Abstract
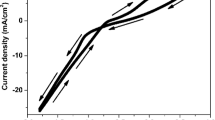
NiO columnar nanostructure has been grown by simultaneous deposition of thermal evaporation and oblique angle deposition (OAD) on stainless steel and glass substrates. The structural properties of NiO columnar nanostructure on both substrates were investigated. The electrical properties of NiO columnar nanostructure on both substrates were investigated by the Hall effect. Thin films on glass substrate showed rough surfaces with irregular distribution of grains, while those on steel substrate showed rough surfaces and flower-like grains with uniform distribution. At temperatures below 410 °K, the resistivity and mobility of NiO columnar nanostructure on both substrates decreased. The resistivity decreased and mobility increased with increasing temperature for NiO thin films on steel and glass at a temperature range of 410–470 °K and 410–520 °K, respectively. At higher temperatures, the resistivity of NiO thin film on steel decreased with temperature, while the resistivity and mobility of NiO thin film on glass remained almost constant.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw data are available on request to the corresponding author.
References
Y.H. Liu, S.J. Young, L.W. Ji, S.J. Chang, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 62, 2924–2927 (2015)
S.J. Chang, B.G. Duan, C.H. Hsiao, C.W. Liu, S.J. Young, IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 26, 66–69 (2013)
K.J. Chen, F.Y. Hung, S.J. Chang, S.J. Young, Z.S. Hu, Curr. Appl. Phys. 11, 1243–1248 (2011)
S.J. Young, C.C. Yang, L.T. Lai, J. Electrochem. Soc. 164, B3013 (2016)
D. Kaya, H.S. Aydınoğlu, E.S. Tüzemen, A. Ekicibil, Thin Solid Films 732, 138800 (2021)
M. Carbone, Appl. Sci. 12, 2839 (2022)
T.P. Mokoena, H.C. Swart, D.E. Motaung, J. Alloys Compd. 805, 267–294 (2019)
N. Tiwari, H. ArianitaDewi, E. Erdenebileg, R. Narayan Chauhan, N. Mathews, S. Mhaisalkar, A. Bruno, Sol. RRL. 6, 2100700 (2022)
I. Jang, G.H. Kelsall, Electrochem. Commun. 137, 107260 (2022)
M. Yang, H. Zhu, Y. Zheng, C. Zhang, G. Luo, Q. Xu, R. Tu, RSC Adv. 12, 10496–10503 (2022)
F.Y. Chuang, D.P. Hasibuan, C.S. Saragih, R.A. Patil, C.H. Tsai, Y. Liou, Y.R. Ma, Surf. Interfaces. 30, 101845 (2022)
Z. Hu, D. Chen, P. Yang, L. Yang, L. Qin, Y. Huang, X. Zhao, Appl. Surf. Sci. 441, 258–264 (2018)
S.J. Mezher, M.O. Dawood, A.A. Beddai, M.K. Mejbel, Mater. Technol. 35, 60–68 (2020)
D. Adler, J. Feinleib, Phys. Rev. B 2, 3112 (1970)
M. Fakharpour, M. GholizadehArashti, M.T. MusazadeMeybodi, JOPN. 6, 25–42 (2021)
M. GholizadehArashti, M. Fakharpour, Eur. Phys. J. B 93, 1–6 (2020)
M. Fakharpour, F. Babaei, H. Savaloni, Plasmonics 11, 1579–1587 (2016)
A. Barranco, A. Borras, A.R. Gonzalez-Elipe, A. Palmero, Prog. Mater Sci. 76, 59–153 (2016)
M. Tyagi, M. Tomar, V. Gupta, Biosens. Bioelectron. 52, 196–201 (2014)
V. Kannan, A.I. Inamdar, S.M. Pawar, H.S. Kim, H.C. Park, H. Kim, H. Im, Y.S. Chae, A.C.S. Appl, Mater. Interfaces. 8, 17220–17225 (2016)
U.M. Patil, R.R. Salunkhe, K.V. Gurav, C.D. Lokhande, Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 2603–2607 (2008)
K. Zhang, C. Rossi, P. Alphonse, C. Tenailleau, Nanotechnology 19, 155605 (2008)
R.K. Jain, Y.K. Gautam, V. Dave, A.K. Chawla, R. Chandra, Appl. Surf. Sci. 283, 332–338 (2013)
F. Ruffino, M.G. Grimaldi, Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 4, 309–315 (2012)
O. Kohmoto, H. Nakagawa, F. Ono, A. Chayahara, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 226, 1627–1628 (2001)
Y.M. Lu, W.S. Hwang, J.S. Yang, Surf. Coat. Technol. 155, 231–235 (2002)
H.L. Chen, Y.M. Lu, W.S. Hwang, Surf. Coat. Technol. 198, 138–142 (2005)
A.M. Reddy, A.S. Reddy, K.S. Lee, P.S. Reddy, Solid State Sci. 13, 314–320 (2011)
S.C. Chen, T.Y. Kuo, T.H. Sun, Surf. Coat. Technol. 205, S236–S240 (2010)
P. Mohan Babu, G. Venkata Rao, P. Sreedhara Reddy, S. Uthanna, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 15, 389–394 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have a same contribution in the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fakharpour, M., Karimi Tafti, M.H. Temperature and substrate effect on the electrical and structural properties of NiO columnar nanostructure. Appl. Phys. A 129, 234 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06454-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06454-y