (ICCT), pp. 400–402 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCT.2015.7399867
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the US National Science Foundation under Grant No. OIA-1946231 and the Louisiana Board of Regents for the Louisiana Materials Design Alliance (LAMDA). The authors would like to thank Dr. Rafael Cueto of the Polymer Analysis Laboratory for use of TGA instrument and the Nanofabrication facility for use of nanofabrication equipment at Louisiana State University. The authors would like to thank Mr. Richard Greco of the Louisiana Accelerator Center for use of SEM instrument.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Young, K., Chowdhury, R. & Jang, S. Copper nanoparticle conductive patterns fabricated by thermal sintering using carboxylic acid vapors and their application for radio-frequency identification antennas. Appl. Phys. A 129, 207 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06504-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06504-5